Summary
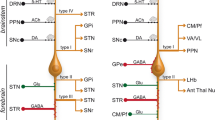
The striatum receives the majority of excitatory amino acidergic input to the basal ganglia from neocortical and allocortical sources. The subthalamic nucleus and the substantia nigra also receive excitatory amino acidergic inputs from neocortex. The subthalamic nucleus, which has prominent projections to the pallidum and nigra, is the only known intrinsic excitatory amino acidergic component of the basal ganglia. Possible excitatory amino acidergic inputs reach the basal ganglia from the intralaminar thalamic nuclei and the pedunculo-pontine nucleus. The striatum is richly endowed with all subtypes of excitatory amino acid receptors and these appear to be inhomogeneously distributed within the striatal complex. The non-striatal nuclei contain lesser levels of excitatory amino acid receptors and the relative proportion of these receptors varies between nuclei. The presence of high densities of excitatory amino acid receptors is a phylogenetically conserved feature of the striatum and its non-mammalian homologues. In Huntington's disease, there is substantial depletion ofα-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid, N-methyl-D-aspartate, and kainate receptors within the striatum. In Parkinson's disease substantia nigra, there is significant loss of N-methyl-D-aspartate andα-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsharpour S (1985) J Comp Neurol 236: 14–28
Albin RL, Aldridge JW, Young AB, Gilman S (1989a) Brain Res 491: 185–188
Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB (1989b) TINS 12: 366–375
Albin RL, Makowiec RL, Hollingsworth Z, Dure L, Penney JB, Young AB (1991) Neuroscience (in press)
Araneda R, Bustos G (1989) J Neurochem 52: 962–970
Beckstead RM (1979) J Comp Neurol 184: 43–62
Beckstead RM (1983) Brain Res 275: 137–142
Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1976) Brain Res 117: 423–435
Cheramy A, Romo R, Glowinski J (1986) Ann N Y Acad Sci 473: 80–91
Christie MJ, James LB, Beart PM (1985a) J Neurochem 45: 477–482
Christie MJ, Bridge S, James LB, Beart PM (1985b) Brain Res 333: 169–172
Dietl MM, Cortes R, Palacios JM (1988a) Brain Res 439: 360–365
Dietl MM, Cortes R, Palacios JM (1988b) Brain Res 439: 366–371
Dietl MM, Palacios JM (1988c) Brain Res 439: 354–359
DiFiglia M (1990) TINS 13: 286–289
Dinopoulos A, Dori I, Davies SW, Parnavelas JG (1989) Exp Neurol 105: 36–44
Donoghue JP, Herkenham M (1986) Brain Res 365: 397–403
Dure LS, Young AB, Penney JB (1991) Ann Neurol (in press)
Errami M, Nieoullon A (1988) J Neurochem 51: 579–586
Fonnum F, Storm-Mathisen J, Divac I (1981) Neuroscience 6: 863–873
Fuller TA, Russchen FT, Price JL (1987) J Comp Neurol 258: 317–338
Gerfen CR (1989) Science 246: 385–388
Girault JA, Barbeito L, Spampinato U, Gozlan H, Glowinski J, Besson M (1986) Neurochemistry 47: 98–106
Godukhin OV, Zharikova AD, Novoselov VI (1980) Neuroscience 5: 2151–2154
Gould E, Woolf NJ, Butcher LL (1989) Neuroscience 28: 611–623
Greenamyre JT, Young AB (1989) Neurosci Lett 101: 133–137
Greenamyre JT, Higgins DS, Young AB, Penney JB (1990) Int J Dev Neurosci 8: 437–445
Groenewegen HJ, Berendse HW (1990) J Comp Neurol 294: 607–622
Hassler R, Haug P, Nitsch C, Kim JS, Paik K (1982) J Neurochem 38: 1087–1098
Herrling PL (1985) Neuroscience 14: 417–426
Higgins DS, Greenamyre JT, Young AB, Penney JB (1989) Soc Neurosci Abstr 15: 1163
Kalivas PW, Duffy P, and Barrow J (1989) J Pharm Exp Ther 251: 378–386
Kemp JM, Powell TPS (1970) Brain 93: 525–546
Kita H, Kitai ST (1987) J Comp Neurol 260: 435–452
Kornhuber J, Kim JS, Kornhuber KE, Kornhuber HH (1985) Brain Res 322: 124–126
Lee HJ, Rye DB, Hallanger AE, Levey AI, Wainer BH (1988) J Comp Neurol 275: 469–492
McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Scherer U, Singh K (1977) Brain Res 128: 369–373
McGeorge AJ, Faull RLM (1989) Neuroscience 29: 503–537
Mitchell IJ, Brotchie JM, Graham WC, Page RD, Robertson RG, Sambrook MA, Crossman AR (1991) In: Bernardi G, Carpenter MB, Di Chiara G, Morelli M, Stanzione P (eds) The basal ganglia III. Plenum, New York London, p 607
Monaghan DT, Olverman HJ, Nguyen L, Watkins JC, Cotman CW (1988) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 9836–9840
Monaghan DT, Bridges RJ, Cotman CW (1989) Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 29: 365–402
Mount H, Quirion R, Chaudieu I, Boksa P (1990) J Neurochem 55: 268–275
Nieoullon A, Scarfone E, Kerkerian L, Errami M, Dusticier N (1985) Neurosci Lett 58: 299–304
Northcutt RG (1981) Ann Rev Neurosci 4: 301–350
Parent A (1986) Comparative neurobiology of the basal ganglia. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Parent A, Smith Y, Filion M, Dumas J (1989) Neurosci Lett 96: 140–144
Parent A (1990) TINS 13: 254–258
Penney JB, Difazio MC, Young AB (1990) Neurochem Int 16: 59
Reiner A, Anderson KD (1990) Brain Res Rev 15: 251–265
Reiner A, Brauth SE, Karten HJ (1984) TINS 320–325
Richfield EK, Albin R, Reiner A, Young AB, Penney JB (1988) Soc Neurosci Abstr 14: 1022
Robinson TG, Beart PM (1988) Brain Res Bull 20: 467–471
Robledo P, Feger J (1990) Brain Res 518: 47–54
Rouzaire-Dubois B, Scarnati E (1987a) Neuroscience 21: 429–440
Rouzaire-Dubois B, Scarnati E (1987b) Brain Res 403: 366–370
Rye DB, Saper CB, Lee HJ, Wainer BH (1987) J Comp Neurol 259: 483–528
Sakurai SY, Albin RL, Reiner A, Young AB (1990) Soc Neurosci Abstr 16: 90
Scarnati E, Proia A, Campana E, Pacitti C (1986) Exp Brain Res 62: 470–478
Schlegel JH, Kriegstein A (1987) J Comp Neurol 265: 521–529
Selemon LD, Goldman-Rakic PS (1985) J Neurosci 5: 776–794
Sladeczek F, Recasens M, Bockaert J (1988) TINS 11: 545–549
Sonsalla PK, Nicklas WJ, Heikkila RE (1989) Science 243: 398–400
Spencer HJ (1976) Brain Research 102: 91–101
Stone TW (1979) Br J Pharmacol 67: 545–551
Streit P (1980) J Comp Neurol 191: 429–463
Tanaka D (1987) J Neurosci 7: 4095–4106
Turski L, Bressler K, Rettig K-J, Loeschmann P-A, Wachtel H (1991) Nature 349: 414–418
Walaas I (1981) Neuroscience 6: 399–401
Walaas I, Fonnum F (1979) Neuroscience 4: 209–216
Young AB, Fagg GE (1990) TIPS 11: 126–133
Young AB, Sakurai SY, Albin RL (1990) Soc Neurosci Abstr 16: 90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albin, R.L., Makowiec, R.L., Hollingsworth, Z. et al. Excitatory amino acidergic pathways and receptors in the basal ganglia. Amino Acids 1, 339–350 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00814003
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00814003