Summary
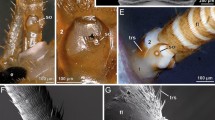
The sensillum capitulum, a hygro- and thermoreceptive sensillum of the cockroach Periplaneta americana L. is comprised of four receptor cells, one glial cell, two gland cells and four enveloping cells. Each receptor cell sends a single axon to the CNS, and has a single dendrite which extends distally. The perikarya of three receptor cells are enclosed by one of the enveloping cells (number one) and the fourth by a gland cell. The dendrites of all four receptor cells are enclosed by the same enveloping cell. The dendrites contain rootlets and many microtubules. The sensory cilia arise at the end of the dendrites at the level of the inner cavity, expand from the connecting cilium in a manner similar to those of the amphinematic scolopidia, and have numerous microtubules. The 1st enveloping cell contains scolopale rod-like structures. The sensory cilia are surrounded distally by a cuticular sheath formed within the 1st enveloping cell. One of the sensory cilia disappears distally, and the remaining ones enter the sensillum cone. Of these, one branches and the other two do not. The distal ends of the unbranched cilia are differentiated into tubular structures. The sensillum cone is comprised of an inner stem and a guard wall, neither of which is perforated. The outer cavity is enclosed by the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th enveloping cells, and distally in the antenna is closely apposed to the cuticular wall. This cavity contains lipid deposits. These structural features are discussed with regard to the mechanism of hygroreception in P. americana.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altner H, Ernst KD, Kolnberger I, Loftus R (1973) Feinstruktur und adäquater Reiz bei Insektensensillen mit Wandporen. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 66:47–53
Altner H, Sass H, Altner I (1977) Relationship between structure and function of antennal chemo-, hygro-, and thermoreceptive sensilla in Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 176:389–405
Altner H, Tichy H, Altner I (1978) Lamellated outer dendritic segments of a sensory cell within a poreless thermo- and hygroreceptive sensillum of the insect Carausius morosus. Cell Tissue Res 191:287–304
Bernard J (1974) Étude électrophysiologique de récepteurs impliqués dans l'orientation vers l'hôte et dans l'acte hématophage chez un Hemiptére: Triatoma infestans. Thése Doct Sci Nat Rennes, pp 1–285
Corbière-Tichané G (1971) Recherches sur l'équipement sensoriel du Coleoptère cavernicole. Thèse Doct Sci Nat Provence, pp 1–65
Davis EE, Sokolove PG (1975) Temperature responses of the antennal thermoreceptor of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. J Comp Physiol 96:223–233
Dethier VG, Schoonhoven LM (1968) Evaluation of evaporation by cold and humidity receptors in caterpillars. J Insect Physiol 14:1049–1054
Ernst K-D (1969) Die Feinstruktur von Riechsensillen auf der Antenne des Aaskäfers Necrophorus (Coleoptera). Z Zellforsch 94:72–102
Ernst K-D (1972) Die Ontogenie der basiconischen Riechsensillen auf der Antenne von Necrophorus (Coleoptera). Z Zellforsch 129:217–236
Hansen K, Heumann H-G (1971) Die Feinstruktur der tarsalen Schmeckhaare der Fliege Phormia terranovae. Z Zellforsch 117:419–442
Howse PE (1968) The fine structure and functional organization of chordotonal organs. Symp zool Soc Lond 23:167–198
Kellogg FE (1970) Water vapour and carbon dioxide receptors in Aedes aegypti. J Insect Physiol 16:99–108
Lacher V (1964) Elektrophsiologische Untersuchungen an einzelnen Rezeptoren für Geruch, Kohlendioxyd, Luftfeuchtigkeit und Temperatur auf den Antennen der Arbeitsbiene und der Drohne (Apis mellifica L.). Z vergl Physiol 48:587–623
Loftus R (1976) Temperature-dependent dry receptor on antenna of Periplaneta. Tonic response. J Comp Physiol 111:153–170
McIver SB (1974) Fine structure of antennal grooved pegs of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Cell Tissue Res 153:327–337
McIver SB (1974) Fine structure of antennal sensilla coeloconica of culicine mosquito. Tissue Cell 5:105–112
McIver SB, Siemicki R (1976) Fine structure of the antennal tip of the crabhole mosquito, Deinocerites cancer Theobald (Diptera: Culicidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 5:319–334
McIver SB, Siemicki R (1979) Fine structure of antennal sensilla of male Aedes aegypti (L.). J Insect Physiol 25:21–28
Moran DT, Rowley III JC (1975) The fine structure of the cockroach subgenual organ. Tissue Cell 7:91–106
Pinet J-M, Bernard J (1972) Essai d'interprétation du mode d'action de la vapeur d'eau et de la température sur un récepteur d'insecte. Ann Zool Écol Anim 4:483–495
Schaller D (1978) Antennal sensory system of Periplaneta americana L. Cell Tissue Res 191:121–139
Schmidt K (1969) Der Feinbau der stiftführenden Sinnesorgane im Pedicellus der Florfliege Chrysopa Leach (Chrysopidae, Planipennia). Z Zellforsch 99:357–388
Schmidt K (1973) Vergleichende morphologische Untersuchungen an Mechanorezeptoren der Insekten. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 66:15–25
Schmidt K (1975) Das Johnstonsche Organ der primär flügellosen Ectognatha (Lepisma, Zygentoma; Machilis, Archaeognatha). Cytobiologie 11:153–171
Smith DS (1969) The fine structure of haltere sensilla in the blowfly, Calliphora erythrocephala (Meig.), with scanning electron microscopic observations on the haltere surface. Tissue Cell 1:443–484
Steinbrecht RA, Müller B (1976) Fine structure of the antennal receptors of the bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. Tissue Cell 8:615–636
Steinbrecht RA, Thies G, Waldow U, Cited by Steinbrecht RA (1969) Comparative morphology of olfactory receptors. In: Pfaffmann (ed) Olfaction and taste III. Rockefeller University Press, New York, pp 3–21
Toh Y (1977) Fine structure of antennal sense organs of the male cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J Ultrastruct Res 60:373–394
Tominaga Y (1975) The taste pore of the fleshfly labellar hair. J Electron Microsc 24:171–174
Waldow U (1970) Elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen an Feuchte-, Trocken-, und Kälterezeptoren auf der Antenne der Wanderheuschrecke Locusta. Z vergl Physiol 69:249–283
Yamasaki T, Narahashi T (1959) The effect of potassium and sodium ions on the resting and action potentials of the cockroach giant axon. J Insect Physiol 3:146–158
Yokohari F (1978) Hygroreceptor mechanism in the antenna of the cockroach Periplaneta. J Comp Physiol 124:53–60
Yokohari F, Tateda H (1976) Moist and dry hygroreceptors for relative humidity of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana L. J Comp Physiol 106:137–152
Yokohari F, Tominaga Y, Ando M, Tateda H (1975) An antennal hygroreceptive sensillum of the cockroach. J Electron Microsc 24:291–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author is greatly indebted to Dr. Y. Toh for his guidance in transmission electron microscopy and to Profs. Drs. H. Tateda and Y. Tominaga for their helpful discussions. He also wishes to express his gratitude to Dr. D.R. Stokes, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. for his revision of the manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokohari, F. The sensillum capitulum, an antennal hygro- and thermoreceptive sensillum of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana L.. Cell Tissue Res. 216, 525–543 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238649
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238649