Summary
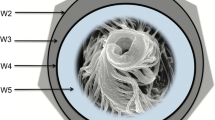
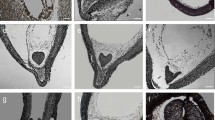
Changes in the structure and composition of cell walls of Fucus gardneri Silva were related to embryo development. Results of histochemical treatments of walls from embryos of different ages were compared with those of differential extractions and electronmicroscopic examinations of isolated walls. At 24 h after fertilization alginic acid, fucoidin and cellulose were structural constituents of the embryo wall. The distribution of alginic acid and cellulose was uniform over the cell walls of embryos of any age, but fucoidin was concentrated at the rhizoid end of cell walls isolated from germinated embryos. Evidence is presented for the presence of sulfated xylogalactofucoglucuronan and β,1-3 glucan in the embryo cell-wall. Electron micrographs of untreated and differentially extracted cell walls showed that alginic acid comprised the fibrillar material and fucoidin comprised the amorphous material of the wall.
Fucus eggs do not have cell walls and the zygotes began wall synthesis within 40 min after fertilization. During the first 2 h there was a rapid deposition of alginic acid. After 4 h the wall thickness increased linearly through 24 h. Embryos treated with cycloheximide ceased wall growth after 6 h. Wall isolated from 24-h-old cycloheximide-treated embryos resembled wall isolated from control embryos 2–4 h old.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R., Jacobsen, L., Joaquin, J., Jaffe, L.: Ionic concentrations in developing Pelvetia eggs. Develop. Biol. 27, 538–545 (1972)
Bidwell, R., Percival, E., Smestad, B.: Photosynthesis and metabolism in marine algae. VIII. Incorporation of 14C into polysaccharides metabolized by Fucus vesiculosis during pulse labelling experiments. Canad. J. Bot. 50, 191–197 (1972)
Bourne, E., Brush, P., Percival, E.: The active carbohydrate metabolites of the brown seaweed, Fucus vesiculosis. Carbohyd. Res. 9, 415–422 (1969)
Brachet, J.: The use of basic dyes and ribonuclease for the cytochemical detection of ribonucleic acid. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 94, 1–10 (1953)
Jaffe, L.: Electrical currents through the developing Fucus egg. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 56, 1102–1109 (1966)
Jaffe, L.: Localization in the developing Fucus egg and the general role of localizing currents. Advanc. Morphog. 7, 295–328 (1968)
Jaffe, L.: On the centripetal course of development, the Fucus egg, and self-electrophoresis. Develop. Biol., Suppl. 3, 83–111 (1970)
Jensen, W.: Botanical histochemistry. San Fransisco: Freeman 1962
McCully, M.: A note on the structure of the cell walls of the brown alga, Fucus. Canad. J. Bot. 43, 1001–1004 (1965)
McCully, M.: Histological studies on the genus Fucus. I. Light microscopy of the mature vegetative plants. Protoplasma (Wien) 62, 287–305 (1966)
McCully, M.: Histological studies on the genus Fucus. II. Histology of the reproductive tissues. Protoplasma (Wien) 66, 205–230 (1968)
McCully, M.: The histological localization of the structural polysaccharides of seaweeds. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 175, 892–911 (1970)
Moon, A., Forman, M.: A procedure for the isolation of cell walls of Fucus furcatus embryos. Protoplasma (Wien) 75, 461–464 (1972)
Nakazawa, S.: Regional concentration of cytoplasmic RNA in Fucus eggs in relation to polarity. Naturwissenschaften 5, 138–139 (1966)
Nakazawa, S., Takamura, K.: An analysis of rhizoid differentiation in Fucus eggs. Cytologia (Tokyo) 32, 408–415 (1966)
Parker, B., Diboll, A.: Alcian stains for histochemical localization of acid and sulfated polysaccarides in algae. Phycologia 1, 37–46 (1966)
Pease, D.: Histochemical techniques for electron microscopy. New York: Acad. Press 1964
Percival, E., McDowell, R.: Chemistry and enzymology of marine algal polysaccharides. London, New York: Acad. Press 1967
Percival, E., Ross, A.: Marine algal cellulose. J. chem. Soc. 1949 3041–3043
Pollack, E.: Fertilization in Fucus. Planta (Berl.) 92, 85–89 (1970)
Sitte, P.: Einfaches Verfahren für stufenlose Gewebe-Entwässerung für die electronenmikroskopische Präparation. Naturwissenschaften 49, 402–403 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novotny, A.M., Forman, M. The composition and development of cell walls of Fucus embryos. Planta 122, 67–78 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385406
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385406