Summary
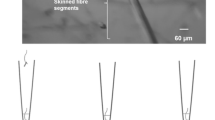
The ultrastructure of normal and glycerol treated fibers of the closer muscle of the ghost crab, Ocypode cursor, was studied. The muscle is composed of presumably phasic (short sarcomeres) and tonic (long sarcomeres) fibers, the latter greatly predominating. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was used as an extracellular tracer to delineate the tubular system (TS), and to determine to what extent this system becomes detached from the extracellular space as a result of glycerol treatment. Sarcolemmal clefts invade deeply into the muscle at Z-lines and I-bands; tubules invaginate into the muscle from the clefts and from the surface sarcolemma at the Z-lines, A-I overlaps and A-bands. A tubules are in frequent diadic or tetradic contact with the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), whereas Z tubules appear to be randomly associated with SR, terminal cisterns (TC) and Z-line fibrils. When HRP was administered to normal muscle, black reaction product was found adjacent to the outer surface of the sarcolemma, within the clefts and within profiles of the TS throughout the tissue. In glycerol treated muscle peripheral vacuolation frequently occurred; black reaction product penetrated only as far as the vacuoles and into dilated Z-line tubules, but was virtually absent from the rest of the TS. This lack of continuity between the extracellular space and the A tubules indicated disruption or constriction of the A tubules as a result of glycerol treatment, although Z tubule contact with the extracellular space appeared unimpaired.
These findings provide ultrastructural correlates of the electrophysiological changes produced by glycerol treatment of the closer muscle of the ghost crab (Papir, 1973), namely, interference with excitation-contraction (e-c) coupling. The random association of the Z tubules with SR and TC, and their resistance to disruption by glycerol treatment, tend to endorse the claims that the Z tubules in crustacean muscle are not directly involved in e-c coupling (Brandt et al., 1965; Peachey, 1967; Selverston, 1967).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- TS:
-
tubular system
- SR:
-
sarcoplasmic reticulum
- TC:
-
terminal cisterns
- e-c:
-
excitation-contraction
- N.A.S.W.:
-
normotonic artificial sea water
- G.A.S.W.:
-
glycerol artificial sea water
- EM:
-
electron microscopy
References
Atwood, H. L.: Crustacean neuromuscular mechanisms. Amer. Zool. 7, 527–551 (1967)
Brandt, P. W., Reuben, J. P., Girardier, L., Grundfest, H.: Correlated morphological and physiological studies in isolated single muscle fibers. I. Fine structure of the crayfish muscle fiber. J. Cell Biol. 25, 233–261 (1965)
Brandt, P. W., Reuben, J. P., Grundfest, H.: Correlated morphological and physiological studies on isolated single muscle fibers. II. The properties of the crayfish transverse tubular system: localization of the sites of reversible swelling. J. Cell Biol. 38, 1 115–129 (1968)
Castel, M., Papir, D., Werman, R.: The ultrastructure of glycerol-treated crab muscle. Israel J. med. Sci. 10, 530 (1973)
Eisenberg, B., Eisenberg, R. S.: Transverse tubular system in glycerol-treated skeletal muscle. Nature (Lond.) 160, 1243–1244 (1968)
Eisenberg, R. S., Gage, P. W.: Frog skeletal muscle fibers: changes in electrical properties after disruption of transverse tubular system. Science (N. Y.) 158, 1700–1701 (1967)
Fahrenbach, W. H.: The structure of fast and slow crustacean muscles. J. Cell Biol. 35, 69–79 (1967)
Franzini-Armstrong, C.: Natural variability in the length of thin and thick filaments in single fibers from a crab, Portunus clepurator. J. Cell Sci. 6, 559–592 (1970)
Fujino, M., Yagamuchi, T., Fujino, S.: “Glycerol effect” in various kinds of muscle cell. Jap. J. Physiol. 22, 477–489 (1972)
Fujino, M., Yagamuchi, T., Syzuki, K.: “Glycerol effect” and the mechanism linking excitation of the plasma membrane with contraction. Nature (Lond.) 192, 1159–1161 (1961)
Gage, P. W., Eisenberg, R. S.: Action potentials and excitation contraction coupling in frog sartorius fibers without transverse tubules. J. gen. Physiol. 53, 298–310 (1969)
Howell, J. N., Jenden, D. J.: T-gubules of skeletal muscle morphological alteration which interrupt excitation contraction coupling. Fed. Proc. 26, 553 (1967)
Howell, J. N., Jenden, D. J.: A lesion of the transverse tubules of skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 201, 515–533 (1969)
Hoyle, G., McNeill, P. A.: Correlated physiological and ultrastructural studies on specialized muscles. J. exp. Zool. 167, 523–550 (1968)
Huxley, A. F., Taylor, R. E.: Local activation of striated muscle fibers. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 144, 426–441 (1958)
Karnovsky, M. J.: The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J. Cell Biol. 35, 213–236 (1967)
Krolenko, S. A.: Changes in the T-system of muscle fibers under the influence of influx and efflux of glycerol. Nature (Lond.) 221, 966–968 (1969)
Krolenko, S. A.: Effect of fluxes of sugars and mineral ions on the light microscopic structure of frog fast muscle fibres. Nature (Lond.) 229, 5284 424–426 (1971)
Nakajima, S., Nakajima, Y., Peachey, L. D.: Speed of repolarization and morphology of glycerol-treated frog muscle fibers. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 234, 465–480 (1973)
Papir, D.: The effect of glycerol treatment on crab muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 230, 313–330 (1973)
Peachey, L. D.: Membrane systems of crab fibers. Amer. Zool. 7, 505–513 (1967)
Reuben, J. P., Brandt, P. W., Garcia, H., Grundfest, H.: Excitation-contraction coupling in crayfish. Amer. Zool. 7, 623–645 (1967)
Selverston, A.: Structure and function of the transverse system in crustacean muscle fibers. Amer. Zool. 7, 515–525 (1967)
Sherman, R. G., Atwood, H. L.: Correlated electrophysiological and ultrastructural studies of a crustacean motor unit. J. gen. Physiol. 59, 586–615 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We thank Professors Robert Werman and Rami Rachamimoff for critical reading of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castel, M., Papir, D. The ultrastructure of normal and glycerol treated muscle in the ghost crab, Ocypode cursor . Cell Tissue Res. 159, 369–378 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221783
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221783