Summary
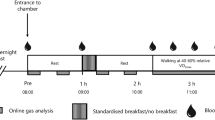
The influence of short-term energy intake and cycle exercise on oxygen consumption in response to a 1.5 MJ test meal was investigated in ten young, adult men. On the morning after a previous day's “low-energy“ intake (LE regimen) of 4.5 MJ, the mean resting oxygen consumption increased by 0.7 ml · kg−1 · min−1 after the test meal (P<0.025). After a “high-energy“ intake (HE regimen) of 18.1 MJ, the resting measurement was unchanged (+0.4 ml · kg−1 · min−1) after the meal (n.s.). These trends are the reverse of what would be expected if oxygen consumption in response to feeding is a factor in the acute control of body weight. The mean fasting oxygen consumption during cycle exercise at 56% of\(\dot V_{O_{2max} } \) (constant work) for both LE and HE prior intakes was not different at 31.1 ml · kg−1 · min−1. Oxygen consumption during exercise increased after feeding by 0.5 ml · kg−1 · min−1 on the LE regimen (n.s.) and decreased by 1.2 ml · kg−1 · min−1 on the HE regimen (n.s.). These results are also the reverse of what would be expected if oxygen consumption in response to exercise is related to short-term energy intake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradley PW, Daniels JT, Hayes J (1983) A pneumatic spirometer for accurate volume measurement during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc (Abstr) 15:168
Bray GA, Whipp BJ, Koyal SN (1974) The acute effects of food intake on energy expenditure during cycle ergometry. Am J Clin Nutr 27:245–259
Dallosso H, James WPT (1981) Dietary thermogenesis and exercise. Proc Nutr Soc 41:35A
Davis JR, Tagliaferro AR, Kertzer R, Gerardo T, Nichols J, Wheeler J (1983) Variations in dietary-induced thermogenesis and body fatness with aerobic capacity. Eur J Appl Physiol 50:319–329
Food and Nutrition Board (1980) Recommended dietary allowances, 9th ed. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C.
Garby L, Lammert O (1977) Effect of the preceeding day's energy intake on the total energy cost of light exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 101:411–417
Jackson AS, Hartung GH, Bradley PW (1983) An evaluation of an automated system for measurement of cardiorespiratory function during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc (Abstr) 15:144
Miller DS, Wise A (1975) Exercise and dietary induced thermogenesis. Lancet 1:1290
Obarzanek E, Levitsky DA (1983) One day of overeating enhances the thermogenic effect of exercise. Fed Proc 42:1189
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1969) Biometry — the principles and practice of statistics in biological research. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, pp 343–366
Snedecor GW, Cochran WS (1967) Statistical methods, 6th ed. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, pp 273–275
Stock MJ (1980) Effects of fasting and refeeding on the metabolic response to a standard meal in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 43:35–40
Tremblay A, Cote J, LeBlanc J (1983) Diminished dietary thermogenesis in exercise-trained human subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 52:1–4.
Zuti W, Golding L (1973) Equations for estimating percent fat and body density of active adult males. Med Sci Sports 5:262–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickson, J.F., Hartung, G.H., Pate, T.D. et al. Effect of short-term energy intake level and exercise on oxygen consumption in men. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 198–201 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00715005
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00715005