Abstract
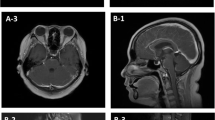
We report a 10-year-old girl with a primary leptomeningeal tumor. She presented with a 5-week history of increased intracranial pressure, progressive cranial nerve deficits, and spinal compression signs. She had previously had a granulosa cell tumor, a benign estrogen-producing ovarian tumor, which was resected 6 months before the initial neurological symptoms developed. At autopsy, the brain and spinal cord showed diffuse neoplastic involvement of the leptomeninges. The tumor was composed of small cells with a high nucleus/cytoplasm ratio, which were immunoreactive for vimentin but not for epithelial membrane antigen or cytokeratin. In addition, the tumor contained many small cellular whorls with desmosome-like junctional complexes between the cells, suggesting that the tumor was a meningioma, basically of the meningothelial type. The term ‘meningeal meningiomatosis’ has been used synonymously with “primary meningeal sarcomatosis”. The present tumor was considered to be a rare example of “meningeal meningiomatosis” of true meningothelial cell origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black BK, Kernohan JW (1950) Primary diffuse tumors of the meninges (so-called meningeal meningiomatosis). Cancer 3:805–819
Brown MH, Kernohan JW (1941) Diffuse meningiomatosis. Arch Pathol 32:651–658
Budka H, Pilz P, Guseo A (1975) Primary leptomeningeal sarcomatosis. Clinicopathological report of six cases. J Neurol 211:77–93
Onofrio BM, Kernohan JW, Uihlein A (1962) Primary meningeal sarcomatosis: a review of the literature and report of 12 cases. Cancer 15:1197–1208
Thibodeau LL, Ariza A, Piepmeier JM (1988) Primary leptomeningeal sarcomatosis. Case report. J Neurosurg 68:802–805
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Obata K, et al. (1992) Immunocy-tochemical localization of synaptic vesicle-specific protein in Lewy body-containing neurons in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 138:237–240
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, et al. (1983) Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 31:13–20
Chen R, Macdonald DR, Ramsay DA (1995) Primary diffuse leptomeningeal oligodendroglioma. Case report. J Neurosurg 83:724–728
Ho K-L, Hoschner JA, Wolfe DE (1981) Primary leptomeningeal gliomatosis: symptoms suggestive of meningitis. Arch Neurol 38:662–666
Kitahara M, Katakura R, Wada T, et al. (1985) Diffuse form of primary leptomeningeal gliomatosis. Case report. J Neurosurg 68:283–287
Korein J, Feigin I, Shapiro MF (1957) Oligodendrogliomatosis with intracranial hypertension. Neurology 7:589–594
Rogers LR, Estes ML, Rosenbloom SA, et al. (1995) Primary leptomeningeal oligodendroglioma: case report. Neurosurgery 36:166–169
Sumi SM, Leffman H (1968) Primary intracranial leptomeningeal glioma with persistent hypoglycorrhachia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 31:190–194
Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, et al. (1992) Primary leptomeningeal glioma: ultrastructural and laminin immunohistochemical studies. Acta Neuropathol 83:538–542
Budka H (1986) Non-glial specificities of immunocytochemistry for the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Triplet expression of GFAP, vimentin and cytokeratins in papillary meningioma and metastasizing renal carcinoma. Acta Neuropathol 72:43–54
Cerasoli S, Gubinelli M, Tison V, et al. (1994) Chordoid meningioma: case report. Brain Pathol 4:439.
Wanschitz J, Schmidbauer M, Maier H, et al. (1995) Suprasellar meningioma with expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein: a pecudiar variant. Acta Neuropathol 90:539–544
Burger PC, Scheithauer BW (1994) Tumors of the central nervous system. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC.
Kepes JJ (1982) Meningiomas: biology, pathology, and differential diagnosis, Masson, New York
Kepes JJ (1976) Cellular whorls in brain tumors other than meningiomas. Cancer 37:2232–2237
Jacobs DH, McFarlane MJ, Holmes F (1987) Female patients with meningioma of the sphenoid ridge and additional primary neoplasms of the breast and genital tract. Cancer 60:3080–3082
Knuckey NW, Stoll J, Epstein MH (1989) Intracranial and spinal meningiomas in patients with breast carcinoma: case reports. Neurosurgery 25:112–117
Michelsen JJ, New PFJ (1969) Brain tumour and pregnancy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 32:305–307
Avellino AM, Hair LS, Symmans WF, et al. (1994) Meningeal meningiomatosis in a child: case report. Clin Neuropathol 13:82–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakabayashi, K., Kawasaki, K., Ono, K. et al. Primary leptomeningeal meningiomatosis with widespread whorl formation. Brain Tumor Pathol 14, 139–143 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478883
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478883