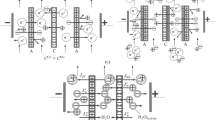
Summary
Interaction between ion exchange membranes and surface active agents was observed by electrodialyzing the salt solution containing the surface active agent. The behavior of the electric resistance of the membrane during the electrodialysis, the current efficiency and the adsorbed or ion-exchanged amount and the permeated amount of the surface active agent were observed. Generally, the electric resistance of the membrane during the electrodialysis increased remarkably when the ionic surface active agent having the opposite charge to ion-exchange groups of the membrane was contained in the solution. And the correlation of the behavior of the electric resistance of the membrane to the electrodialysis condition, species of surface active agents and species of membranes was mainly observed. Results were as follows. 1) The adsorption' or ion-exchange of ionic surface active agent on the membrane was remarkably emphasized by the electric field. 2) The degree of the increase in the electric resistance of the membrane was remarkable when the surface active agent had the high molecular weight and the bulky molecular structure. 3) The degree of the increase in the electric resistance was remarkably various according to species of the membranes.
From these results, a protecting method for the change of these membrane properties was examined. When the ion exchange membrane was treated with the polyelectrolyte solution having the opposite charge to ion exchange groups of the membrane, the increase in the electric resistance by ionic surface active agent was depressed. Generally, though the change of electrodialysic properties of the membrane by the ionic surface active agent was remarkable in the membrane having the tight structure, the change of the properties of the membrane having the tight structure was easy to be protected by the polyelectrolyte treatment. Though the ionic surface active agent having the bulky molecular structure made the properties of the membrane change remarkably, the change of the properties of the membrane by the bulky surface active agent could be easily protected by the polyelectrolyte treatment.
Zusammenfassung
Die Wechselwirkung von Ionenaustauschermembranen mit grenzflächenaktiven Stoffen wird durch Elektrodialyse untersucht. Der elektrische Widerstand der Membranen steigt während der Elektrodialyse beträchtlich an, wenn die grenzflächenaktiven Ionen entgegengesetzte Ladungen wie die Austauschergruppen der Membranen haben. Es wurde gefunden, daß 1. die Adsorption oder der Ionenaustausch der grenzflächenaktiven Ionen an der Membran beträchtlich durch das elektrische Feld verstärkt wird; 2. die Zunahme des elektrischen Widerstandes groß ist, wenn das grenzflächenaktive Ion ein hohes Molekulargewicht hat und möglichst sperrig ist; 3. die Widerstandsänderung merklich von der Art der Membran beeinflußt wird. Auf Grund dieser Versuche wurde die Möglichkeit geprüft, die Zunahme des Membranwiderstandes bei Gegenwart grenzflächenaktiver Stoffe durch Adsorption von Polyelektrolyten zu reduzieren.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamamushi, B., K. Tamaki, Trans. Faraday Soc.55, 1013 (1959).
Hale, D. K., D. I. Packham, K. W. Pepper, J. Chem. Soc. 844 (1954).
Small, H., J. Amer, Chem. Soc.90, 2217 (1968).
Small, H., R. C. Gardner, Saline Water Research and Development Progress Report. No. 565.
Kobus, E. J. M., P. M. Heertjes, Desalination12, 333 (1973).
Korngold, E., F. de Körösy, R. Rahav, M. F. Toboch, Desalination,8, 195 (1970).
van Duin, P. J., International Symposium on Fresh Water from the Sea2, 141 (1970); ibid3, 252 (1973).
Sata, T., R. Izuo, Y. Mizutani, R. Yamane, J. Colloid Interf. Sci.40, 317 (1972).
Sata, T., Electrochimica Acta18, 199 (1973).
Sata, T., J. Colloid Interf. Sci.44, 393 (1973).
Mizutani, Y., R. Yamane, H. Ibara, H. Motomura, Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan.36, 361 (1963);Y. Mizutani, R. Yamane, H. Motomura, Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan38, 689 (1965).
Mizutani, Y., W. Tesbima, S. Akiyama, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 368/1966;Y. Mizutani, R. Yamane, H. Motomura, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 8778/1969 etc. 13)Mizutani, Y., W. Teshima, S. Akiyama, R. Yamane, H. Ihara, U. S. Pat.3, 451, 951 (1969).
Hummel, D. O., F. Scholl, Infrared Analysis of Polymers, Resins and Additives, An Atlas (Chichester/Sussex 1969).
Lincoln, P. A., C. C. T. Chinnick, Analyst81, 100 (1956).
Jacobs, P. T., E. V. Anacker, J. Colloid Interf. Sci.44, 505 (1973).
Geer, R. D., E. H. Eylar, E. W. Anacker, J. Phys. Chem.75, 369 (1971).
Anacker, E. W., R. D. Geer, J. Colloid Interf. Sci.35, 441 (1971).
Mizutani, Y., Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan42, 2459 (1969) ;Y. Mizutani, ibid,43, 595 (1970);Y. Mizutani, M. Nishimura, J. Appl. Polymer Sci.14, 1847 (1970).
Mizutani, Y., R. Yamane, T. Sata, R. Izuo, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 23607/1971 (Application Date: November 16, 1965); U. S. Pat. 3510417, 3510418; British Pat. 1238656; France Pat. 1578880; Israel Pat. 29761 etc.
Mizutani, Y., R. Yamane, T. Sata, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 42082/1971, No. 4638/1975 (Application Date: October 27, 1967);Y. Mizutani, R. Yamane, T. Sata, R. Izuo, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 3801/1972, No. 3802/1972, (Application Date: April 2, 1969); U. S. Pat. 3647086; Brit. Pat. 1251550; France Pat. 2057257; etc.
Mizutani, Y., R. Yamane, T. Sata, R. Izuo, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 4352/1975 (Application Date: September 16, 1970); U. S. Pat. 3784457; British Pat. 1373392; France Pat. 2107644; West Germ. Pat. 2145904; Italy Pat. 960014; etc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sata, T. Modification of properties of ion exchange membranes. Colloid & Polymer Sci 256, 62–77 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01746692
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01746692