Abstract
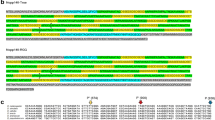
He-T sequences are a complex repetitive family of DNA sequences in Drosophila that are associated with telomeric regions, pericentromeric heterochromatin, and the Y chromosome. A component of the He-T family containing open reading frames (ORFs) is described. These ORF-containing elements within the He-T family are designated T-elements, since hybridization in situ with the polytene salivary gland chromosomes results in detectable signal exclusively at the chromosome tips. One T-element that has been sequenced includes ORFs of 1,428 and 1,614 bp. The ORFs are overlapping but one nucleotide out of frame with respect to each other. The longer ORF contains cysteine-histidine motifs strongly resembling nucleic acid binding domains of gag-like proteins, and the overall organization of the T-element ORFs is reminiscent of LINE elements. The T-elements are transcribed and appear to be conserved in Drosophila species related to D. melanogaster. The results suggest that T-elements may play a role in the structure and/or function of telomeres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biessmann H, Mason JM, Ferry K, D'Hulst M, Valgeirsdottir K, Traverse KL, Pardue ML (1990) Addition of telomere-associated He-T DNA sequences heals broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell 61:663–673
Cavener DR, Ray SC (1991) Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3185–3192
Covey SN (1986) Amino acid sequence homology in gag region of reverse transcribing elements and the coast protein gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res 14:623–633
Danilevskaya ON, Lapta GE (1991) Long telomeres in the polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster are associated with amplification of subtelomeric repeat sequences. Genet Sel Evol 23:15–24
Danilevskaya ON, Kurenova EV, Leibovitch BA, Shevelev AY, Bass IA, Khesin R (1984) Telomeres and P-element of Drosophila melanogaster contain sequences that replicate autonomously in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet 197:342–344
Danilevskaya ON, Kurenova EV, Pavlova MN, Link AJ, Koga A, Vellek A, Hartl DL (1991) He-T family DNA sequences in the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster share homology with the X-linked Stellate genes. Chromosoma 100:118–124
DiNocera PP (1988) Close relationship between non-viral retroposons in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 16:4041–4052
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1984) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity: Addendum. Anal Biochem 137:266–267
Garza D, Ajioka JW, Burke DT, Hartl DL (1989) Mapping the Drosophila genome with yeast artificial chromosomes. Science 246:641–646
HutchisonIII CA, Hardies SC, Loeb DD, Shehee WR, Edgell MH (1989) LINEs and related retroposons: Long interspersed repeated sequences in the eucaryotic genome. In: Berg DE, Howe MM (eds) Mobile DNA. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 593–617
Icho T, Wickner RB (1989) The double-stranded RNA genome of yeast virus L-A encodes its own putative RNA polymerase by fusing two open reading frames. J Biol Chem 264:6716–6723
Jacks T, Madhani HD, Masiarz FR, Varmus HE (1988) Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell 55:447–458
Jakubczak JL, Xiong Y, Eickbush TH (1990) Type I (R1) and type II (R2) ribosomal DNA insertion of Drosophila melanogaster are retrotransposable elements closely related to those of Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol 212:37–52
Johnson-Schlitz D, Lim JK (1987) Cytogenetics of Notch mutations arising in the unstable X chromosome Uc of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 115:701–709
Lis JT, Simon JA, Sutton CA (1983) New heat shock puffs and beta-galactosidase activity resulting from transformation of Drosophila with an hsp70-lacZ hybrid gene. Cell 35:403–410
Louis EJ, Haber JE (1992) The structure and evolution of subtelomeric Y' repeats in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 131:559–574
Lundblad V, Szostak JW (1989) A mutant with a defect in telomere elongation leads to senescence in yeast. Cell 57:633–643
Pardue ML, Hennig W (1990) Heterochromatin: Junk or collectors item? Chromosoma 100:3–7
Priimagi AF, Mizrokhi LJ, Ilyin JV (1988) The Drosophila mobile element Jockey belongs to LINEs and contains coding sequences homologous to some retroviral proteins. Gene 70:253–262
Rajavashisth TB, Taylor AK, Andalibi A, Svenson KL, Lusis AJ (1989) Identification of a zinc finger protein that binds to the sterol regulatory element. Science 241:640–643
Renkawitz-Pohl R, Bialojan S (1984) A DNA sequence of Drosophila melanogaster with a different telomeric distribution. Chromosoma 89:206–211
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-termination inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Schwarz-Sommer Z, Leclercq L, Gobel E, Saedler H (1987) Cin4, an insert altering the structure of the A1 gene in Zea mays, exhibits properties of nonviral retrotransposons. EMBO J 6:3873–3880
Smoller DA, Petrov D, Hartl DL (1991) Characterization of bacteriophage P1 library contain inserts of Drosophila DNA of 75–100 kilobase pairs. Chromosoma 100:487–494
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Traverse KL, Pardue ML (1988) A spontaneously opened ring chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster has acquired He-T DNA sequences at both new telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8116–8120
Traverse KL, Pardue ML (1989) Studies of He-T DNA sequences in the pericentric regions of Drosophila chromosomes. Chromosoma 97:261–271
Valgeirsdottir K, Traverse KL, Pardue ML (1990) He-T DNA: A family of mosaic repeated sequences specific for heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7998–8002
Young BS, Pession A, Traverse KL, French C, Pardue ML (1983) Telomere regions in Drosophila share complex DNA sequences with pericentric heterochromatin. Cell 34:85–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by W. Hennig
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danilevskaya, O.N., Petrov, D.A., Pavlova, M.N. et al. A repetitive DNA element, associated with telomeric sequences in Drosophila melanogaster, contains open reading frames. Chromosoma 102, 32–40 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352288
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352288