Abstract
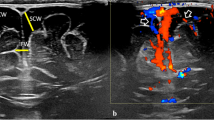
Two cases of unilateral subependymal germinal matrix haemorrhage associated with homolateral periventricular haemorrhagic infarction (PVHI) are reported in two premature newborns. This association is rather rare. Indeed, PVHI occurs generally with large intraventricular haemorrhage. Diagnosis is made by brain imaging (ultrasound, MRI) scans and single photon emission computed tomography. PVHI is probably caused by obstruction of periventricular venous drainage by large intraventricular haemorrhage leading to a haemorrhagic venous infarction. From our cases, we conclude that extraventricular haemorrhage leading to a large subependymal haematoma can result in obstruction of periventricular venous drainage, subsequent PVHI and abnormal neuromotor development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
cerebral computed tomography
- ICH:
-
intracranial haemorrhage
- IPI:
-
intraparenchymal cerebral involvement
- IVH:
-
intraventricular haemorrhage
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- PVHI:
-
periventricular haemorrhagic infarction
- SEH:
-
subependymal germinal matrix haemorrhage
- SPECT:
-
single photon emission computed tomography
- US:
-
cerebral ultrasound
References
Gould SJ, Howard S, Hope PL, Reynolds EOR (1987) Periventricular intraparenchymal cerebral hemorhage in preterm infants: the role of venous infarction. J Pathol 151:197–202
Guzetta F, Shackelford GD, Volpe S, Perelman JM, Volpe JJ (1986) Periventricular intraparenchymal echodensities in the premature newborn: critical determinant of neurological outcome. Pediatrics 78:995–1006
Haddad J, Christmann D, Roy E, Messer J, Willard D (1990) Cerebral magnetic resonance imaging of the neonate. Pédiatrie 45:665–675
Roland EH, Flodmark O, Hill A (1990) Thalamic hemorrhage with intraventricular hemorrhage in the full-term neonates. Pediatrics 85:737–742
Takashima S, Mito T, Ando Y (1986) Pathogenesis of periventricular white matter hemorrhage in preterm infants. Brain Dev 8:25–30
Uvebrant P (1988) Hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Aetiology and outcome. Acta Paediatr Scand [Suppl] 345:15–42
Volpe JJ (1989) Intraventricular hemorrhage and brain injury in the premature infant: diagnosis prognosis and prevention. Clin Perinatol 16:387–412
Volpe JJ (1989) Intraventricular hemorrhage and brain injury in the premature infant. Neuropathology and pathogenesis. Clin Perinatol 16:361–386
Volpe JJ, Herschovitch P, Perlman J, Raichle ME (1983) Positron emission tomography in the newborn: extensive impairment of regional cerebral blood flow with intraventricular hemorrhage and hemorrhagic intracerebral involvement. Pediatrics 72:589–601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddad, J., Messer, J. & Aranda, J. Periventricular haemorrhagic infarction associated with subependymal germinal matrix haemorrhage in the premature newborn. Report of two cases. Eur J Pediatr 151, 63–65 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02073896
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02073896