Abstract
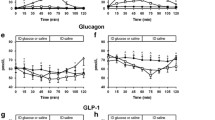
Blood glucose, insulin, C-peptide and glucagon were evaluated in 36 newborn term infants at birth, and before and 60 min after the first feed during the first day of life. Under basal conditions glycaemia diminished during the first day of life and glucagon increased, while insulin and C-peptide did not show any variation. The C-peptide: insulin molar ratio was higher in the newborn than in adults because of the longer half-life of C-peptide, probably due to reduced renal function in the neonatal period.
The subjects were divided into two groups: 18 newborn infants were given a feed of commercially available milk powder reconstituted in water at 10% (5 ml/kg); the other 18 were given a feed of 5 ml/kg 10% glucose solution. In each group 6 were given the first feed after a fast of 6 h, 6 after a fast of 12 h, and 6 after a fast of 24 h from birth. After the first feed with milk, the average increase of glycaemia was 19.83 mg%, of insulin 6.06 μU/ml, and of C-peptide 1.88 ng/ml. After the first feed with glucose the average increase of glycaemia was 13.59 mg%, of insulin 2.46 μU/ml, and of C-peptide 0.59 ng/ml. Glucagon did not show significant changes after the first feed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, P. A. J., Teramo, K., Raiha, N., Gitlin, D., Schwartz, R.: Human fetal insulin metabolism early in gestation: response to acute elevation of the fetal glucose concentration and placental transfer of human insulin I-131. Diabetes 18, 409 (1969)
Asplund, K., Westman, S., Hellerstrom, C.: Glucose stimulation of insulin secretion from the isolated pancreas of foetal and newborn rats. Diabetologia 5, 260 (1969)
Aynsley-Green, A., Bloom, S. R., Williamson, D. H., Turner, R. C.: Endocrine and metabolic response in the human newborn to first feed of breast milk. Arch. Dis. Childh. 52, 291 (1977)
Blasquez, E., Sugasse, T., Blasquez, M., Foà, P. P.: Neonatal changes in the concentration of rat liver AMP of the serum glucose, free fatty acids, insulin, pancreatic and total glucagon in man and in the rat. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 83, 957 (1974)
Falorni, A., Fracassini, F., Massi-Benedetti, F., Maffei, S.: Glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in the newborn infant. Comparisons between the responses observed the first and seventh day of life to intravenous and oral glucose tolerance tests. Diabetes 23, 172 (1974)
Falorni, A., Massi-Benedetti, F., Gallo, S., Romizi, S.: Blood glucose and plasma insulin and glucagon response to arginin infusion in low birth weight infants. Pediat. Res. 9, 55 (1975)
Grajwer, L. A., Sperling, M. A., Sack, J., Fisher, D. A.: Possible mechanisms and significance of the neonatal surge in glucagon secretion: studies in newborn lambs. Pediat. Res. 11, 833 (1977)
Grasso, S., Messina, A., Distefano, G., Vigo, R., Reitano, G.: Insulin secretion in the premature infant. Response to glucose and aminoacids. Diabetes 22, 349 (1973)
Johnston, D. I., Bloom, S. R.: Plasma glucagon in the full-term human infant and the effect of hypoxia. Arch. Dis. Childh. 48 451 (1973)
Johnston, D. I., Bloom, S. R., Green, K. R., Beard, R. W.: Failure of the human placenta to transfer pancreatic glucagon. Biol. Neonate 21, 375 (1975)
Kaneko, T., Oka, H., Munemura, M., Oda, T., Yamashita, K., Suzuki, S., Yanaihara, N., Hashimoto, T., Yanaihara, C.: Radioimmunoassay of human proinsulin C-Peptide using synthetic human connecting peptide. Endocr. Jap. 21, 141 (1974)
Krause, U., Cordes, U., Beyer, J.: C-Peptide: Sekretion und Stoffwechsel bei unterschiedlichen Funktionszuständen und Störungen der B-Zellen der Langerhansschen Inseln. Dtsch. Med. Wschr. 102, 785 (1977)
Kuzuya, T., Matsuda, A.: Disappearance rate of endogenous human C-Peptide from blood. Diabetologia 12, 519 (1976)
Lucas, A., Bloom, S. R., Aynsley-Green, A.: Metabolic and endocrine events at the time of the first feed of human milk in preterm and term infants. Arch. Dis. Childh. 53, 731 (1978)
Luychx, A. S., Massi-Benedetti, F., Deconninck, B., Falorni, A., Lefebvre, P. J.: Glucagon, insulin et rapport insulin-glucagon chez le nouveau-né de mère normale or diabétique. Rev. Franç. Endocrin. Clin. 15, 29 (1974)
Milner, R. D. G., Chouksey, S. K., Mickleson, K. N. P., Assan, R.: Plasma pancreatic glucagon and insulin: glucagon ratio at birth. Arch. Dis. Childh. 49, 241 (1973)
Nakai, T., Kajinuma, H., Kanazawa, Y.: Pancreatic glucagon and total immunoreactive glucagon (IRG) levels in umbilical vessels and IRG response to milk load in newborns. Acta Neonatol. Jpn. 13, 177 (1977)
Rubenstein, A. H., Clark, J. L., Melani, F., Steiner, D. F.: Secretion of proinsulin C-Peptide by pancreatic β-cells and its circulation in blood. Nature 224, 697 (1969)
Salle, B. L., Ruiton-Ugliengo, A.: Effects of oral glucose and protein load on plasma glucagon and insulin concentrations in small for gestational age infants. Pediat. Res. 11, 108 (1977)
Sann, L., Ruitton, M., Mathieu, M., Bourgeois, J., Genoud, J.: Effect of intravenous L-alanine administration on plasma glucose, insulin and glucagon, blood pyruvate, lactate and beta-hydroxybutyrate concentrations in newborn infants. Study in term and preterm newborn infants. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 67, 297 (1978)
Sperling, M. A., DeLamater, P. V., Phelps, D., Fiser, R. H., Oh, W., Fisher, D. A.: Spontaneous and aminoacids stimulated secretion in the immediate postnatal period. Relation to glucose and insulin. J. Clin. Invest. 53, 1159 (1974)
Sperling, M. A., Grajwer, L. A., Leake, R., Fisher, D. A.: Role of glucagon in perinatal glucose homeostasis. Metabolism 25, Suppl. 1, 1385 (1976)
Unger, R. H.: Alpha and beta-cell interrelationships in health and disease. Metabolism 23, 581 (1974)
Weir, G. C., Turner, R. C., Martin, D. B.: Glucagon radioimmunoassay using antiserum 30K: interference by plasma. Horm. Metab. Res. 5, 241 (1973)
Wise, J. K., Santokh, S. L., Hendler, R., Felig, P.: Evidence of stimulation of glucagon secretion by alanine in the human fetus at term. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 37, 345 (1973)
Yallow, R. S., Berson, S. A.: Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J. Clin. Invest. 39, 1157 (1960)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamboni, G., Rigosa, C., Mantovanelli, F. et al. Pancreatic endocrine response to the first feed in term newborn infants. Eur J Pediatr 132, 189–195 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442435
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442435