Abstract
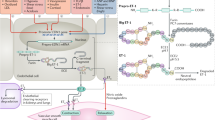
The endothelins comprise a family of three isopeptides ET-1, ET-2 and ET-3, whereby ET-1 appears to be the most relevant in humans. They act in a paracrine manner on ETA and ETB receptors. ET-1 plays an important role in the cardiovascular system. In addition, it modulates vasomotion and growth processes, and it participates in thrombogenesis and neutrophil adhesion. This review summarizes some of the current literature pertaining to the physiological and pathophysiological significance of ET-1, focusing the assets and drawbacks of elevated ET-1 levels. In this regard, modulation of the endothelin system by either receptor blockade or by inhibition of endothelin converting enzyme is expected to provide novel therapeutic drug strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 September 1999, Returned for revision: 2 November 1999, Revision received: 2 March 2000, Accepted: 23 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz-Spanke, S., Schipke, J. Potential role of endothelin-1 and endothelin antagonists in cardiovascular diseases. Basic Res Cardiol 95, 290–298 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003950070048
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003950070048