Summary
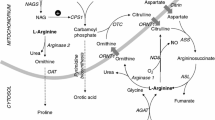
The present paper reports on two cases of a congenital metabolic disease which involves an enzyme defect in the urea cycle. A low level of arginase activity, demonstrated in blood cell hemolysates, results in an accumulation of arginine in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid. The increased excretion of arginine with the urine classifies this biochemical abnormality as an overflow amino acidurina. The main clinical features are convulsions presenting themselves together with febrile illnesses, periodical vomiting, mental and locomotor retardation, spasticity, paresis, ataxia, tremors, electroencephalographic dysrhythmia, and hepatopathia. All these features are possibly due to an ammonia intoxication, which is caused by a defect in arginase, one of the enzymes which mediates the metabolism of the urea cycle. Because of a normal urea concentration in the serum it is suggested that this defect is only a partial one. High ammonia levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid can be reduced by a low-protein diet. The locomotor development of the two affected girls progressed under physiotherapeutic treatment (special gymnastic, method after Vojta).
Zusammenfassung
Es wird über eine neue angeborene Stoffwechselstörung berichtet. Es handelt sich dabei um einen Enzymdefekt im Harnstoffcyclus. Die Verminderung der Arginaseaktivität, nachgewiesen im Erythrocytenhämolysat, führt zu einem Anstieg des Arginins im Serum und Liquor. Die vermehrte Ausscheidung von Arginin im Urin charakterisiert die Störung als Aminoacidurie vom Überfließtyp. Führende klinische Symptome sind hirnorganische Anfälle, die sich zumeist als Fieberkrämpfe manifestieren, periodisches Erbrechen, eine psychomotorische Retardierung, spastische Paresen, Ataxie, Tremor, eine Hepatopathie sowie eine Dysrhythmie im Elektroencephalogramm. Ursache der klinischen Erscheinungen ist moglicherweise die als Folge des Enzymdefektes aufgetretene Hyperammonämie. Die normalen Harnstoffwerte im Serum sprechen dafür, daß der Enzymdefekt nur partiell ist. Die erhöhten Ammoniakwerte im Serum und Liquor konnten durch eine eiweißarme Diät gesenkt werden. Die motorische Entwicklung der beiden Patienten wurde durch eine krankengymnastische Behandlung nach Vojta günstig beeinflußt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allan, J. D., D. C. Cusworth, C. E. Dent, and V. D. Wilson: A disease, probably heriditary, characterized by severe mental deficiency and a constant gross abnormality of amino acid metabolism. Lancet 1958 I, 182.
Armstrong, M. D., K. N. Yakd, and M. G. Stemmermann: An occurrence of argininosuccinicaciduria. Pediatrics 33, 280 (1964).
Atkinson, M., and J. C. Goligher: Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by surgical excision of the colon. Lancet 1960 I, 461.
Baumgartner, R., S. Scheidegger, G., Stalder u. A. Hottinger: Argininbernsteinsäure-Krankheit des Neugeborenen mit letalem Verlauf. Helv. paediat. Acta 23, 77 (1968).
Benavides, L. V., J. Kumate, J. L. P. Navarrette, J. Sagaon, and J. Carillo: Treatment of hepatic coma complicating viral hepatitis. Pediatrics 15, 568 (1955).
Bickel, H., D. Feist, H. Müller u. G. Quadbeck: Ornithinämie, eine weitere Aminosäurenstoffwechselstörung mit Hirnschädigung. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 93, 2247 (1968).
Carson, N. A. J., and D. W. Neill: Metabolic abnormalities detected in a survey of mentally backward children in Northern Ireland. Arch. Dis. Child. 37, 505 (1962).
: A Biochemical Study of Mentally Retarded Individuals in Northern Ireland with a View to Assessing the Type and Incidence of Metabolic Disorders. Thesis, M. D. Queen's University, Belfast 1963.
, Persönliche Mitteilung an M. L. Efron, Disorders of the Urea Cycle. In: J. B. Stanbury, J. B. Wyngaarden, and D. S. Fredrickson: The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. 2. Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co. 1966.
Colombo, J. P., W. Bürgi, R. Richterich, and E. Rossi: Congenital lysine intolerance with periodic ammonia intoxication: A defect in L-lysine degradation. Metabolism 16, 910 (1965).
, F. Vassella, R. Humbel, and W. Bürgi: Lysine intolerance with periodic ammonia intoxication. Amer. J. Dis. Child. 113, 138 (1967).
Coryell, M. E., W. K. Hall, T. G. Thevaos, D. A. Welter, A. J. Gatz, B. F. Horton, B. D. Sisson, J. W. Looper, and R. T. Farrow: A familial study of a human enzyme defect, argininosuccinicaciduria. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 14, 307 (1964).
Dawson, A. M., J. McLaren, and S. Sherlock: Neomycin in the treatment of hepatic coma. Lancet 1957 II, 1262.
Edkins, E., and A. Hockey: 4th Ann. Interstate Conference on Mental Deficiency. Melbourne, Okt. 1965.
Efron, M. L.: Disorders of the Urea Cycle. In: J. B. Stanbury, J. B. Wyngaarden, and D. S. Fredrickson: The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. 2. Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co. 1966.
: Diet therapy for inborn errors of amino acid metabolism. J. Amer. diet Ass. 51, 40 (1967).
Freeman, J. M., J. F. Nicholson, W. S. Masland, L. P. Rowland, and S. Carter: Ammonia intoxication due to a congenital defect in urea synthesis. J. Pediat. 65, 1039 (1964).
Gabuzda, G. J.: Hepatic coma: clinical considerations, pathogenesis and management. Advanc. intern. Med. 11, 11–73 (1962).
Geisen, K., I. Lombeck, H. G. Sieberth u. V. Weidtman: Peritonealdialyse bei einem Fall von Leberkoma im Kindesalter. Z. Kinderheilk. 101, 1 (1967).
Ghadimi, H., P. Kottmeier, R. Achs, R. Prabhu, and B. Jaffe: 35th Ann. Meeting, Soc. Pediatric Research, Philadelphia, Pa. May 1965.
Hooft, C., D. Carton et F. de Schrijver: soc. Ped. de l'est et du nord. Lille, Mai 1968.
Hopkins, I. J., J. F. Connelly, A. G. Dawson, F. J. R. Hird, and T. G. Maddison: Hyperammonaemia due to ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Arch. Dis. Child. 44, 143 (1969).
Kekomäki, M., J. Visakorpi, J. Perheentupa, and L. Saxen: Familial protein intolerance with deficient transport of basic amino acids. An analysis of 10 patients. Acta paediat. scand. 56, 617 (1967).
Levin, B., H. M. M., Mackay, and V. G. Oberholzer: Argininosuccinic aciduria. An inborn error of amino acid metabolism. Arch. Dis. Child. 36, 622 (1961).
Levin, B., Symposium of the Society for the Study of Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Zürich 1968.
, J. M. Abraham, V. G. Oberholzer, and E. A. Burgess: Hyperammonaemia: a deficiency of liver ornithine transcarbamylase: Occurrence in mother and child. Arch. Dis. Child. 44, 152 (1969).
, R. H., Dobbs, E. A. Burgess, and T. Palmer: Hyperammonaemia: a variant type of deficiency of liver ornithine transcarbamylase. Arch. Dis. Child. 44, 162 (1969).
Macbeth, W. A. A. G., E. H. Kass, and W. V. McDermott, jr.: Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by alteration of intestinal flora with Lactobacillus acidophilus. Lancet 1965 I, 399.
McDermott, W. F., jr., and R. D. Adams: Exclusion of the colon in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. New Engl. J. Med. 267, 850 (1962).
, M. Victor, and W. W. Pont: Episodic stupor associated with an Eck fistula in the human with particular reference to the metabolism of ammonia. J. clin. Invest. 33, 1 (1954).
McDonald, R., and P. L. De la Harpe: Hepatic coma in childhood. J. Pediat. 63, 916 (1963).
McMurray, W. C., F. Mohyuddin, R. J. Rossiter, J. C. Rathburn, G. H. Valentine, S. J. Koegler, and D. E. Zarfas: Citrullinuria: a new aminoaciduria associated with mental retardation. Lancet 1962 I, 138.
, J. C. Rathburn, F. Mohyuddin, and S. J. Koegler: Citrullinuria. Pediatrics 32, 347 (1963).
Mohyuddin, F., J. C. Rathburn, and W. C. McMurray: Studies on amino acid metabolism in citrullinuria. Amer. J. Dis. Child. 113, 152 (1967).
Moore, P. T., M. C. Martin, V. P. Coffey, and B. M. Stockes: Argininosuccinicaciduria. A case report on a rare condition. J. Irish med. Ass. 61, 172 (1968).
Morrow, G.: Citrullinemia. Amer. J. Dis. Child. 113, 157 (1967).
, L. A. Barness, and M. L. Efron: Citrullinemia with defective urea production. Pediatrics 40, 565 (1967).
Moser, H. W., M. L. Efron, H. Brown, R. Diamond, and C. G. Neumann: Argininosuccinic aciduria: Report of two new cases and demonstration of intermittent elevation of blood ammonia. Amer. J. Med. 42, 9 (1967).
Müting, D., H. Reikowski, W. Eschrich, Chr. Klein u. D. Doenecke: Normalisierende Wirkung einer Bacterium-bifidum-Milch auf den Eiweißstoffwechsel bei Leberzirrhose. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 93, 1313 (1968).
Nordmann, R.: Therapie der Hyperammoniämie. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 94, 230 (1969).
Peralta Serrano, A.: Argininuria, convulsiones y oligofrenia; un nuevo error innato del metabolismo? Rev. clin. esp. 97, 176 (1965).
Perheentupa, J., and J. K. Visakorpi: Protein intolerance with deficient transport of basic amino acids. Another inborn error of metabolism. Lancet 1965 II, 813.
Russel, A., B. Levin, V. G. Oberholzer, and L. Sinclair: Hyperammonemia: a new instance of an inborn enzymatic defect of the biosynthesis of urea. Lancet 1962 II, 699.
Schreier, K. u. G. Leuchte: Argininbernsteinsäure-Krankheit. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 90, 864 (1965).
Shih, V. E., M. L. Efron, and H. W. Moser: Hyperornithinemia and homocitrullinuria with ammonia intoxication, myoclonic seizures and mental retardation, a new disorder of amino acid metabolism. Amer. J. Dis. Child. 117, 83 (1969).
Silen, W., H. A. Harper, D. L. Mawdsley, and W. L. Weirich: Effect of antibacterial agents on ammonia production within the intestine. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 88, 138 (1955).
Soriano, J. R., L. S. Taitz, C. M. Edelmann, and L. Kauffman: Hyperammonemic Ketosis in So-Called Idiopathic Hyperglycinemia (Abstract). Proc. Soc. Ped. Res., Atlantic-City, April 29–30, 1966.
Starer, F., and R. Couch: Cerebral atrophy in hyperammonemia. Clin. Radiol. 14, 353 (1963).
Tomlinson, S., and R. G. Westall: Argininosuccinic aciduria, argininosuccinase and arginase in human blood cells. Clin. Sci. 26, 261 (1964).
Wallis, K., S. Beer, and J. Fischl: A family affected by argininosuccinic aciduria. Helv. paediat. Acta 18, 339 (1963).
Westall, R. G.: Argininosuccinic aciduria. In: Proceedings of the Fourth Internat. Congress on Biochemistry, V. 168, Vienna 1958.
: Argininosuccinicaciduria: identification and reactions of the abnormal metabolites in a newly described form of mental disease, with some preliminary metabolic studies. Biochem. J. 77, 135 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terheggen, H.G., Schwenk, A., Lowenthal, A. et al. Hyperargininämie mit Arginasedefekt Eine neue familiäre Stoffwechselstörung. Z. Kinder-Heilk. 107, 298–312 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00438892
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00438892