Abstract
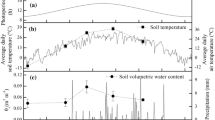
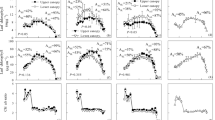
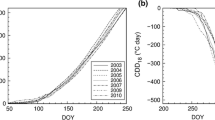
The relationship between the microclimate within an Oak-Hickory forest and photosynthetic characters of two resident evergreen herbs with contrasting leaf phenologies was investigated on a monthly basis for 1 full year. Heuchera americana has leaf flushes in the spring and fall, with average leaf life spans of 6–7 months. Hexastylis arifolia produces a single cohort of leaves each spring with a leaf life span of 12–13 months. We predicted that among evergreen plants inhabiting a seasonal habitat, a species for which the frequency of leaf turnover is greater than the frequency of seasonal extremes would have a greater annual range in photosynthetic capacity than a species that only produced a single flush of leaves during the year. Photosynthetic parameters, including apparent quantum yield, maximum photosynthetic capacity (Pmax), temperature of maximum photosynthesis, photochemical efficiency of PSII and leaf nitrogen (N) and chlorophyll concentrations, were periodically measured under laboratory conditions in leaves sampled from natural populations of both species. Mature leaves of both species acclimated to changing understory conditions with the mean seasonal differences being significantly greater for Heuchera than for Hexastylis. Area based maximum photosynthetic rates at 25°C were approximately 250% and 100% greater in winter leaves than summer leaves for Heuchera and Hexastylis respectively. Nitrogen concentrations were highest in winter leaves. Chlorophyll concentrations were highest in summer leaves. Low Pmax/N values for these species suggest preferential allocation of leaf nitrogen into non-photosynthetic pools and/or light-harvesting function at the expense of photosynthetic enzymes and electron transport components. Despite the increase in photosynthetic capacity, there was evidence of chronic winter photoinhibition in Hexastylis, but not in Heuchera. Among these ecologically similar species, there appears to be a trade-off between the frequency of leaf production and the balance of photosynthetic acclimation and photoinhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM, Osmond CB (1987) Shade-sun responses: compromises between acclimation and photoinhibition. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB, Arntzen CJ (eds) Photoinhibition (Topics in photosynthesis, vol 9) Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–38
Bazzaz FA, Chiariello NR, Coley PD, Pitelka LF (1987) Allocating resources to reproduction and defense. BioScience 37: 58–67
Berry JA, Raison JK (1981) Responses of macrophytes to temperature. In: Lange OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Ziegler H (eds) Physiological plant ecology. (Encyclopedia of plant physiology; new series, vol 12A) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 278–329
Björkman O (1981) Responses to different quantum flux densities. In: Lange OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Ziegler H (eds) Physiological plant ecology. (Encyclopedia of plant physiology; new series, vol 12A) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 57–107
Chabot BF, Hicks DJ (1982) The ecology of leaf life spans. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 13: 229–259
Chapin FS III, Cleve K van (1989) Approaches to studying nutrient uptake, use and loss in plants. In: Pearcy RW, Ehleringer J, Mooney HA, Rundel PW (eds) Plant physiological ecology field methods and instrumentation. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 185–207
Demmig-Adams B, Adams WW III (1992) Photoprotection and other responses of plants to high light stress. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 43: 599–626
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78: 9–19
Evans JR (1993) Photosynthetic acclimation and nitrogen partitioning within a Lucerne canopy. Aust J Plant Physiol 20: 55–67
Field C, Mooney HA (1986) The photosynthesis-nitrogen relationship in wild plants. In: Givinish T (ed) On the economy of plant form and function. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 25–55
Gonzalez VC (1972) The ecology of Hexastylis arifolia, an evergreen herb in the North Carolina deciduous forest. PhD dissertation. Duke University, Durham
Graves JD (1990) A model of the seasonal pattern of carbon acquisition in two woodland herbs, Mercurialis perennis L and Geum urbanum L. Oecologia 83: 479–484
Hicks DJ, Chabot BF (1985) Deciduous forests. In: Chabot BF, Mooney HA (eds) Physiological ecology of North American plant communities. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 257–277
Jurik TW, Chabot JF, Chabot BF (1979) Ontogeny of photosynthetic performance in Fragaria virginia under changing light regimes. Plant Physiol 63: 542–547
Kawano S, Masuda J (1979) The productive and reproductive biology of plants. V. Assimilation behavior and reproductive allocation of Coptis japonica (Thunb) Makino (Ranunculaceae). J Coll Lib Arts Toyama Univ (Nat Sci) 12: 49–63
Kawano S, Okumara H, Masuda J (1980) The productive and reproductive biology of plants. VIII. Assimilation behavior and dry matter allocation of Hepatica noblis var japonica f variegata (Makino) Kitam (Ranunculaceace). J Coll Lib Arts Toyama Univ (Nat Sci) 13: 33–46
Koizumi H (1989) Studies on the life history of the population of an evergreen herb, Pyrola japonica, on the forest floor in a warm temperate region. 2. Photosynthesis, respiration and gross production. Bot Mag Tokyo 102: 521–532
Krause GH (1988) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis. An evaluation of damaging and protective mechanisms. Physiol Plant 74: 566–574
Krause GH, Weis E (1991) Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: the basics. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 42: 313–349
Long SP, Humphries S Falkowski PG (1994) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in nature. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 45: 633–662
Mooney HA, Gulmon SL (1979) Environmental and evolutionary constraints on photosynthetic characteristics of higher plants. In: Solbrig OT, Jain S, Johnson GB, Raven PB (eds) Topics in plant population biology. Colombia University Press, New York, pp 316–337
Oberhuber W, Bauer H (1991) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis under natural conditions in ivy (Hedera helix L) growing in an understory of deciduous trees. Planta 185: 545–553
Oosting HJ (1956) The study of plant communities, 2nd edn. Freeman, San Francisco
Osmond CB (1981) Photorespiration and photoinhibition: some implications for the energetics of photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 77–98
Osmond CB (1994) What is photoinhibition? Some insights from comparisons of sun and shade plants. In: Baker NR, Bowyer JR (eds) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis-from molecular mechanisms to the field. Bios Sci, Oxford, pp 1–24
Pearcy RW, Sims DA (1994) Photosynthetic acclimation to ehanging light environments: scaling from the leaf to the whole plant. In: Caldwell M, Pearcy RW (eds) Exploitation of environmental heterogeneity in plants. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 145–174
Porra RJ, Thompson WA, Kriedmann PE (1989) Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 975: 384–394
Powles SB (1984) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis induced by visible light. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35: 15–44
Radford AE, Ahles HE, Bell CR (1968) Manual of the vascular flora of the Carolinas. UNC Press, Chapel Hill
Reich PB (1993) Reconciling apparent discrepancies among studies relating life span, structure and function of leaves in contrasting plant life forms and climates: ‘the blind men and the elephant retold’. Funct Ecol 7: 721–725
Röhrig E (1991) Climatic conditions. In: Röhrig E, Ulrich B (eds) Temperate deciduous forests. (Ecosystems of the World, vol 7) Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 7–16
Ruffner JA, Blair FE (1987) Weather of US cities. Gale Research Company, United States
Seemann JR, Sharkey TD, Wang J, Osmond CB (1987) Environmental effects on photosynthesis, nitrogen-use efficiency, and metabolite pools in leaves of sun and shade plants. Plant Physiol 84: 796–802
Sims DA, Pearcy RW (1992) Responses of leaf anatomy and photosynthetic capacity in Alocasia macrorrhiza (Araceae) to a transfer from low to high light. Am J Bot 79: 160–168
Skillman JB (1994) Environmental effects on photosynthesis and photoinhibition in evergreen perennials native to a seasonal habitat. PhD dissertation. Duke University, Durham
Strain BR, Higginbotham KO, Mulroy JC (1976) Temperature preconditioning and photosynthetic capacity of Pinus taeda L. Photosynthetica 10: 47–53
Tissue DT, Skillman JB, MacDonald EP, Strain BR (1995) Photosynthesis and carbon allocation in Tipularia discolor (Orchidaceae), a winter-active understory herb. Am J Bot 82: 1249–1256
Tranquillini W (1964) The physiology of plants at high altitudes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 15: 345–360
Walker DA (1990) Use of the oxygen electrode and fluorescence probes in simple measurements of photosynthesis. Oxygraphics Limited, Packard, Chichester
Yoshie F, Kawano S (1986) Seasonal changes in photosynthetic characteristics of Pachysandra terminalis (buxaceae), an evergreen chamaephyte, in the cool temperate regions of Japan. Oecologia 71: 6–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skillman, J.B., Strain, B.R. & Osmond, C.B. Contrasting patterns of photosynthetic acclimation and photoinhibition in two evergreen herbs from a winter deciduous forest. Oecologia 107, 446–455 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333934
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333934