Abstract
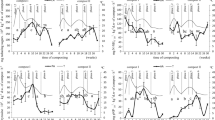
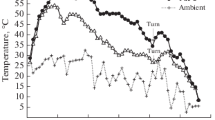
The composting process found in real compost heaps was simulated in the laboratory with three treatments, nil, and urea, and cyanamide additions. Total N was separated into hydrolysable, amino acid, and amino sugar N. These fractions were related to counts of viable bacteria and spore-forming bacteria. The content of amino acid N and amino sugar N increased in all three treatments. The ratios of amino acid to amino sugar C and glucosamine to galactosamine decreased in all three treatments during composting of wheat straw. The increased contents of the N components were all significantly correlated with the number of spore-forming bacteria but not with viable bacterial counts. The closest correlation was found between spores and galactosamine. Amounts equivalent to 74% (urea treatment) or 48% (cyanamide treatment) of the added N were lost, mainly in the period after the maximum temperature was passed. The increased amounts of amino acid and amino sugar N accounted for 89% (urea treatment) and 68% (cyanamide treatment) of the added N remaining in compost.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannick CG (1988) Untersuchungen über den Stickstoffeinbau in die Huminstoffmatrix während der Kompostierung in einem Laborkomposter. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkd Ges 56:119–123
Bannick CG (1989) Simulationsversuche zur Mietenkompostierung unter Berücksichtigung der Wirkung verschiedener Stickstoffzusätze auf den Abbau organischer Stoffgruppen und die Bildung von Huminstoffen. PhD thesis, University of Göttingen, Göttingen
Bannick CG, Ziechmann W (1991) Huminstoffbildung während der Kompostierung. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 154:233–236
Beckwith CP, Parsons JW (1980) The influence of mineral amendments on the changes of the organic nitrogen components of composts. Plant and Soil 54:269–270
Bondietti E, Martin JP, Haider K (1972) Stabilization of amino sugar units in humic type polymers. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 36:597–602
Calzada JF, de Leon R, de Arriola MC, Rolz C (1987) Growth of mushrooms on wheat straw and coffee pulp: Strain selection. Biol Wastes 20:217–226
Domsch KH, Anderson JPE (1986) Biomasse und Abbauleistung der Pilze und Bakterien im Boden. In: Ellenberg H, Mayer R, Schauermann J (eds) Ökosystemforschung. Ergebnisse des Sollingprojektes. Ulmer, Stuttgart, pp 284–287
Frankland JC, Lindley KD, Swift MJ (1978) A comparison of two methods for estimation of mycelial biomass in leaf litter. Soil Biol Biochem 10:323–333
Graham JP, Ellis FB, Christian DG, Cannell RQ (1986) Effects of straw residues on the establishment, growth and yield of autumn-sown cereals. J Agric Eng Res 33:39–49
Gupta VK, Bakshi MPS, Langar PN (1987) Microbiological changes during natural fermentation of urea-wheat straw. Biol Wastes 21:291–299
Hicks RE, Newell SY (1984) A comparison of glucosamine and biovolume conversion factors for estimating fungal biomass. Oikos 42:355–360
Jenkinson DS, Ladd JN (1981) Microbial biomass in soil: Measurement and turnover. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil Biochemistry, vol. 5. Dekker, New York, pp 415–471
Joergensen RG (1991) Organic matter and element dynamics of the litter layer on a forest Rendzina under beech. Biol Fertil Soils 11:163–169
Joergensen RG, Meyer B (1990) Chemical change in organic matter decomposing in and on a forest Rendzina under beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). J Soil Sci 41:279–293
Joergensen RG, Richter GM (1992) Composition of carbon fractions and potential denitrification in drained peat soils. J Soil Sci 43:347–358
Joergensen RG, Mueller T, Meyer B (1988) Spezifische Zellkomponenten von Organismen in der organischen Substanz als Indikatoren der Zersetzung und zur Bestimmung der Biomasse. Anwendung auf eine Kompostierung von Weizenstroh. Mitt Dtsch Bodenkd Ges 56:191–196
Kinber RWL (1973) Phytotoxicity from plant residues. III. The relative effect of toxins and nitrogen immobilization on the germination and growth of wheat. Plant and Soil 38:543–555
Kögel I, Bochter R (1985) Amino sugar determination in organic soils by capillary gas chromatography using a nitrogen-selective detector. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 148:260–267
Laukevics JJ, Apsite AF, Viesturs UE, Tengerdy RP (1984) Solid substrate fermentation of wheat straw to fungal protein. Biotech Bioeng 26:1464–1474
Lynch JM (1985) Microbial saphrophytic activity on straw and other residues: Consequences for plants. In: Fitter AH (ed) Ecological interactions in soil. Blackwell, London, pp 181–191
Parsons JW (1981) Chemistry and distribution of amino sugars in soils and soil organisms. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol. 5. Dekker, New York, pp 197–227
Scholle G, Joergensen RG, Schaefer M, Wolters V (1993) Hexosamines in the organic layer of two beech forest soils: Effects of mesofauna exclusion. Biol Fertil Soils 15:301–307
Sowden FJ, Ivarson KC (1974) Effects of temperature on changes in the nitrogenous constituents of mixed forest litters during decomposition after inoculation with various microbial cultures. Can J Soil Sci 54:387–394
Sowden FJ, Morita H, Levesque M (1978) Organic nitrogen in selected peats and peat fractions. Can J Soil Sci 58:237–249
Vilsmeyer K, Amberger A (1980) Umsetzung von Cyanamid, Harnstoff und Ammonsulfat in Abhängigkeit von Temperatur und Bodenfeuchte. Z Pfanzenernähr Bodenkd 143:47–54
Zadrazil F (1979) Screening of basidio mycetes for optimal utilization of straw. In: Grossbard E (ed) Straw decay and its effects on disposal and utilization. Wiley, New York, pp 139–146
Zelles L, Hund K, Stepper K (1987) Methoden zur relativen Quantifizierung der pilzlichen Biomasse im Boden. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 150:249–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bannick, C.G., Joergensen, R.G. Change in N fractions during composting of wheat straw. Biol Fert Soils 16, 269–274 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369303
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369303