Abstract
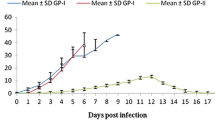
The phagocytic activity and cytotoxicity of peripheral blood monocytes (against toxoplasma tachyzoites) was studied in acute, chronic and reactivated toxoplasma infected Swiss albino mice. During acute infection, a low phygocytic activity was observed on the 4th day post infection (dpi) (P<0.01) and a low monocyte cytotoxicity was noticed after the 2nd dpi (P<0.01) which further decreased till the 8th dpi. In contrast, both the parameters were significantly increased during chronic infection. Increase in monocytic cytotoxicity was manifested on the 3rd dpi (P<0.001) whereas phagocytosis showed an increase on the 12th dpi (P<0.05). The reactivated group showed no change in both the parameters when compared with the control immunosuppressed group (P>0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borges JS, Jhonson WD Jr (1975) Inhibition of mulitplication ofToxoplasma gondii by human monocytes exposed to T Lymphocyte products. J Exp Med 141:483–496
Boyum A (1968) Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. J Clin Lab Invest 8:77–89
Catterall JR, Sharma SD, Remington JS (1986) Oxygen independent killing by alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med 163:1113–1131
Chinchilla M, Guerrero OM, Solano E (1982) Lack of multiplication of Toxoplasma in macrophages of rats in vitro. J Parasitol 68:952–955
Dempster RF (1984)Toxoplasma gondii: Purification of zoites from peritoneal exudates by eight methods. Exp Parasitol 57:195–207
Gardner ID, Remington JS (1978) Aging and the immune response. II. Lymphocyte responsiveness and macrophage activation inToxoplasma gondii infected mice. Immunol 120:944–949
Goyal M, Ganguly NK, Mahajan RC (1986) Lymphocyte function in acute and chronic murine toxoplasmosis. Ind J Med Res 83:487–494
Goyal M, Ganguly NK, Mahajan RC (1988) Natural killer cell activity in acute and chronic murine toxoplasmosis. Med Sci Res 16:375–376
Hauser WE, Sharma SD, Remington JS (1982) Natural killer cells induced by acute and chronic toxoplasma infection. Cell immunol 69:330–346
Hibbs JB Jr, Lambert LH, Remington JS (1972) Adjuvant induced resistance to tumor development in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 139:1053
Hirsch JG, Jones TC, Len L (1974) Interactions in vitro betweenToxoplasma gondii and mouse cells. In: Ciba Foundation 25, Parasites in the Immunized Host: Mechanism of survival. 25 Elsevier Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 205–244
Hof H, Hohne K, Seelinger HPR (1976) Macrophage function and host resistance against infection withToxoplasma gondii. Can J Microbiol 22:1453–1457
Jacob L, Lunde MN (1957) A haemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis. J Parasitol 43:308–314
Jones TC, Len L, Hirsch JG (1975) Assessment in vitro of immunity againstToxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med 141:466–482
Lindberg RE, Frenkel JK (1977) Toxoplasmosis in nude mice. J Parasitol 63:219–221
Lloyd RS, Levick PL (1977) Monocyte dysfunction in thermal injury. Burns 3:245–252
McCabe RE, Remington JS (1986) Mechanism of killing ofToxoplasma gondii by rat peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun 52:151–155
Mcleod R, Estes RG (1985) Role of lymphocyte blastogenesis toToxoplasma gondii antigens in containment of chronic, latentT. gondii infection in humans. Clin Exp Immun 62:24–30
Mcleod R, Bensch KG, Smith SM, Remington JS (1980) Effects of human peripheral blood monocytes, monocytes derived macrophages and spleen mononuclear phagocytes onToxoplasma gondii. Cell Immunol 54:330–350
Murray HW, Juengbhanich CW, Nathan CF, Cohn ZA (1979) Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. II. The role of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med 150:950–964
Remington JS (1961) Experiments on the transmission of toxoplasmosis. Surv Ophtholmol 6:856–867
Remington JS, Melton ML, Jacobs L (1961) Induced and spontaneous recurrent parasitaemia in chronic infections with avirulent strains ofToxoplasma gondii. J Immunol 87:578–581
Remington JS, Krahenbuhl JL, Mendenhall JW (1972) A role for activated macrophages in resistance to infection with toxoplasma. Infect Immun 6:829–834
Sethi KK, Pelster B, Suzuki N, Piekarski G, Brandis H (1975) Immunity toToxoplasma gondii induced in vitro in non-immune mouse macrophages with specifically immune lymphocytes. J Immunol 115:1151–1158
Shirahata T, Shimizu K, Suzuki N (1976) Effects of immune lymphocyte products and serum antibody on the multiplication of Toxoplasma in murine peritoneal macrophages. Z Parasitenkd 49:11–23
Sibley LD, Weidner E, Krahenbuhl JL (1985) Phagosome acidification blocked by intracellularToxoplasma gondii. Nature 6:516–419
Suzuki Y, Watanabe N, Kobayahi A (1981) Nonspecific suppression of primary antibody responses and presence of plastic-adherent suppressor cells inToxoplasma gondii infected mice. Infect Immun 34:30–35
Swatzerberg JE, Krahenbuhl JL, Remington JS (1975) Dichotomy between macrophage activation and degree of protection against Listeria monocytogenes andToxoplasma gondii in mice stimulated with Corynebacterium parvum. Infect Immun 12:1037–1043
Wilson CB, Westall J (1985) Activation of neonatal and adult human macrophages by alpha, beta and gamma interferon. Infect Immun 49:351–356
Wilson CB, Tsai V, Remington JS (1980) Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages. Possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med 151:328–346
Wing EJ, Boehmar SM, Christner LK (1983)Toxoplasma gondii: Decreased resistance to intracellular bacteria in mice. Exp Parasitol 56:1–8
Yam LT, Li CY, Crosby WH (1971) Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol 55:283–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, M., Ganguly, N.K. & Mahajan, R.C. Cytotoxic activity of monocytes againstToxoplasma gondii in acute, chronic and reactivated murine toxoplasmosis. Med Microbiol Immunol 177, 339–348 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02389906
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02389906