Abstract
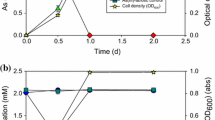
Actinomycetes were isolated from activated sludge acclimated to thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (T2C) or 5-methyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (T5M2C). These isolates were apparently identical and were identified as strains ofRhodococcus. The strains could grow on T2C, T5M2C, or thiophene-2-acetic acid as sole sources of carbon and energy, but could not use thiophene, methyl thiophenes, several other substituted thiophenes, dibenzothiophene, dimethyl sulfide, or pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid. T2C was degraded quantitatively to sulfate, and its carbon was converted almost entirely to cell biomass and carbon dioxide. Growth yields indicated about 25% conversion of T2C-carbon to cell-carbon. Growth was not supported by thiosulfate or methionine, nor were these compounds oxidized.Rhodococcus strain TTD-1 grown on T2C oxidized both T2C and T5M2C with an apparent Km of 1.3×10−5 M. Sulfide was also oxidized by T2C-grown organisms. This is the first demonstration of an actinomycete capable of the complete degradation of thiophene derivatives and of their use by it as sole substrates for growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amphlett MJ, Callely AG (1969) The degradation of 2-thiophenecarboxylic acid by aFlavobacterium species. Biochem J 112:12P
Birkenshaw JH, Chaplen P (1955) Biochemistry of the wood-rotting fungi. 8. Volatile metabolic products ofDaedelea juniperina Murr. Biochem J 60:255–261
Challenger F (1959) Aspects of the organic chemistry of sulphur. Butterworth, London, p 73
Cripps RE (1973) The microbial metabolism of thiophene-2-carboxylate. Biochem J 134:353–366
Drushel HV, Sommers AL (1967) Isolation and characterization of sulfur compounds in high-boiling petroleum fractions. Anal Chem 39:1819–1829
Fedorak PM, Westlake DWS (1983) Microbial degradation of organic sulfur compounds in Prudhoe Bay crude oil. Can J Microbiol 29:291–296
Gianturco MA, Giammarino AS, Friedel P (1968) Volatile constituents of coffee. V. Nature 210:1358–1360
Goodfellow M, Alderson G (1977) The actinomycete-genus Rhodococcus: a home for the “rhodochrous” complex. J Gen Microbiol 100:99–122
Kanagawa T, Dazai M, Fukuoka S (1982) Degradation of O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate byThiobacillus thioparus andPseudomonas AK-2. Agr Biol Chem 46:2571–2578
Kargi F, Robinson JM (1984) Microbial oxidation of dibenzothiophene by the thermophilic organismSulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:687–690
Kelly DP, Syrett PJ (1966) [35S]Thiosulphate oxidation byThiobacillus strain C. Biochem J 98:537–545
Kelly DP, Chambers LA, Trudinger PA (1969) Cyanolysis and spectrophotometric estimation of trithionate in mixture with thiosulfate and tetrathionate. Anal Chem 41:898–901
Kodama K, Nakatani S, Umehara K, Shimuza K, Minoda Y, Yamada K (1970) Microbial conversion of petro-sulfur compounds. III. Isolation and identification of products from dibenzothiophene. Agr Biol Chem 34:1320–1324
Kodama K, Umehara K, Shimuza K, Nakatani S, Minoda Y, Yamada K (1973) Identification of microbial products from dibenzothiophene and its proposed oxidation pathway. Agr Biol Chem 37:45–50
Kurita S, Endo T, Nakamura A, Yagi T, Tamuja N (1971) Decomposition of some organic sulfur compounds in petroleum by anaerobic bacteria. J Gen Appl Microbiol 17:185–198
Laborde AL, Gibson DT (1977) Metabolism of dibenzothiophene by aBeijerinckia species. Appl Env Microbiol 34:783–790
McCarthy TE, Sullivan MX (1941) A new and highly specific colorimetric test for methionine. J Biol Chem 141:871–876
Meyers RA (1977) Coal desulfurization. Marcel Dekker, New York
Nakatani S, Akasaki T, Kodama K, Minoda Y, Yamada K (1968) Microbial conversion of petro-sulfur compounds. II. Culture conditions of dibenzothiophene-utilizing bacteria. Agr Biol Chem 32:1205–1211
Nishiota M, Lee ML, Kudo H, Michiri DR, Baldwin LJ, Pakray S, Stuart JG, Castle RN (1985) Determination of hydroxylated thiophenic compounds in a coal liquid. Anal Chem 57:1327–1330
Roy AB, Trudinger PA (1970) Biochemistry of inorganic compounds of sulphur. The University Press, Cambridge, pp 71–72
Sagardia F, Rigau JJ, Martinez-Lahoz A, Fuentes F, Lopez C, Flores W (1975) Degradation of benzothiophene and related compounds by a soilPseudomonas in an oil-aqueous environment. Appl Microbiol 29:722–725
Stoll M, Winter M, Gaukschi F, Flament I, Willhalm B (1967) Recherches sur les arômes. Sur l'arôme de café. I Helv Chim Acta 50:628–694
Tuovinen OH, Kelly DP (1973) Studies on the growth ofThiobacillus ferrooxidans. Arch Mikrobiol 88:285–298
Willey C, Iwao M, Castle RM, Lee ML (1981) Determination of sulfur heterocycles in coal liquids and shale oils. Anal Chem 53:400–407
Yamada K, Minoda Y, Kodama K, Nakatani S, Aasaki T (1968) Microbial conversion of petro-sulfur compounds. I. Isolation and identification of dibenzothiophene-utilizing bacteria. Agr Biol Chem 32:840–845
Zechmeister L, Sease JW (1947) A blue-fluorescing compound, terthienyl, isolated from marigolds. JACS 69:273–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanagawa, T., Kelly, D.P. Degradation of substituted thiophenes by bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Microb Ecol 13, 47–57 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014962
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014962