Summary
-
1.
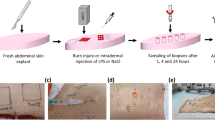
A new technique to apply high temperature burns and scalds under controlled conditions in living mice has been established.
-
2.
The difference between scalds and high temperature heat injuries with respect to the histological changes, the temperature profile within the skin and the mortality rate has been demonstrated. A mechanism for toxin formation shown to occurin vitro in mammalian skin under standardized energy application was reproducedin vivo.
-
3.
The toxic effect of the isolated product and the lethal burn injury(in vivo) upon kidney function measured by serum creatinine and urea has been shown.
-
4.
The relationship between the surface area injured and the animal's body weight and total surface as a critical parameter with respect to the survival chance has been established.
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Es wurde ein neues Verbrennungsmodell der Maus entwickelt, das es erlaubt, Verbrennungen und Verbrühungen unter kontrollierten Bedingungen am lebenden Tier vorzunehmen.
-
2.
Der Unterschied zwischen Verbrennung und Verbrühung in bezug auf die Mortalität, den Temperaturverlauf in der Haut und die histologischen Unterschiede konnte gezeigt werden. Der mechanismus für eine Toxinbildung bei der Verbrennung wurde bewiesen.
-
3.
Der Einfluß des isolierten Toxins und der letalen Verbrennung auf die Nierenfunktion wurde an Veränderungen der Kreatinin- und Harnstoffwerte im Serum nachgewiesen.
-
4.
Das Größenverhältnis der durch thermische Energie geschädigten Haut zum Körpergewicht und der Oberfläche zeigte sich als kritischer Parameter der Mortalität.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allgöwer, M., Burri, C., Cueni, L., Engley, F., Fleisch, H., Gruber, U. F., Harder, F., Russell, R. G. G.: Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.150, 807 (1968).
Bailey, B. N.: Brit. J. plast. Surg.14, 243 (1961).
Caldwell, F. T., Osterholm, J. H., Lower, N. D., Moyer, C. A.: Ann. Surg.150, 976 (1959).
Contram, R. S., Remensnyder, J. P.: Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.150, 495 (1968).
Cueni, L. B., Allgöwer, M., Schoenenberger, G. A.: Z. ges. exp. Med.156, 110 (1971).
Holder, I. A., Jogan, M.: Experientia (Basel)26, 1363 (1970).
Horn, S. H., Malm, O. J.: Report to the Committee on Shock and Trauma. Nat. Acad. Sci., Research Council, 1958.
Jones, R. J., Lawrence, J. C.: Brit. J. exp. Path.45, 198 (1964).
Jones, A.: J. clin. Path.17, 470 (1964).
Köhnlein, H. E., Lemperle, G. In: Research in Burns, p. 179, Matter, P. Barclay, T. L., Konickova, Z. (Eds.). Bern: Huber 1970.
Koslowski, L., Urbascheck, B., Versteyl, R. In: Research in Burns, p. 421, Wallace, A. B., Wilkinson, A. W. (Eds.). London: Livingstone 1966.
Malm, O. J., Slawikowski, G. J. M. In: Research in Burns, p. 282, Artz, C. P. (Ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Sci. Publ. 1962.
O'Neill, J. A., Ritcher, C. R., Mason, D., Villarreal, Y.: Surg. Gynec. Obstet.131, 29 (1970).
Phillips, A. W., Cope, O. In: Research in Burns, p. 1, Artz, C. P. (Ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Sci. Publ. 1962.
Prinzmetal, M., Hechter, O.: Surgery16, 906 (1944).
Renner, K.: Strahlentherapie132, 33 (1967).
Rosenthal, S. M., Tabor, H.: Arch. Surg.51, 244 (1945).
Rosenthal, S. R., Hunter, A. S., Finamore, F. I., Williams, F., Roman, I. N.: Fed. Proc.14, 124 (1955).
Rubner, M.: Z. Biol.19, 535 (1883).
Schoenenberger, G. A., Matter, P., Allgöwer, M.: Excerpta med. (Amst.) Int. Congr. Ser.190, 119 (1969).
Schoenenberger, G. A., Cueni, L. B., Bauer, U., Eppenberger, U., Allgöwer, M.: Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) (im Druck).
Schoenenberger, G. A., Bauer, U., Cueni, L. B., Eppenberger, U., Städtler, K., Allgöwer, M.: Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) (im Druck).
Städtler, K., Allgöwer, M., Cueni, L. B., Schoenenberger, G. A.: Europ. Surg. Res. (im Druck).
Tait, M. J., Franks, F.: Nature (Lond.)230, 91 (1971).
Ussing, H. H.: Harvey Lect.59, 13 (1963–1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Diese Arbeit wurde unterstützt mit Beiträgen des Schweizerischen Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaften (Kredit-Nummern 3.284.69 und 3.349.70).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Städtler, K., Allgöwer, M., Cueni, L.B. et al. Pathophysiologische Untersuchungen an einem Verbrennungsmodell der Maus. Res. Exp. Med. 158, 23–33 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851683
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851683