Summary
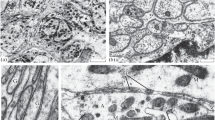
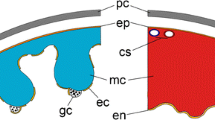
The antibiotic ionophores Br-X-537A and A-23187 alter the ultrastructure of neurohaemal tissue on the transverse nerve of the stick insect, Carausius morosus. Br-X-537A induces dramatic changes in the ultrastructural appearance of all three types of neurosecretory fibres present in the neurohaemal tissue. The neurosecretory granules become more electron-lucent and the mitochondria become more electron-opaque. The bounding membrane of the granules is frequently ruptured. A-23187, on the other hand, has no effect on two of the three types of fibres, but does produce an increase in the number of exocytotic profiles in the third.
The two ionophores therefore have different effects on the same tissue. The results are discussed in the light of previous work with the use of these ionophores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew, R.D., Shivers, R.R;: Ultrastructure of neurosecretory granule exocytosis by crayfish sinus gland induced with ionic manipulations. J. Morphol. 150, 253–278 (1976)
Bunt, A.H.: Formation of coated and ‘synaptic’ vesicles within neurosecretory axon terminals of the crustacean sinus gland. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 28, 411–421 (1969)
Bunt, A.H., Ashby, E.A.: Ultrastructural changes in the crayfish sinus gland following electrical stimulation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 10, 376–382 (1968)
Douglas, W.W., Nagasawa, J., Schultz, R.: Electron microscopic studies on the mechanism of secretion of posterior pituitary hormones and significance of microvesicles (‘synaptic vesicles’): Evidence of secretion by exocytosis and formation of microvesicles as a by-product of this process. Mem. Soc. Endocrinol. 19, 353–378 (1971)
Fifield, S.M., Finlayson, L.H.: Peripheral neurons and peripheral neurosecretion in the stick insect, Carausius morosus. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. [Biol.] 200, 63–85 (1978)
Finlayson, L.H., Osborne, M.P.: Peripheral neurosecretory cells in the stick insect (Carausius morosus) and the blowfly larva (Phormia terme-novae). J. Insect Physiol. 14, 1793–1801 (1968)
Finlayson, L.H., Osborne, M.P.: Secretory activity of neurons and related electrical activity. Adv. Comp. Physiol. Biochem. 6, 165–258 (1975)
Foreman, J.C., Mongar, J.L., Gomperts, B.D.: Calcium ionophores and movement of calcium ions following the physiological stimulus to a secretory process. Nature 245, 249–251 (1973)
Garcia, A.G., Kirpekar, S.M., Prat, J.C.: A calcium ionophore stimulating the secretion of catecholamines from the cat adrenal. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 244, 253–262 (1975)
Holz, R.W.: The release of dopamine from synaptosomes from rat striatum by the ionophore X-537A and A-23187. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 375, 138–152 (1975)
Kagayama, M., Douglas, W.W.: Electron microscope evidence of calcium-induced exocytosis in mast cells treated with 48/80 or the ionophores A-23187 and X-537A. J. Cell Biol. 62, 519–526 (1974)
Kita, H., Van der Kloot, W.: Calcium ionophore X-537A increases spontaneous and phasic quantal release by acetylcholine at frog neuromuscular junction. Nature 250, 658–660 (1974)
Livingston, A.: Ultrastructure of the rat neural lobe during recovery from hypertonic saline treatment. Z. Zellforsch. 137, 361–374 (1973)
Maddrell, S.H.P.: The site of release of the diuretic hormone in Rhodnius — a new neurohaemal system in insects. J. Exp. Biol. 45, 499–508 (1966)
Maddrell, S.H.P.: Neurosecretory control systems in insects. In: Insect ultrastructure (A.C. Neville, ed.), pp. 101–116. Oxford: Blackwell 1970
Manton, I.: The possible significance of some details of flagellar bases inplants. J.R. Micr. Soc. 82, 274–285 (1964)
Monroe, B.G., Scott, D.E.: Ultrastructural changes in the neural lobe of the hypophysis of the rat during lactation and suckling. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 14, 497–517 (1966)
Nagasawa, J., Douglas, W.W., Schultz, R.A.: Ultrastructural evidence of secretion by exocytosis and of “synaptic vesicle” formation in posterior pituitary glands. Nature 227, 407–409 (1970)
Nakazato, Y., Douglas, W.W.: Vasopressin release from the isolated neurohypophysis induced by a calcium ionophore, X-537A. Nature 249, 479–481 (1974)
Normann, T.C.: Experimentally induced exocytosis of neurosecretory granules. Exp. Cell Res. 55, 285–287 (1969)
Normann, T.C.: The mechanism of hormone release from neurosecretory axon endings in the insect Calliphora erythrocephala. In Aspects of neurocrinology (W. Bargmann and B. Scharrer, eds.), pp. 30–42. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970
Pressman, B.C.: Biological applications of ionophores. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 45, 501–530 (1976)
Raabe, M.: Étude des phénomènes de neurosécrétion au niveau de la chaîne nerveuse ventrale des Phasmides. Bull. Soc. Zool. France 90, 631–654 (1965)
Ricci, A., Sanders, K.M., Portmore, J., Van der Kloot, W.G.: Effects of the ionophores, X-537A and A-23187 on catecholamine release from the in vitro frog adrenal. Life Sci. 16, 177–184 (1975)
Santolaya, R.C., Bridges, T.E., Lederis, K.: Elementary granules, small vesicles and exocytosis in rat neurohypophysis after acute haemorrhage. Z. Zellforsch. 125, 277–288 (1972)
Smalley, K.N.: The median neurosecretory cells in the abdominal ganglia of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J. Insect Physiol. 16, 241–250 (1970)
Smith, U., Smith, D.S.: Observations on the secretory process in the corpus cardiacum of the stick insect, Carausius morosus. J. Cell Sci. 1, 59–66 (1966)
Thoa, N.B., Costa, J.L., Moss, J., Kopin, I.J.: Mechanism of release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurons by the calcium ionophore X-537A and A-23187. Life Sci. 14, 1705–1719 (1974)
Weitzman, M.: Ultrastructural study on the release of neurosecretory material from the sinus gland of the land crab, Geocarcinus lateralis. Z. Zellforsch. 94, 147–154 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We wish to thank Mrs. J. Birch for assistance with the electron micrographs, and Roche Products Ltd. and Lilly Research Centre Ltd. for gifts of the ionophores Br-X-537A and A-23187. The work was supported by the Science Research Council
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orchard, I., Osborne, M.P. & Finlayson, L.H. Ultrastructural changes in neurohaemal tissue of the stick insect, Carausius morosus, induced by the ionophores Br-X-537 A and A-23187. Cell Tissue Res. 197, 227–234 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233916
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233916