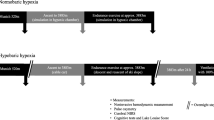
Summary
The functional characteristics at rest in responding to stepwise acute exposure to simulated altitude (6000 m) were compared in 10 acclimatized mountaineers (highlanders), residents of Zermatt (1616 m) working at an altitude up to about 4000 m, and in 11 nonacclimatized control subjects (lowlanders) living and working in Zurich (450 m). In comparison with the lowlanders, the highlanders showed at altitude significantly greater hyperventilation, lower heart rate and systolic blood pressure, smaller haemoconcentration, lower urodilatin secretion and natriuresis, and a preserved neuropsychological ability (attentiveness) and vasomotor tone (diastolic blood pressure); the critical altitude at which hypoxic short-term adaptation became insufficient was 6000 m. The lowlanders, however, manifested reduced tolerance of hypoxia, i.e. insufficient short-term adjustment with subjective and objective distress coinciding with the first signs of hypoxia of the central nervous system, already apparent at and above 4000 m. It was concluded that the functional differences between highlanders and lowlanders in responding to acute gradual hypoxia indicated factors contributing to altitude acclimatization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bebout DE, Story D, Roca D, Hogan MC, Poole DC, Gonzalez-Camarena R, Ueno O, Haab P, Wagner PD (1989) Effects of altitude acclimatization on pulmonary gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol 67:2286–2295
Brickenkamp R (1981) Test d2. Aufmerksamkeits-Belastungs-Test. Verlag für Psychologie Dr. Hogrefe CJ, Göttingen
Bub A, Manzi G, Weiker H, Forssmann WG (1989) Freisetzung kardialer Hormone bei Höhenexposition. In: Bönning D, Braumann KM, Busse MW, Maassen N, Schmidt W (eds) Sport, Rettung oder Risiko für die Gesundheit. Deutscher Aerzte-Verlag, Cologne, pp 235–240
Burki NK (1984) Effects of acute exposure to high altitude on ventilatory drive and respiratory pattern. J Appl Physiol 56:1027–1031
Byrne-Quinn E, Weil JV, Sodal IE, Filley GF, Grover RF (1971) Ventilatory control in the athlete. J Appl Physiol 30:91–98
Curran-Everett DC, Meredith MP, Krasney JA (1992) Acclimatization to hypoxia alters cerebral convective and diffusive OZ delivery. Respir Physiol 88:365–371
Dempsey JA, Smith CA (1989) Where does [H+] fit in the scheme of ventilatory acclimatization to hypoxia? In: Paganelli ChV, Fahri LE (eds) Physiological functions in special environments. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg New York, pp 15–30
Drummer C, Fiedler F, König A, Gerzer R (1991) Urodilatin, a kidney-derived natriuretic factor, is secreted with a circadian rhythm and is stimulated by saline infusion in man. J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1109–1113
Dürr JA, Vallotton MB, Simon CA, Krähenbühl B (1978) Non invasive method for measuring central venous pressure. Lancet 1:586–587
Emmeluth C, Drummer C, Gerzer R, Bie P (1992) Roles of cephalic Na+ concentration and Urodilatin in control of renal Na+ excretion. Am J Physiol 262:F513–516
Forssmann WG, Kleefeld D, Bub A, Biebl A, Raida M, Mägert HJ, Adermann K (1992) Urodilatin: molecular forms and specific radioimmunoassay. Acta Endocrinol 126 [Suppl 4]:165
Gellhorn E, Lambert EH (1939) The vasomotor system in anoxia and asphyxia. Illinois University Press, Urbana, p 62
Goetz K, Drummer C, Zhu JL, Leadley R, Fiedler F, Gerzer R (1991) Evidence that Urodilatin, rather than ANP, regulates renal sodium excretion. J Am Soc Nephrol 1:867–874
Goldberg SV, Schoene RB, Haynor D, Trimble B, Swenson ER, Morrison JB, Banister EJ (1992) Brain tissue pH and ventilatory acclimatization to high altitude. J Appl Physiol 72:58–63
Hammill SC, Wagner WW, Latham LP, Forst WW, Weil JV (1979) Autonomic cardiovascular control during hypoxia in the dog. Circ Res 44:569–575
Heath D, Williams DR (1977) Man at high altitude. The pathophysiology of acclimatization and adaptation. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 159–161
Houston ChS, Sutton JR, Cymerman A, Reeves JT (1987) Operation Everest II: man at extreme altitude. J Appl Physiol 63:877–882
Hurtado A (1971) The influence of high altitude on physiology. In: Porter R, Knight J (eds) High altitude physiology: cardiac and respiratory aspects. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 3–8
Koller EA, Drechsel S, Hess T, Macherel P, Boutellier U (1988) Effects of atropine and propranolol on the respiratory, circulatory and ECG responses to high altitude in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:163–172
Koller EA, Bischoff M, Bührer A, Felder L, Schopen M (1991a) Respiratory, circulatory and neuropsychological responses to acute hypoxia in acclimatized and non-acclimatized subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:67–72
Koller EA, Bührer A, Felder L, Schopen M, Vallotton MB (1991b) Altitude diuresis: endocrine and renal responses to acute hypoxia of acclimatized and non-acclimatized subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:228–234
Laciga P, Koller EA (1976) Respiratory, circulatory, and ECG changes during acute exposure to high altitude. J Appl Physiol 41:159–167
Mahler DA, Moritz ED, Loke J (1982) Ventilatory responses at rest and during exercise in marathon runners. J Appl Physiol 52:388–392
Martin III WH, Spina RJ, Korte E, Ogawa T (1991) Effects of chronic and acute exercise on cardiovascularβ-adrenergic responses. J Appl Physiol 71:1523–1528
Oelz O, Howald H, di Prampero PE, Hoppeler H, Claassen H, Jenni R, Bühlmann A, Ferretti G, Brückner JC, Veicsteinas A, Gussoni M, Cerretelli P (1986) Physiological profile of worldclass high-altitude climbers. J Appl Physiol 60:1734–1742
Pietsch P (1984) Das rechnerunterstützte Atmungsanalysesystem des Physiologischen Institutes Zürich. Thesis, University of Zurich, Zurich
Saxenhofer H, Raselli A, Weidmann P (1990) Urodilatin, a natriuretic factor from kidneys, can modify renal and cardiovascular function in men. Am J Physiol 259:F832-F838
Schoene RB, Roach RC, Hackett PH, Sutton JR, Cymerman A, Houston ChS (1990) Operation Everest II: ventilatory adaptation during gradual decompression to extreme altitude. Med Sci Sports Exerc 22:804–810
Schulz-Knappe P, Forssmann K, Herbst F, Hock D, Pipkorn R, Forssmann WG (1988) Isolation and structural analysis of “Urodilatin”, a new peptide of the cardiodilatin-(ANP)-family, extracted from human urine. Klin Wochenschr 66:752–759
Severinghaus JW, Mitchell RA, Richardson BW, Singer MM (1963) Respiratory control at high altitude suggesting active transport regulation of CSF pH. J Appl Physiol 18:1155–1166
Sutton JR, Reeves JT, Wagner PD, Groves BM, Cymerman A, Malconian MK, Rock PB, Young PM, Walter StD, Houston ChS (1988) Operation Everest II: oxygen transport during exercise at extreme simulated altitude. J Appl Physiol 64:1309–1321
Tenney SM, Jones RM (1992) Water balance and lung fluids in rats at high altitude. Respir Physiol 87:397–406
Van Beaumont W, Underkofler S, Van Beaumont S (1981) Erythrocyte volume, plasma volume, and acid-base changes in exercise and heat dehydration. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 50:1255–1262
Van Liere EJ, Stickney JC (1963) Hypoxia. Chicago University Press, Chicago, p 6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. F. J. Wagenhäuser on the occasion of his retirement.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koller, E.A., Lesniewska, B., Bührer, A. et al. The effects of acute altitude exposure in swiss highlanders and lowlanders. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 66, 146–154 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01427056
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01427056