Abstract
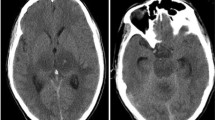
A 25-year-old chronically immunosuppressed woman with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) died after developing subacute granulomatous encephalitis caused byAcanthamoeba. Amoebic trophozoites were also found in the lung, suggesting a primary pulmonary focus of infection. The infectious encephalitis was difficult to differentiate from a flare-up of central nervous system lupus. This case illustrates thatAcanthamoeba can cause fatal encephalitis in lupus patients, as well as in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome as previously reported. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of granulomatous amoebic encephalitis due toAcanthamoeba in a patient with SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pistiner M, Wallace DJ, Nessim S, Metzger AL, Klinenberg JR. Lupus erythematosus in the 1980s: a survey of 570 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1991;21:55–64.
Ruskin J, Remington JS. The compromised host and infection. I. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. JAMA 1967;202:96–100.
Gorevic P, Katler E, Agus B. Pulmonary nocardiosis occurrence in men with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med 1980;140:361–3.
Chan J, Hensley G, Moskowitz L. Toxoplasmosis in the central nervous system. Ann Intern Med 1984;100:615–6.
Visvesvara GS, Stehr-Green JK. Epidemiology of free-living ameba infections. J Protozool 1990;37:25S-33S.
Gregorio CD, Rivasi F, Mongiardo N, Rienzo BD, Wallace S, Visvesvara GS.Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1992;116:1363–5.
Futrell N, Schultz L, Millikan C. Central nervous system disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 1992;42:1649–57.
Slater CA, Sickel JZ, Visvesvara GS, Pabico RC, Gaspari AA. Successful treatment of disseminatedAcanthamoeba infection in an immunocompromised patient. N Engl J Med 1994;331:85–7.
Martinez AJ. IsAcanthamoeba encephalitis an opportunistic infection? Neurology 1980;30:567–74.
Grunnet ML, Cannon GH, Kushner JP. Fulminant amebic meningoencephalitis due toAcanthamoeba. Neurology 1981;31:174–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koide, J., Okusawa, E., Ito, T. et al. Granulomatous amoebic encephalitis caused byAcanthamoeba in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 17, 329–332 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01451015
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01451015