Summary
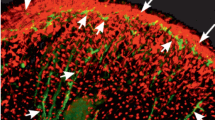
In a prosobranch mollusc, Rapana thomasiana, the catch-relaxing peptide H-Ala-Met-Pro-Met-Leu-Arg-Leu-NH2 (CARP) was found to depress the contraction of the radula protractor and retractor elicited by electrical stimulations. The action of CARP was in contrast to that of other neuropeptides, H-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FMRFamide) and H-Phe-Leu-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FLRFamide), which enhanced the contraction of the radula protractor and retractor, respectively. By immunohistochemical examinations, FMRFamide-like immunoreactive neurons were found on the rostral side of the right buccal ganglion and the caudal side of the left ganglion, where some CARP-like immunoreactive neurons were also distributed, indicating a possible coexistence of FMRFamide and CARP. FMRFamide- and CARP-like immunoreactivities were also detected in the neuropile of buccal ganglia, radula nerves arising from the ganglia, and nerve fibers in the radula muscles. The present results suggest that FMRFamide- and CARP-like peptides are involved in the regulation of the contraction of the radula muscles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cropper EC, Tenenbaum R, Kolks MAG, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1987) Myomodulin: a bioactive neuropeptide present in an identified cholinergic buccal motor neuron of Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5483–5486
Cropper EC, Miller MW, Tenenbaum R, Kolks MAG, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1988) Structure and action of buccalin: a modulatory neuropeptide localized to an identified small cardioactive peptide-containing cholinergic motor neuron of Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6177–6181
Furukawa Y, Kobayashi M (1985) Neural mechanisms underlying the feeding movements of a mollusc, Rapana thomasiana. Comp Biochem Physiol 81A:779–786
Hirata T, Kubota I, Takabatake I, Kawahara A, Shimamoto N, Muneoka Y (1987) Catch-relaxing peptide isolated from Mytilus pedal ganglia. Brain Res 422:374–376
Hirata T, Kubota I, Imada M, Muneoka Y, Kobayashi M (1989) Effects of the catch-relaxing peptide on molluscan muscles. Comp Biochem Physiol 92C:283–288
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Kiss T (1988) Catch-relaxing peptide (CARP) decreases the Capermeability of snail neuronal membrane. Experientia 44:998–1000
Kobayashi M (1972) Electrical and mechanical activities in the radula protractor of a mollusc, Rapana thomasiana. J Comp Physiol 78:1–10
Kobayashi M, Muneoka Y (1980) Modulatory actions of octopamine and serotonin on the contraction of buccal muscles in Rapana thomasiana. I. Enhancement of contraction in radula protractor. Comp Biochem Physiol 65C:73–79
Kobayashi M, Muneoka Y (1989) Functions, receptors, and mechanisms of the FMRFamide-related peptides. Biol Bull 177:206–209
Kyriakides MA, McCrohan CR (1989) Effect of putative neuromodulators on rhythmic buccal motor output in Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurobiol 20:635–650
Lloyd PE, Frankfurt M, Stevens P, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1987) Biochemical and immunocytological localization of the neuropeptides FMRFamide, SCPA, SCPB, to neurons involved in the regulation of feeding in Aplysia. J Neurosci 7:1123–1132
Mangerich S, Keller R, Dircksen H, Rao KR, Riehm JP (1987) Immunocytochemical localization of pigment-dispersing hormone (PDH) and its coexistence with FMR Famide-immunoreactive material in the eyestalks of the decapod crustaceans Carcinus maenas and Orconectes limosus. Cell Tissue Res 250:365–375
Masinovsky B, Lloyd PE, Willows AOD (1985) Morphology of two pairs of identified peptidergic neurons in the buccal ganglia of the mollusc Tritonia diomedea. J Neurobiol 16:27–39
Muneoka Y, Kobayashi M (1980) Modulatory actions of octopamine and serotonin on the contraction of buccal muscles in Rapana thomasiana. II. Inhibition of contraction in radula retractor. Comp Biochem Physiol 65C:81–86
Muneoka Y, Twarog BM (1977) Lanthanum block of contraction and of relaxation in response to serotonin and dopamine in molluscan catch muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 202:601–609
Murphy AD, Lukowiak K, Stell WK (1985) Peptidergic modulation of patterned motor activity in identified neurons of Helisoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7140–7144
Ohtomi M, Fujii K, Kobayashi H (1989) Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the brain and neurohypophysis of the lamprey, Lampetra japonica. Cell Tissue Res 256:581–584
Pearson WL, Lloyd PE (1989) Immunocytological localization of pedal peptide in the central nervous system and periphery of Aplysia. J Neurosci 9:318–325
Schot LPC, Boer HH (1982) Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic cells in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis with an antiserum to the molluscan cardioactive tetrapeptide FMRFamide. Cell Tissue Res 225:347–354
Sossin WS, Kirk MD, Scheller RH (1987) Peptidergic modulation of neuronal circuitry controlling feeding in Aplysia. J Neurosci 7:671–681
Walker RJ (1986) Transmitters and modulators. In: Willows AOD (ed) The mollusca. Academic Press, New York, pp 279–485
Yanagawa M, Takabatake I, Muneoka Y, Kobayashi M (1987) Further pharmacological study on the cholinergic and glutaminergic properties of the radula muscles of a mollusc, Rapana thomasiana. Comp Biochem Physiol 88C:301–306
Yanagawa M, Fujiwara M, Takabatake I, Muneoka Y, Kobayashi M (1988) Potentiating effects of some invertebrate neuropeptides on twitch contraction of the radula muscles of a mollusc, Rapana thomasiana. Comp Biochem Physiol 90C:73–77
Zoran MJ, Haydon PG, Matthews PJ (1989) Aminergic and peptidergic modulation of motor function at an identified neuromuscular junction in Helisoma. J Exp Biol 142:225–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara-Sakata, M., Muneoka, Y. & Kobayashi, M. Action and immunoreactivity of neuropeptides in the buccal neuromuscular system of a prosobranch mollusc, Rapana thomasiana . Cell Tissue Res 264, 57–62 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305722
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305722