Summary
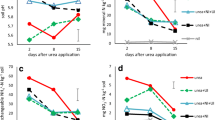
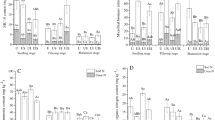
A greenhouse experiment was conducted to study the comparative efficiency of urea as an N fertilizer with and without the addition of different urease inhibitors. Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) was used as the test plant and the N balance technique with 15N was applied. Three urease inhibitors, hydroquinone, phenyl phosphorodiamidate (PPDA), and N-(n-butyl) phosphorothioic triamide (NBPT), were evaluated for their effects on urea-N uptake as well as on grass yield. The addition of urease inhibitors, except for hydroquinone in the later growth period, did not significantly influence the dry matter weight. Throughout the whole growth period, only NBPT significantly increased the total urea-N uptake. In the uninhibited system, the major fertilizer N loss occurred during the first period of grass growth, presumably via NH3 volatilization, since the environment did not favour the other pathways of N loss. However, an appreciable amount of urea N was lost during the later growth period in all inhibited systems, especially in the hydroquinone-treated system. This indicates that the application of urease inhibitors could not eliminate the urea N loss. The greater N loss in the hydroquinone-treated soil appears to be related to the inhibition by hydroquinone of nitrification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyrouty CA, Sommers LE, Nelson DW (1988) Ammonia volatilization from surface applied urea as affected by several phosphoroamide compounds. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:1173–1178
Bremner JM, Chai HS (1989) Effects of phosphoroamides on ammonia volatilization and nitrite accumulation in soil treated with urea. Biol Fertil Soils 8:227–230
Bremner JM, Mulvaney RL (1982) Total nitrogen. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Agronomy 9, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 595–624
Bundy LG, Bremner JM (1974) Effect of urease inhibitors on nitrification in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 6:27–30
Buresh RJ, De Datta SK, Padilia JL, Samson MI (1988) Effect of two urease inhibitors on floodwater ammonia following urea application to lowland rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:856–861
Byrnes BH, Savant NK, Craswell ET (1983) Effect of a urease inhibitor phenyl phosphorodiamidate on the efficiency of urea applied to rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:270–274
Fiedler R, Proksch G (1975) The determination of 15N by emission and mass spectrometry in biochemical analysis: A review. Anal Chim Acta 78:1–62
Fillery IRP, De Datta SK, Craswell ET (1986) Effect of phenyl phosphorodiamidate on the fate of urea applied to wetland fields. Fert Res 9:251–262
McCarty DB, Nelson DW, Huber DW (1989) Effect of N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide on hydrolysis of urea by plant, microbial, and soil urease. Biol Fertil Soils 8:123–127
Mulvaney RL, Bremner JM (1981) Control of urea transformations in soils. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol 5. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 153–196
Rao DLN, Ghai DK (1985) Effect of phenyl phosphorodiamidate on urea hydrolysis, ammonia volatilization and rice growth in an alkali soil. Plant and Soil 94:313–320
Rao DLN, Ghai SK (1986) Urease inhibitors: Effect on wheat growth in an alkali soil. Soil Biol Biochem 18:255–258
Reddy KR, Patrick WH Jr (1980) Losses of applied ammonium 15N, urea 15N and organic 15N in flooded soils. Soil Sci 130:326–330
Schlegel AJ, Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1986) Field evaluation of urease inhibitors for corn production. Agron J 78:1007–1012
Schlegel AJ, Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1987) Use of urease inhibitors and urea fertilizer on winter wheat. Fert Res 11:97–11
Simpson JR, Freney JR, Muirhead WA, Leuning R (1985) Effects of phenyl phosphorodiamidate and dicyandiamide on nitrogen loss from flooded rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:1426–1431
Vlek PLG, Byrnes BH (1986) The efficiency and loss of fertilizer N in lowland rice. Fert Res 9:131–147
Vlek PLG, Craswell ET (1981) Ammonia volatilization from flooded soils. Fert Res 2:227–245
Wang ZP, Van Cleemput O, Baert L (1990) Effect of urease inhibitors on nitrification in soil. Soil Use Manage 6:41–43
Wang ZP, Van Cleemput O, Baert L (1991) Effect of urease inhibitors on urea hydrolysis and ammonia volatilization. Biol Fertil Soils 11:43–47
Weeraratna CS, Craswell ET (1985) Nitrogen losses from labelled ammonium sulphate and urea applied to a flooded rice soil. Fert Res 6:199–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liantie, L., Wang, Z.P., Van Cleemput, O. et al. Urea N uptake efficiency of ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) in the presence of urease inhibitors. Biol Fertil Soils 15, 225–228 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361616
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361616