Abstract
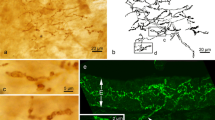
Indirect double immunofluorescence labelling in the pharynx and lung of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, demonstrated the occurrence, distribution, and coexistence of two neuropeptides. In the pharynx, immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) were localized in nerve fibers distributed within and just beneath the ciliated epithelium. In the lung, CGRP and SP were localized in nerve fibers in five principal locations: 1) within the smooth muscle layer in the interfaveolar septa; 2) in the luminal thickened edges of the septa; 3) around the pulmonary vasculature; 4) within, and 5) under the ciliated epithelium. Within the smooth muscle layer in the septa, luminal thickened septa, and around blood vessels, almost all fibers showed coexistence of CGRP and SP. Within and just beneath the ciliated epithelium in the thickened septa, all fibers showed coexistence of CGRP and SP. No immunoreactivity for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, neuropeptide Y, galanin, somatostatin, FMRFamide, and leucine-and methionine-enkephalins was detected in the nerve fibers within the larynx and the lung. Together with our previous data, the present findings suggest that peptidergic mechanisms are involved in the regulation of amphibian respiratory systems throughout their life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aursudkij B, Barnes PJ, Belvisi MG, Dijk S, Evans TW, Rogers DF (1988) Effect of substance P, neurokinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide on microvascular permeability in guineapig airways. J Physiol 398:51P
Barnes PJ (1986) Neural control of human airways in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 134:1289–1314
Cadieux A, Springall DR, Mulderry PK, Rodrigo J, Ghatei MA, Terengi G, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1986) Occurrence, distribution and ontogeny of CGRP immunoreactivity in the rat lower respiratory tract: effect of capsaicin treatment and surgical denervations. Neuroscience 19:605–627
Cheung A, Polak JM, Bauer FE, Cadieux A, Christofides ND, Springall DR, Bloom SR (1985) Distribution of galanin immunoreactivity in the respiratory tract of pig, guinea pig, rat, and dog. Thorax 40:889–896
Duellman WE, Trueb L (1986) Biology of amphibians. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 397–405
Finney MJB, Karlsson JA, Persson CGA (1985) Effects of bronchoconstrictors and bronchodilators on a novel human small airway preparation. Br J Pharmacol 85:29–36
Ghatei MA, Sheppard MN, O'Shaughnessy DJ, Adrian TE, McGregor GP, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1982) Regulatory peptides in the mammalian respiratory tract. Endocrinology 111:1248–1254
Ishii K, Honda K, Ishii K (1966) The function of the carotid labyrinth in the toad. Tohoku J Exp Med 88:103–116
Kusakabe T (1992) Ontogeny of substance P-, CGRP-, and VIP-containing nerve fibers in the amphibian carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana: an immunohistochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 269:79–85
Kusakabe T, Kawakami T (1992) Distribution of CGRP, substance P, VIP and somatostatin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the internal gills of larvae of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. Arch Histol Cytol 55:243–249
Kusakabe T, Anglade P Tsuji S (1991) Localization of substance P, CGRP, VIP, neuropeptide Y, and somatostatin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the carotid labyrinths of some amphibian species. Histochemistry 96:255–260
Kusakabe T, Kawakami T, Takenaka T (1993a) Distribution of FMRFamide-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana in corresponding differential interference-contrast (Nomarski) images. Arch Histol Cytol 56:277–282
Kusakabe T, Kawakami T, Hori H, Bandou Y, Takenaka T (1993b) Immunohistochemical coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in the nerve fibers of the internal gills of bullfrog, (Rana catesbeiana) larvae. Neurosci Lett 158:59–62
Kusakabe T, Kawakami T, Tanabe Y, Fujii S, Bandou Y, Takenaka T (1993c) Coexistence of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the nerve fibers of the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. Brain Res 603:153–156
Kusakabe T, Kawakami T, Takenaka T (1994a) Coexistence of substance P, neuropeptide Y, VIP, and CGRP in the nerve fibers of the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana: a double-labelling immunofluorescence study in combination with alternate consecutive sections. Cell Tissue Res 276:91–97
Kusakabe T, Kawakami T, Takenaka T (1994b) Localization of immunoreactive neuropeptides in the kidney of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, by immunofluorescence. Cell Tissue Res 278:41–44
Laitinen LA, Laitinen MA, Widdicombe JG (1987) Dose-related effects of pharmacological mediators on tracheal vascular resistance in dogs. Br J Pharmacol 92:703–709
Lundberg JM, Martling CR, Saria A (1983) Substance P and capsaicin-induced contraction of human bronchi. Acta Physiol Scand 119:243–252
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Martling CR, Saria A, Cuello C (1984) Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res 235:251–261
Luts A, Uddman R, Sundler F (1989) Neuronal galanin is widely distributed in the chicken respiratory tract and coexists with multiple neuropeptides. Cell Tissue Res 256:95–103
McCormack DG, Salonen RO, Barnes PJ (1989) Effect of sensory neuropeptides on canine bronchial and pulmonary vessels in vivo. Life Sci 45:2405–2412
Nilsson G, Dahlberg K, Brodin E, Sundler F, Strandberg K (1977) Distribution and constrictor effect of substance P guinea-pig tracheobronchial tissue. In: Euler US von, Pernow B (eds) Substance P, Raven Press, New York, pp 57–61
Palmer JB, Cuss FM, Muldberry PK, Ghatei MA, Sprigall DR, Cadieux A, Bloom SR, Polak JM, Barnes PJ (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is localized to human airway nerves and potently constricts human airway smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 91:95–101
Salvi E, Renda T (1992) An immunohistochemical study on neurons and paraneurons of the pre-and post-natal chicken lung. Arch Histol Cytol 55:125–135
Shimada K, Kobayashi S (1965) Neural control of the pulmonary smooth muscle in the toad. Acta Med Biol 13:297–303
Terada M, Iwanaga T, Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Adachi I, Aeakawa M, Fujita T (1992) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive nerves in the tracheal epithelium of rats: an immunohistochemical study by means of whole mount preparations. Arch Histol Cytol 55:219–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T. & Takenaka, T. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in the pharynx and lung of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana . Cell Tissue Res 279, 115–121 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300698
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300698