Summary
Aim of our study was the comparison of bipolar ECG quality (with a 4cm lead distance) at different sites within the anterior thorax to find the preferable implantation site for an ECG event recorder (ECG-ER).
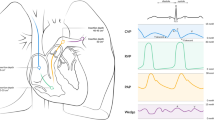
In 70 patients a bipolar ECG with a short electrode distance and in the vertical position was registered at the following sites: left and right subclavicular, left and right parasternal (4th–5th ICR), left and right anterior axillar (4th–5th ICR), at the heart apex and subxiphoidal. Then it was compared to the standard lead II. In 34 patients, an additional comparison between vertical and horizontal ECG registration was performed at the above mentioned sites.
During implantation of an ECG-ER in 5 patients, ECG signals were compared with electrodes placed towards the skin or towards the muscle. The best ECG quality (greatest QRS amplitude, visible P-wave and pacemaker spike, measurable QT period and bundle-branch block) and the best agreement with standard lead II was found in 67% left parasternal, significant less often (p<0.001) right parasternal (14.3%), left subclavicular (7.1%), apical (5.7%), and subxiphoidal (4.3%).
In a vertical electrode position a significantly higher QRS amplitude and a more often visible P wave was found in comparison to a horizontal electrode position. In all cases, there was good agreement between bipolar surface ECG at the implantation site and ECG-ER stored signals. When the ECG-ER is positioned with electrodes towards the muscle, significant noise-signal occurred in all 5 patients. Only in 3 patients was a P wave visible, but with a slightly greater QRS amplitude than in ECG-ERs positioned with electrodes towards the skin.
From these results, it is recommended to implant ECG-ERs vertically with electrodes towards the skin and in the parasternal position.
Zusammenfassung
Ziel dieser Untersuchung war der Vergleich der EKG-Qualität an verschiedenen Stellen des vorderen Thorax bei einer bipolaren Ableitung mit einem Elektrodenabstand von 4 cm.
Bei 70 Patienten (Mittleres Alter 48±7 J, 36 Männer, 22 Übergewicht, 17 Untergewicht, 57 Sinusrhythmus oder AAI-Stimulation, 27 Schenkelblock, 22 davon VVI oder VAT-Stimulation) wurde ein bipolares EKG mit kurzem Elektrodenabstand links und rechts subclaviculär, links und rechts parasternal (4.–5. ICR), im Bereich der linken und rechten anterioren Axillarlinie (4.–5. ICR), im Bereich der Herzspitze und subxiphoidal bei vertikaler Anlage der Elektroden registriert und mit der Standardableitung II verglichen. In 34 Fällen ist zudem zum Vergleich das EKG an o.g. Stellen sowohl bei vertikaler als auch bei horizontaler Anlage der Elektroden dokumentiert worden. Während der Implantation eines EKG-Event-Recorders (EKG-ER) bei 5 Patienten wurde ein EKG bei Plazierung des Gerätes mit den Elektroden zur Haut und zum Muskel aufgezeichnet und die Signale verglichen.
Die beste EKG-Qualität (größte QRS-Amplitude, sichtbare P-Welle und SM-Impuls, meßbare QT-Zeit und Schenkelblockmorphologie) und Übereinstimmung mit dem Standard-EKG wurde in 67% der Fälle links parasternal, viel seltener (p<0,001) rechts parasternal (14,3%), links subclaviculär (7,1%), im Bereich der Herzspitze (5,7%) und subxiphoidal (4,3%) erzielt. Bei vertikaler Anlage der Elektroden konnte eine signifikant größere QRS-Amplitude und in den parasternalen Ableitungen viel häufiger eine P-Welle im Vergleich zur horizontalen Anlage der Elektroden dokumentiert werden. Diese Ergebnisse waren unabhängig vom Körpergewicht.
Das bipolare Oberflächen-EKG am Implantationsort stimmte in allen Fällen mit den vom implantierten EKG-ER aufgezeichneten Signalen sehr gut überein. Bei Plazierung des EKG-ER mit den Elektroden zum Muskel wurde bei jedem der 5 Patienten ein deutliches Störsignal und nur in 3 Fällen eine sichtbare P-Welle, jedoch eine etwas größere QRS-Amplitude im Vergleich zu der Plazierung des Gerätes mit den Elektroden zur Haut registriert.
Aufgrund dieser Ergebnisse sollte EKG-Event-Rekorder vertikal, mit den Elektroden zur Haut und in der Regel parasternal implantiert werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Eingegangen: 21. Juli 1999/Akzeptiert: 2. November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Himmrich, E., Zellerhoff, C., Nebeling, D. et al. An welcher Stelle soll ein implantierbarer EKG-Event-Recorder plaziert werden?. Z Kardiol 89, 289–294 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920050487
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920050487