Abstract
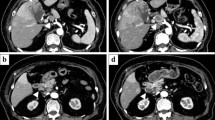
We report here a case of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)-producing esophageal carcinoma in a 66-year-old man. The International Union Against Cancer (UICC) staging was IV A, and a diagnosis of moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma was made, based on histopathology. The diagnosis was based on marked leukocytosis (41 500 leukocytes/mm3) and an elevated serum level of G-CSF (154 pg/ml). Immunofluorescent histochemistry and northern blot analysis confirmed the expression of G-CSF protein in cancer cells and its mRNA in cancer tissue. We paid special attention to any change in serum G-CSF levels during aggressive cancer treatment. Subtotal esophagectomy induced a significant decrease in G-CSF level. Adjuvant chemo-radiotherapy, targeting celiac lymph node metastasis, and radiotherapy, targeting solitary lung metastasis, together effectively maintained a low serum G-CSF level, despite a recurrence of the tumor in the lungs, in the form of multiple metastases, with an increase in serum G-CSF levels. The patient's clinical course suggested that serum G-CSF would be a useful marker for monitoring the effects of treatment on G-CSF-producing carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others

Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: November 26, 1999 / Accepted: June 28, 2000
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, G., Ise, H., Kimura, Y. et al. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor-producing esophageal carcinoma: serum level as a marker for monitoring the effects of treatment. Int J Clin Oncol 5, 328–333 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012058
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012058