Summary
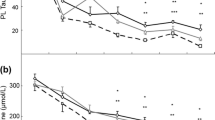
This study reports quantitative and qualitative differences in intestinal bile acids and cholesterol in miniature pigs following dietary casein or soy protein isolate. The total amount of bile acids in the small intestine was significantly higher when soy protein isolate was fed in comparison to casein. The values were (mean±SEM) 4.51 ±0.39 mmol and 2.43±0.08 mmol, respectively, when the proteins were given as the sole component of the diet. When the proteins were given as part of a semipurified diet, these values were 6.44±1.04 mmol and 3.95±0.39 mmol, respectively. Hyocholic acid amounted to 39.6%, hyodeoxycholic acid to 31 %, and chenodeoxycholic acid to 27.6% of total bile acids in the small intestine when casein was fed. The soy-fed animals tended to have more secondary bile acids.
The total small bowel chymus content, on a wet weight basis, was 63 % higher in the soy group. In all experimental conditions studied, there was a close correlation between small bowel chyme content and bile acid content. The distribution of bile acids in the small intestine showed that the soy fed animals tended to have more bile acids in the distal parts of the jejunum.
The intestinal cholesterol contents were not significantly different between dietary groups.
Zusammenfassung
In der vorliegenden Studie werden quantitative und qualitative Unterschiede im Gehalt an Gallensäuren und Cholesterin beschrieben, die im Dünndarm von Miniaturschweinen nach Diäten beobachtet wurden, die entweder Casein oder Sojaproteinisolat enthielten. Die intestinale Gesamtmenge an Gallensäuren war signifikant höher, wenn Sojaproteinisolat gefüttert worden war. Wurde das Protein als einzige Komponente verfüttert, so lagen die Werte bei 4.51±0.39 mmol, während die Caseingruppe 2.43±0.08 mmol aufwies. Wurde das Protein als Teil einer semisynthetischen Diät gegeben, waren die Werte für die Sojagruppe 6.44±1.04 mmol und für die Caseingruppe 3.95±0.39 mmol. Bei der Caseingruppe lagen die prozentualen Anteile an der Gesamtmenge der Gallensäuren im Dünndarm bei 39.6 % Hyocholsäure, 31% Hyodeoxycholsäure und 27.6% Chenodeoxycholsäure. Die Tiere, die Sojaproteinisolat bekamen, hatten in der Tendenz mehr sekundäre Gallensäuren.
Das Chymusfrischgewicht im Dünndarm lag in der Sojagruppe um 63 % über dem der Caseingruppe. Unter allen experimentellen Bedingungen wurde eine enge Beziehung zwischen dem Gehalt an Chymus und Gallensäuren im Dünndarm beobachtet. Die Sojagruppe wies in der Tendenz höhere Mengen an Gallensäuren im distalen Jejunum auf.
Die Soja- und Caseingruppe wiesen keine Unterschiede im Cholesteringehalt des Dünndarms auf.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beynen AC, Winnubst ENW, West CE (1983) The effect of replacement of dietary soybean protein by casein on the fecal excretion of neutral steroids in rabbits. Z Tierphysiol Tierernährg u Futtermittelkde 49:43–49
Bronzert TJ, Brewer HB (1977) A new micromethod for measuring cholesterol in plasma lipoprotein fractions. Clin Chem 23:2089–2098
Carroll KK (1981) Soy protein and atherosclerosis. J Am Oil Chem Soc 58:416–419
Edenharder R, Slemr J (1981) Gas-chromatographic and mass spectrometric analysis of bile acids as trifluoroacetyl-hexafluorisopropyl and heptafluorobutyl derivatives. J Chrom 222:1–12
Forsythe WA, Miller ER, Hill GM, Romsos DR, Simpson RC (1980) Effects of dietary protein and fat sources on plasma cholesterol parameters, LCAT activity and amino acid levels and on tissue lipid content of growing pigs. J Nutr 110:2467–2479
Grundy SM, Ahrens EH JR, Salen G (1971) Interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man: comparative effects of cholestyramine and ileal exclusion on cholesterol metabolism. J Lab Clin Med 78:94–121
Hagemeister H, Scholz K, Kinder E, Barth CA, Drochner W (1985) Digestion, transit time and biliary secretion following different dietary proteins in the adult pig. In: Just A, Jorgensen H, Fernandez JA (eds) Digestive physiology in the pig. Trykt i Frederiksberg Bogtrykkeri Kobenhavn, pp 124–127
Huff MW, Hamilton RMG, Carroll KK (1977) Plasma cholesterol levels in rabbits fed low fat, cholesterol-free semipurified diets: Effects of dietary proteins, protein hydrolysates and amino acid mixtures. Atherosclerosis 28:187–195
Huff MW, Carroll KK (1980) Effects of dietary protein on turnover, oxidation and absorption of cholesterol and on steroid excretion in rabbits. J Lipid Res 21:546–558
Kay PM, Truswell AS (1977) Effect of citrus pectin on blood lipids and fecal steroid excretion in man. Am J Clin Nutr 30:171–175
Kim DN, Reiner KT, Thomas WA (1978) Effects of a soy protein product on serum and tissue cholesterol concentrations in swine fed high-fat, high-cholesterol diets. Exp Molec Path 29:385–399
Kim DN, Lee KT, Reiner JM, Thomas WA (1980) Increased steroid excretion in swine fed high-fat, high-cholesterol diet with soy protein. Exp Molec Pathol 33:25–35
Koss FW, Mayer D, Haindl H (1979) Gallensäuren. In: Bergmeyer HU (Hrsg), Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse; Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1934–1937
Kostner GH (1976) Enzymatic determination of cholesterol in high-density lipoprotein fractions prepared by polyanion precipitation. Clin Chem 22:695
Kritchevsky D, Klurfeld DM (1983) Gallstone formation in hamsters: effect of varying animal and vegetable protein levels. Am J Clin Nutr 37:802–804
Lack L, Weiner IM (1966) Intestinal bile salt transport: structure-activity relationships and other properties. Am J Physiol 210:1142–1152
Leiss O, Murawski U, Egge H (1979) Mikrobestimmung von Lipoproteinlipiden im Serum. J clin Chem clin Biochem 17:619–625
Nagata Y, Sugano M (1982) Studies on the mechanism of antihypercholesterolemic action of soy protein and soy protein-type amino acid mixture in relation to the casein counterparts in rats. J Nutr 112:1614–1625
Nagata Y, Tanaka K, Sugano M (1981) Further studies on the hypocholesterolaemic effect of soya-bean protein in rats. Br J Nutr 45:233–241
Röschlau P, Bernt E, Gruber W (1974) Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamtcholesterins im Serum. Z klin Chem-klin Biochem 12:403–407
Roseleur OJ, van Gent CM (1978) Simplified method for determination of steroids in diets and feces. Clin Chim Acta 82:13–23
Roy DM, Schneeman BO (1981) Effect of soy protein, casein and trypsin inhibitor on cholesterol, bile acids and pancreatic enzymes in mice. J Nutr 111:878–885
Schneeman BO (1979) Acute pancreatic and biliary response to protein, cellulose and pectin. Nutr Rep Int 20:45–48
Seegraber FJ, Morrill JL (1982) Effect of soy protein on calves' intestinal absorptive ability and morphology determined by scanning electron microscopy. J Dairy Sci 65:1962–1970
Sklan D, Budowski P, Hurwitz S (1979) Absorption of oleic and taurocholic acids from the intestine of the chick. Interactions and interference by proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 573:31–39
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical methods, Iowa State University Press, Ames, IA
Sugano M, Ishiwaki N, Nagata Y, Imaizumi K (1982) Effects of arginine and lysine addition to casein and soya-bean protein on serum lipids, apolipoproteins, insulin and glucagon in rats. Br J Nutr 48:211–221
Sugano M (1983) Hypocholesterolaemic effect of plant protein in relation to animal protein: Mechanism of action. In: Gibney MJ, Kritchevsky D (eds) Current topics in nutrition and disease; Vol 9. Animal and vegetable proteins in lipid metabolism. Alan R Liss Inc, New York, pp 19–49
Tanaka K, Aso B, Sugano M (1984) Biliary steroid excretion in rats fed soybean protein and casein or their amino acid mixtures. J Nutr 114:26–32
Tanaka C, Watanuki M, Nozaki Y (1983) Effect of soybean protein on coprostanol production and cholesterol metabolism in cholesterol-fed rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 29:447–454
Terpstra AHM, Hermus RJJ, West CE (1983) The role of dietary protein in cholesterol metabolism. Wld Rev Nutr Diet 42:1–55
Terpstra AHM, Hermus RJJ, West CE (1983) Dietary protein and cholesterol metabolism in rabbits and rats. In: Gibney MJ, Kritchevsky D (eds) Current topics in nutrition and disease; Vol 9. Animal and vegetable proteins in lipid metabolism. Alan R Liss Inc, New York, pp 19–49
West CE, Beynen AC, Scholz KE, Terpstra AHM, Schutte JB, Deuring K, Van Gils (1984) Treatment of dietary casein with formaldehyde reduces its hypercholesterolemic effect in rabbits. J Nutr 114:17–25
Woodward CJH, West CE (1984) Bile acid binding and the cholesterolaemic effect of dietary proteins. Proc Nutr Sci 43/2) 63A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholz, K.E., Kinder, E., Hagemeister, H. et al. Influence of dietary casein and soy protein isolate on intestinal cholesterol and bile acid concentration. Z Ernährungswiss 24, 158–171 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019354
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019354