Abstract
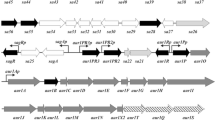
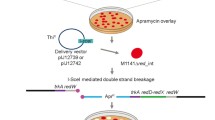
We have analyzed an anthracycline biosynthesis gene cluster fromStreptomyces nogalater. Based on sequence analysis, a contiguous region of 11 kb is deduced to include genes for the early steps in anthracycline biosynthesis, a regulatory gene (snoA) promoting the expression of the biosynthetic genes, and at least one gene whose product might have a role in modification of the glycoside moiety. The three ORFs encoding a minimal polyketide synthase (PKS) are separated from the regulatory gene (snoA) by a comparatively AT-rich region (GC content 60%). Subfragments of the DNA region were transferred toStreptomyces galilaeus mutants blocked in aclacinomycin biosynthesis, and to a regulatory mutant ofS. nogalater. TheS. galilaeus mutants carrying theS. nogalater minimal PKS genes produced auramycinone glycosides, demonstrating replacement of the starter unit for polyketide biosynthesis. The product ofsnoA seems to be needed for expression of at least the genes for the minimal PKS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bibb MJ, Cohen SN (1982) Gene expression inStreptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors inStreptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet 187:265–277
Bibb MJ, Janssen GR, Ward JM (1985) Cloning and analysis of the promoter region of the erythromycin resistance gene (ermE) ofStreptomyces erythraeus. Gene 38:215–226
Dickens ML, Ye J, Strohl WR (1995) Analysis of clustered genes encoding both early and late steps in daunomycin biosynthesis byStreptomyces sp. strain C5. J Bacteriol 177:536–543
Fernandez-Moreno M, Caballero J, Hopwood DA, Malpartida F (1991) Theact cluster contains regulatory and antibiotic export genes, direct targets for translational control by thebldA tRNA gene ofStreptomyces. Cell 66:769–780
Fu H, Ebert-Khosla S, Hopwood DA, Khosla C (1994) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides: dissection of the catalytic specificity of theact ketoreductase. J Am Chem Soc 116:4166–4170
Fujiwara A, Hoshino T, Tazoe M, Fujiwara M (1981) Auramycins and sulfurmycins, new anthracycline antibiotics: characterization of aglycones, auramycinone and sulfurmycinone. J Antibiot 34:608–610
Fujiwara A, Hoshino T, Tazoe M (1980) Process to produce aclacinomycins A and B: U.S. Patent 4 375 511. Published 1.3.1983, priority 27.10.1980
Geistlich M, Losick R, Turner JR, Rao RN (1992) Characterization of a novel regulatory gene governing the expression of a polyketide synthase gene inStreptomyces ambofaciens. Mol Microbiol 6:2019–2029
Grimm A, Madduri K, Ali A, Hutchinson CR (1994) Characterization of theStreptomyces peucetius ATCC29050 genes encoding doxorubicin polyketide synthase. Gene 151:1–10
Hopwood DA, Bibb MJ, Chater KF, Kieser T, Bruton CJ, Kieser HM, Lydiate DJ, Smith CP, Ward JM, Schrempf H (1985) Genetic manipulation ofStreptomyces: a laboratory manual. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Horinouchi S, Kito M, Nishiyama M, Furuya K, Hong S.-K, Miyake K, Beppu T (1990) Primary structure of AfsR, a global regulatory protein for secondary metabolite formation inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Gene 95:49–56
Kim E-S, Bibb MJ, Hopwood DA, Sherman DH (1994) Sequences of the oxytetracycline polyketide synthase-encodingotc genes fromStreptomyces rimosus. Gene 141:141–142
Malpartida F, Hallam SE, Kieser HM, Motamedi H, Hutchinson CR, Butler MJ, Sugden DA, Warren M, McKillop C, Bailey CR, Humphreys GO, Hopwood DA (1987) Homology betweenStreptomyces genes coding for synthesis of different polyketides and its use to clone antibiotic biosynthetic genes. Nature 325:818–821
Matsuzawa Y, Yoshimoto A, Shibamoto N, Tobe H, Oki T, Naganawa H, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H (1981) New anthracycline metabolites from mutant strains ofStreptomyces galilaeus MA144-M1. II. Structure of 2-OH aklavinone and new aklavinone glycosides. J Antibiot 34:959–964
McDaniel R, Ebert-Khosla S, Hopwood DA, Khosla C (1993) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides. Science 262:1546–1550
McDaniel R, Ebert-Khosla S, Fu H, Hopwood DA, Khosla C (1994a) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides: influence of a downstream enzyme on the catalytic specificity of a minimal aromatic polyketide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11542–11546
McDaniel R, Ebert-Khosla S, Hopwood DA, Khosla C (1994b) Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides:actVII andactIV genes encode aromatase and cyclase enzymes, respectively. J Am Chem Soc 116:10855–10859
Narva KE, Feitelson JS (1990) Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of theredD locus ofStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 172:326–333
Niemi J, Mäntsälä P (1995) Nucleotide sequences and expression of genes fromStreptomyces purpurascens that cause the production of new anthracyclines inStreptomyces galilaeus. J Bacteriol 177:2942–2945
Niemi J, Ylihonko K, Hakala J, Pärssinen R, Kopio A, Mäntsälä P (1994) Hybrid anthracycline antibiotics: production of new anthracyclines by cloned genes fromStreptomyces purpurascens inStreptomyces galilaeus. Microbiology 140:1351–1358
Oki T, Matsuzawa Y, Yoshimoto A, Numata K, Kitamura I, Hori S, Takamatsu A, Umezawa H, Ishizuka M, Naganawa H, Suda H, Hamada M, Takeuchi T (1975) New antitumor antibiotics, aclacinomycins A and B. J Antibiot 28:830–834
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd edn). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sherman DH, Malpartida F, Bibb MJ, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA (1989) Structure and deduced function of the granaticin-producing polyketide synthase gene cluster ofStreptomyces violaceoruber Tü22. EMBO J 8:2717–2725
Stein D, Cohen SN (1989) A cloned regulatory gene ofStreptomyces lividans can suppress the pigment deficiency phenotype of different developmental mutants. J Bacteriol 171:2258–2261
Stutzman-Engwall K, Otten S, Hutchinson CR (1992) Regulation of secondary metabolism inStreptomyces spp. and overproduction of daunorubicin inStreptomyces peucetius. J Bacteriol 174:144–154
Summers RG, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Motamedi H, Hutchinson CR (1993) ThetcmVI region of the tetracenomycin C biosynthetic gene cluster ofStreptomyces glaucescens encodes the tetracenomycin F1 monooxygenase, tetracenomycin F2 cyclase, and, most likely, a second cyclase. J Bacteriol 175:7571–7580
Tsukamoto N, Fujii I, Ebizuka Y, Sankawa U (1992) Cloning of aklavinone biosynthesis genes fromStreptomyces galilaeus. J Antibiot 45:1286–1294
Ward JM, Janssen GR, Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Bibb MJ (1986) Construction and characterization of a series of multicopy promoter-probe plasmid vectors forStreptomyces using the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase from Tn5 as indicator. Mol Gen Genet 203:468–478
Wiley PF, MacKellar FA, Caron EL, Kelly RB (1968) Isolation, characterization and degradation of nogalamycin. Tetrahedron Lett 663–668
Wright F, Bibb MJ (1992) Codon usage in the G+C-richStreptomyces genome. Gene 113:55–65
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Ye J, Dickens M, Plater R, Li Y, Lawrence J, Strohl W (1994) Isolation and sequence analysis of polyketide synthase genes from the daunomycin-producingStreptomyces sp. strain C5. J Bacteriol 176:6270–6280
Ylihonko K, Hakala J, Niemi J, Lundell J, Mäntsälä P (1994) Isolation and characterization of aclacinomycin A-non-producingStreptomyces galilaeus (ATCC31615) mutants. Microbiology 140:1359–1365
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kondorosi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ylihonko, K., Tuikkanen, J., Jussila, S. et al. A gene cluster involved in nogalamycin biosynthesis fromStreptomyces nogalater: sequence analysis and complementation of early-block mutations in the anthracycline pathway. Molec. Gen. Genet. 251, 113–120 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02172908
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02172908