Abstract
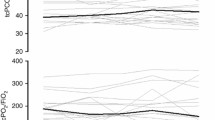
The effects of high frequency oscillation (HFO) on dynamic lung inflation were examined in 22 neonates ventilated for respiratory disease. HFO was combined with conventional ventilation and a series of frequencies from 2–25 Hz was tested. Dynamic lung inflation was measured using a jacket plethysmograph which was converted to a measure of alveolar pressure using the complicance of the respiratory system obtained during conventional ventilation. The results showed an increase in dynamic lung inflation with frequency such that volume increased by 0.4 ml for each increase of 10 Hz. Alveolar pressure increased by 1.2 cm H2O for each increase of 10 Hz. Dynamic lung inflation also increased with increased volumes of oscillation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPAP:
-
continuous positive airways pressure
- ET:
-
endotracheal
- HFO:
-
high frequency oscillation
- IPPV:
-
intermittent positive airways pressure
- PEEP:
-
positive end expiratory pressure
References
Armengol J, Jones RL, King EG (1985) Alveolar pressures and lung volumes during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in dogs. Crit Care Med 13no8:632–636
Bancalari A, Gerhardt T, Suguihara C, Hehre D, Reifenberg, Goldberg R, Bancalari E (1986) Air trapping with high frequency jet (HFJ) and oscillatory (HFO) ventilation. Pediatr Res 20no4:423A
Beamer WC, Prough DS, Royster RL, Johnston WE, Johnson JC (1984) High-frequency jet ventilation produces auto-PEEP. Crit Care Med 12no9:734–737
Boynton BR, Mannino FL, Davis RF, Kopotic RJ, Friederichsen G (1984) Combined high-frequency oscillatory ventilation and intermittent mandatory ventilation in critically ill neonates. J Pediatr 105:297–302
Bryan AC, Slutsky AS (1986) Lung volume during high frequency oscillation. Am Rev Respir Dis 133:928–930
Field DJ, Milner AD, Hopkin IE (1984) High and conventional rates of positive pressure ventilation. Arch Dis Child 59no1:1151–1154
Frantz IF III, Werthammer J, Stark AR (1983) High-frequency ventilation in premature infants with lung disease: adequate gas exchange at low tracheal pressure. Pediatr 71; 4:483–488
Froese AB, Bryan AC (1984) High frequency ventilation. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:1363–1374
Helms P, Taylor BW, Milner AD, Hatch DJ (1982) Critical assessment of jacket plethysmographs for use in young children. J Appl Physiol 52no1:267–273
Hoskyns EW, Milner AD, Hopkin IE (1991) Combined conventional ventilation with high frequency oscillation in neonates. Eur J Pediatr 150:357–361
Hoskyns EW, Milner AD, Hopkin IE (1992) Measurement of tidal volumes during high frequency oscillation in neonates. J Biomed Eng 14:16–20
Isabey D, Chang HK (1981) Steady and unsteady pressure-flow relationships in central airways. J Appl Physiol 51no5: 1338–1348
Kolton M, Cattran CB, Kent G, Volgyesi G, Froese AB (1982) Oxygenation during high frequency ventilation compared with conventional mechanical ventilation in two models of lung injury. Anesth Analg 61:323–332
Mansel JK, Gillespie DJ (1986) Oxygenation during ventilation by high-frequency oscillation in dogs with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 14no11:955–959
Schlachter MD, Perry ME (1984) Effect of continuous positive airway pressure on lung mechanics during high-frequency jet ventilation. Crit Care Med 12no9:755–758
Simbruner G (1986) Inadvertent positive end-expiratory pressure in mechanically ventilated newborn infants: Detection and effect on lung mechanics and gas exchange. J Pediatr 108: 589–595
Simon BA, Wienmann GG, Mitzner W (1984) Mean airway pressure and alveolar pressure during high-frequency ventilation. J Appl Physiol 157no4:1069–1078
Weisberger SA, Carlo WA, Chatburn RL, Fouke JM, Martin RJ (1986) Effect of varying inspiratory and expiratory times during high-frequency jet ventilation. J Pediatr 108:596–600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoskyns, E.W., Milner, A.D. & Hopkin, I.E. Dynamic lung inflation during high frequency oscillation in neonates. Eur J Pediatr 151, 846–850 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957938
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957938