Summary
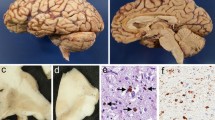
An 18-year-old girl died following a slowly progressive neurodegenerative disease of nine years duration. At 9 years of age, she developed intellectual deterioration associated with speach difficulty, pseudobulbar palsy and ataxia. The progression included spastic quadriplegia, anarthria, severe dysphagia, ophthalmoplegia, and pes cavus. There was no family history. The brain was uniformly small and the substantia nigra was not pigmented. Neuronal loss and gliosis involving globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, thalamic nuclei, brain stem, cerebellum, and spinal cord gave the picture of multisystem atrophy. Intranuclear hyaline inclusions were observed in numerous neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system. These were auto-fluorescent and were made up of intermingled straight filaments (8–9 nm in diameter).
Only two previously reported cases showing these same inclusions are known. They are reviewed, compared, and discussed in relation to primary neuronal degenerations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
David S, Nathaniel EJH (1978) Intranuclear inclusions in the developing neurons of the rat cuneate nuclei. Cell Tissue Res 193:525–532
Janota I (1979) Widespread intranuclear neuronal corpuscles (Marinesco bodies) associated with a familial spinal degeneration with cranial and peripheral nerve involvement. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 5:311–317
Lindenberg R, Rubinstein LJ, Herman MM, Haydon GB (1968) A light and electron microscopy study of an unusual widespread nuclear inclusion body disease. A possible residuum of an old herpes virus infection. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 10:54–73
Oppenheimer DR (1976) Disease of basal ganglia, cerebellum and motor neurons. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. E. Arnold, London, pp 608–651
Sung JH, Ramirez-Lassepas M, Mastri AR, Larkin S (1980) An unusual degenerative disorder of neurons associated with a novel intranuclear hyaline inclusion (neuronal intranuclear hyaline inclusion disease). A clinicopathological study of a case. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:107–130
Sung JH (1980) Light, fluorescence and electron microscopic features of neuronal intranuclear hyaline inclusions associated with multisystem atrophy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 50:115–120
Waggener JD, Beggs J, Sidell AD (1972) Virus-like filaments in juvenile parkinsonism. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 31:187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michaud, J., Gilbert, J.J. Multiple system atrophy with neuronal intranuclear hyaline inclusions. Acta Neuropathol 54, 113–119 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689403
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689403