Abstract
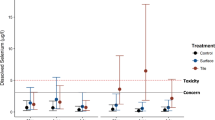
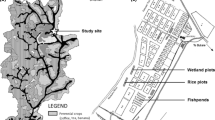
Kesterson Reservoir (Kesterson) received subsurface agricultural drainwater containing high levels of salts and selenium from farmland in the San Joaquin Valley of California. The accumulation of selenium in wetlands and waterfowl foods at Kesterson was investigated during May, August, and December of 1984. High concentrations of selenium were found in water, sediments, terrestrial and aquatic vegetation, and aquatic insects. Mean selenium concentrations in aquatic plants and insects ranged from 1.5 to 170 (μg/g dry weight and were about 11 to 290 times those found at a nearby reference site. Concentrations in some waterfowl food plants and insects at Kesterson were up to 64 times those reported to be a health hazard to birds. Selenium concentrations were more seasonally variable in aquatic plants than in aquatic insects. Few differences in selenium accumulation were found among ponds. Deposition of selenium in plant parts was not uniform; rhizomes contained higher concentrations than seeds and leaves were intermediate. Most biota bioaccumulated maximum selenium concentrations that were 1,000 to nearly 5,000 times the concentration in the water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WJ, Johnson HE (1977) Survey of the selenium content in the aquatic biota of western Lake Erie. J Great Lakes Res 3:10–14
Arnold RL, Olson OE, Carlson CW (1973) Dietary selenium and arsenic additions and their effects on tissue and egg selenium. Poult Sci 52:847–854
Beath OA, Eppson HF, Gilbert CS (1937) Selenium distribution in and seasonal variation of type vegetation occurring on seleniferous soils. J Amer Pharm Assoc 26:394–405
Bisbjerg B, Gissel-Nielsen G (1969) The uptake of applied selenium by agricultural plants. I. The influence of soil type and plant species. Plant and Soil 31:287–298
Brown TA, Shrift A (1982) Selenium: toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. Biol Rev 57:59–84
Connelly DP, Chesemore DL (1980) Food habits of pintails,Anas acuta, wintering on seasonally flooded wetlands in the northern San Joaquin Valley, California. Calif Fish Game 66:233–237
Cowgill UM (1973) Biogeochemical cycles for the chemical elements inNymphaea odorata Ait. and the aphidRhopalosiphum nymphaeae (L.) living in Linsley Pond. Sci Total Environ. 2:259–303
El-Begearmi MM, Sunde ML, Ganther HE (1977) A mutual protective effect of mercury and selenium in Japanese quail. Poult Sci 56:313–322
Euliss NH Jr (1984) The feeding ecology of pintail and green-winged teal wintering on Kern National Wildlife Refuge. MS Thesis, Humbolt State Univ, Arcata, CA, 188 pp
Fowler SG, Benayoun G (1976) Accumulation and distribution of selenium in mussel and shrimp tissues. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 16:339–346
Furr AK, Parkinson TF, Youngs WD, Berg CO, Gutenman WH, Pakkala IS (1979) Elemental content of aquatic organisms inhabiting a pond contaminated with coalfly ash. NY Fish Game J 26:154–161
Gilmer DS, Miller MR, Bauer RD, LeDonne JR (1982) California's Central Valley wintering waterfowl: Concerns and challenges. Trans N Am Wildl Nat Resour Conf 47:443–452
Gissel-Nielsen G (1971) Selenium content of some fertilizers and their influence on uptake of selenium in plants. J Agric Food Chem 19:564–566
Hamilton JW, Beath OA (1964) Amount and chemical form of selenium in vegetable plants. Amer J Bot 25:372–380
Heinz GH, Hoffman DJ, Gold LG (1989) Impaired reproduction of mallards fed an organic form of selenium. J Wildl Manage 53:418–428
Heinz GH, Hoffman DJ, Krynitsky AJ, Weller DMG (1987) Reproduction of mallards fed selenium. Environ Toxicol Chem 6:423–433
Hothem RL, Ohlendorf HM (1989) Contaminants in foods of aquatic birds at Kesterson Reservoir, California, 1985. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:773–786
Ives JH, Hazel CR, Gaffrey P, Nelson AW (1977) An evaluation of the feasibility of utilizing agricultural tile drainage water for marsh management in the San Joaquin Valley, California. Jones and Stokes Assoc, Inc, Sacramento, CA, 172 pp
Johnson CM, Asher CJ, Broyer TC (1967) Distribution of selenium in plants. In: Muth OH, Oldfield JE, Weswig PH (eds) Symposium: Selenium in biomedicine, pp 57–75
Moxon AL, Olson OE, Searight WV (1950) Selenium in rocks, soils, and plants. South Dakota Agr Expt Sta Revised Tech Bull No 2:1–94
Nassos PA, Coats JR, Metcalf RL, Brown DD, Hansen LG (1980) Model ecosystem, toxicity, and uptake evaluation of75Se-selenite. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 24:752–758
National Research Council (NRC) (1983) Selenium in nutrition. Nat Acad Press, Washington, DC, 174 pp
Ohlendorf HM (1989) Bioaccumulation and effects of selenium in wildlife. In: Jacobs LW (ed) Selenium in agriculture and the environment. Special Publ No. 23, Soil Sci Soc of Amer, Madison WI, pp 133–177
Ohlendorf HM, Hoffman DJ, Saiki MK, Aldrich TW (1986a) Embryonic mortality and abnormalities of aquatic birds: Apparent impacts of selenium from irrigation drainwater. Sci Total Environ 52:49–63
Ohlendorf HM, Hothem RL, Bunck CM, Aldrich TW, Moore JF (1986b) Relationships between selenium concentrations and avian reproduction. Trans N Am Wildl Nat Resour Conf 51:330–342
Ohlendorf HM, Hothem RL, Bunck CM, Marois KC (1990) Bioaccumulation of selenium in birds at Kesterson Reservoir, California. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:485–497
Ohlendorf HM, Kilness AW, Simmons JL, Stroud RK, Hoffman DJ, Moore JF (1988) Selenium toxicosis in wild aquatic birds. J Toxicol Environ Health 24:67–92
Ohlendorf HM, Skorupa JP (in press) Selenium in relation to wildlife and agricultural drainage water. Proc 4th Int Symp on Uses of Selenium and Tellurium, Banff, Alberta, May 7–10, 1989. Selenium-Tellurium Development Assoc, Darien, CT
Ort JF, Latshaw JD (1978) The toxic level of sodium selenite in the diet of laying chickens. J Nutr 108:1114–1120
Pennak RW (1978) Fresh-water invertebrates of the United States. Ronald Press Co, NY, pp 551–556, 567–585, 666–709
Presser TS, Barnes I (1984) Selenium concentrations in waters tributary to and in the vicinity of the Kesterson National Wildlife Refuge, Fresno and Merced Counties, California. Water Resour Invest Report No 84-4122, US Geological Survey, Menlo Park, CA, 26 pp
—,— (1985) Dissolved constituents including selenium in waters in the vicinity of Kesterson National Wildlife Refuge and the west Grassland, Fresno and Merced Counties, California. Water Resour Invest Report No 85-4220, US Geological Survey, Menlo Park, CA, 73 pp
Presser TS, Ohlendorf HM (1987) Biogeochemical cycling of selenium in the San Joaquin Valley of California, USA. Environ Manage 11:805–821
Rosenfeld I, Beath OA (1964) Selenium: geobotany, biochemistry, toxicity and nutrition. Academic Press, New York, 411 pp
Saiki ML (1986) Concentrations of selenium in aquatic food-chain organisms and fish exposed to agricultural tiller drainage water. In: Selenium in agricultural drainage: Implications for San Francisco Bay and the California environment, Symp II. The Bay Institute of San Francisco, Tiburon, CA, pp 25–33
Saiki ML, Lowe TP (1987) Selenium in aquatic organisms from subsurface agricultural drainage water, San Joaquin Valley, California. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 16:657–670
Sandholm M, Oksanen HE, Pesonen L (1973) Uptake of selenium by aquatic organisms. Limnol Oceanogr 18:496–499
Schuler CA (1987) Impacts of agricultural drainwater and contaminants on wetlands at Kesterson Reservoir, California. MS Thesis, Oregon State Univ, Corvallis, OR, 136 pp
Smith GJ, Heinz GH, Hoffman DJ, Spann JW, Krynitsky AJ (1988) Reproduction in black-crowned night-herons fed selenium. Lake Reserv Manage 4:175–180
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods. Iowa State Univ Press, Ames, IA 507 pp
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry. WH Freeman, San Francisco, 859 pp
US Bureau of Reclamation (USBR) (1984) Kesterson Reservoir and waterfowl: Information Bulletin 2, Mid-Pacific Regional Office 780, 2800 Cottage Way, Sacramento, CA, 11 pp
— (1986) Final Environmental Impact Statement, Kesterson Program, Volumes I and II. Mid-Pacific Region, in cooperation with US Fish and Wildl Serv and US Army Corps of Engineers, Sacramento, CA
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1983) Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes. Method 270.3 US Environ Prot Agency, Environ Monit and Support Lab, Cincinnati, OH, EPA-600/4-79-020
Wells JR, Kaufman PB, Jones JD (1980) Heavy metal contents in some macrophytes from Saginaw Bay (Lake Huron, USA). Aquatic Bot 9:185–193
Whetter PA, Ullrey DE (1978) Improved fluorometric method for determining selenium. J Assoc Office Anal Chem 61:927–930
Wiggett G, Alfors J (1986) Selenium. Calif Geology, Sacramento, CA, May, pp 99–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuler, C.A., Anthony, R.G. & Ohlendorf, H.M. Selenium in wetlands and waterfowl foods at Kesterson Reservoir, California, 1984. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19, 845–853 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055049
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055049