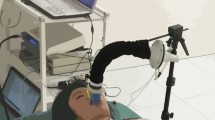
Abstract
An automatic 2-channel strain-gauge plethysmograph, based on an absolute resistance measurement technique, will be described in the paper. This device is compact, easy to use, provides inherent self-calibration for any gauge and any length of that gauge, automatically performs the measured cycle, and generates annotated graphical printouts of the measurement data, along with the results which it computes from that data.
Sommaire
L'appareil qui en a résulté, un pléthysmographe automatique à extensomètre à deux voies basé sur des techniques de mesure de résistance absolue, est décrit dans l'article. Il s'agit d'un apparei compact facile à utiliser, assurant un auto-calibrage inhérent pour n'importe quel extensomètre et quelle que soit sa longueur, qui effectue automatique la mesure, du cycle étudié et donne un tracé graphique annoté des données mesurées ainsi que les résultats qu'il calcule à partir desdites données.
Zusammenfassung
Das Endresultat, ein Plethysmograph mit automatischem, zweikanaligen Dehnungsmeßgerät, der auf der absoluten Widerstandsmessungstechnik basiert, wird im folgenden beschrieben. Dieses Gerät ist kompakt, leicht zu handhaben, hat eine eingebaute Selbsteichung für jedes Meßgerät und jede Länge dieses Meßgeräts, führt einen automatischen Meßzyklus aus und erzeugt beschriftete, grafische Druckkopien der Meßdaten zusammen mit den Resultaten, die es aus diesen Daten berechnet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenfield, A. D. M. et al. (1963) Methods for the investigation of peripheral blood flow.Brit. Med. Bull. 19, 2.
Hallböök, T., Mansson, B. andNilsén, R. (1970) A strain gauge plethysmograph with electrical calibration.Scand. J. Clin. Lab Invest. 25, pp. 413–8.
Hokanson, D., Sumner, D. S. andStrandness, D. E. Jun. (1975) Electrically calibrated plethysmograph for direct measurement of limb blood flow.IEEE Trans. BME-221, pp 25–29.
Hope, C. (1973) Computer applications in the determination of peripheral flow by plethysmography.In (Ed.)Roberts, C. blood flow measurement, Sector, London.
Sigdell, J. E. (1969) A critical review of the theory of the mercury strain gauge plethysmograph.Med. & Biol. Eng. 7, pp. 365–371.
Whitney, R. J. (1953) The measurement of volume changes in human limbs.J. Physiol. 121, 1–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, M.G., Coghlan, B.A., Beasley, M.G. et al. Automated strain-gauge plethysmograph. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 16, 554–558 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02457808
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02457808