Abstract
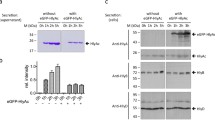
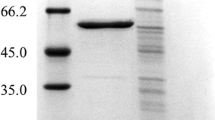
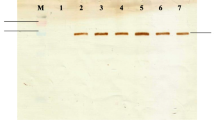
A simple and efficient procedure for the construction of secreted fusion proteins inEscherichia coli is described that uses a new minitransposon, termed TnhlyAs, carrying the secretion signal (HlyAs) ofE. coli hemolysin (HlyA). This transposon permits the generation of random gene fusions encoding proteins that carry the HlyAs at their C-termini. For the construction of model gene fusions we usedlacZ, encoding the cytoplasmicβ-galactosidase (β-Gal), andphoA, encoding the periplasmic alkaline phosphatase, as target genes. Our data suggest that allβ-Gal-HlyAs fusion proteins generated are secreted, albeit with varying efficiencies, by the HlyB/HlyD/TolC hemolysin secretion machinery under Sec-proficient conditions. In contrast, the PhoA-HlyAs fusion proteins are efficiently secreted in asecA mutant strain only under SecA-deficient conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banz R, Maier E, Gentschev I (1993) TolC ofEscherichia coli functions as an outer membrane channel. Zentralbl Bakteriol 278:187–196
Blight MA, Holland IB (1994) Heterologous protein secretion and the versatileEscherichia coli haemolysin translocator. Trends Biotechnol 12:450–455
de Lorenzo V, Herrero M, Jakubzik U, Timmis KN (1990) Mini-Tn5 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis, promoter probing, and chromosomal insertion of cloned DNA in gramnegative eubacteria. J Bacteriol 172:6568–6572
Gentschev I, Goebel W (1992) Topological and functional studies on HlyB ofEscherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 232:40–48
Gentschev I, Hess J, Goebel W (1990) Change in the cellular localization of alkaline phosphatase by alteration of its carboxyterminal sequence. Mol Gen Genet 222:211–216
Gentschev I, Mollenkopf H-J, Sokolovic Z, Hess J, Kaufmann SHE, Goebel W (1996) Bacterial virulence — molecular mechanisms and practical applications. Gene, in press
Gray L, Baker K, Kenny B, Mackman N, Haigh R, Holland IB (1989) A novel C-terminal signal sequence target Escherichia coli haemolysin directly to the medium. J Cell Sci [Suppl] 11:45–57
Herrero M, de Lorenzo V, Timmis KN (1990) Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in gramnegative bacteria. J Bacteriol 172:6557–6567
Hess J, Wels W, Vogel M, Goebel W (1986) Nucleotide sequence of a plasmid-encoded determinant and its comparison with corresponding chromosomal haemolysin sequence. FEMS Microbiol Lett 34:1–11
Hess J, Gentschev I, Goebel W, Jarchau T (1990) Analysis of the haemolysin secretion system by PhoA-HlyA fusion proteins. Mol Gen Genet 224:201–208
Hess J, Gentschev I, Miko D, Welzel M, Ladel Ch, Goebel W, Kaufmann SHE (1996) Superior efficacy of secreted over somatic antigen display in vaccine induced protection against an intracellular bacterial pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1458–1463
Jarchau T, Chakraborty T, Garcia F, Goebel W (1994) Selection for transport competence of C-terminal polypeptides derived fromEscherichia coli haemolysin: the shortest peptide capable of autonomous HlyB-HlyD-dependent secretion comprises the C-terminal 62 amino acids of HlyA. Mol Gen Genet 245:53–60
Kalnins A, Otto K, Rüther U, Müller-Hill B (1983) Sequence of thelacZ gene ofEscherichia coli. EMBO J 2:593–597
Kenny B, Haigh R, Holland IB (1992) Identification of individual amino acids required for secretion within the haemolysin (HlyA) C-terminal targeting region. Mol Microbiol 8:1163–1175
Koronakis V, Koronakis E, Hughes C (1989) Isolation and analysis of the C-terminal signal directing export ofEscherichia coli haemolysin across both bacterial membranes. EMBO J 8:595–605
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Ludwig A, Goebel W (1996) Haemolysins ofE. coli. In: Mechanisms of virulence. Cambridge University Press, in press
Manoil C, Beckwith J (1985) TnPhoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:8129–8133
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Miller VL, Makalanos JJA (1988) A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants inVibrio cholerae requirestoxR. J Bacteriol 170:2575–2583
O'Callaghan D, Morris CHA, Kirby SM, Shinger AH (1972) β-Lactamase assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1:283–288
Pugsley AP (1993) The complete general secretory pathway in Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev 57:50–108
Rüther U, Müller-Hill B (1983) Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J 2:1791–1794
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Habor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Habor, New York
Schülein R (1993) PhD thesis, Würzburg University
Shuttleworth H, Taylor J, Minton N (1986) Sequence of the gene for alkaline phosphatase fromEscherichia coli JM83. Nucleic Acids Res 14:8689
Towbin H, Staehelin H, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Vogel M, Hess J, Then I, Juarez A, Goebel W (1988) Characterisation of a sequence (hlyR) which enhances synthesis and secretion of haemolysin inEscherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 212:76–84
Wagner W, Vogel M, Goebel W (1983) Transport of haemolysin across the outer membrane ofEscherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol 154:200–210
Wandersman C (1992) Secretion across the bacterial outer membrane. Trends Genet 8:317–322
Wandersman C, Delepelaire P (1990) TolC, anEscherichia coli outer membrane protein required for haemolysin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:4776–4780
Wanner BL (1987) Phosphate regulation of gene expression inEscherichia coli. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds)Escherichia coli andSalmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 1326–1333
Wolfe BP, Rice M, Wickner W (1985) Effects of twosec genes on protein assembly into the plasma membrane ofEscherichia coli. J Biol Chem 260:1836–1841
Zhang F, Greig DI, Ling V (1993) Functional replacement of the haemolysin A transport signal by a different primary sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4211–4215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by E. Bautz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gentschev, I., Maier, G., Kranig, A. et al. Mini-TnhlyAs: a new tool for the construction of secreted fusion proteins. Molec. Gen. Genet. 252, 266–274 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173772
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173772