Summary
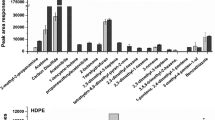
Elastomeric stoppers for injectables have been surveyed by means of GC/MS screening. Residual contamination by hexanes (2-methylpentane, 3-methylpentane, n-hexane, methylcyclopentane, cyclohexane) toluene and xylenes occurred in all the samples tested.
A headspace GC purity test is suggested, by using these residual chemicals as purity indexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farmacopea Ufficiale Repubblica Italiana, IX Ed. (Italian Republic Official Pharmacopoeia, 9th Ed.) Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato, Roma, 1985; Vol. 1, p. 442.
European Pharmacopoeia, Council of Europe; Draft Monograph “Rubber closures for containers for aqueous preparations for parenteral use” Strasbourg, 1981.
Hewlett Packard Application Brief, AB85-13, Publ.n. 23-5953-8059 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gramiccioni, L., Milana, M.R., Maggio, A. et al. An experimental study of residual chemicals in elastomeric stoppers for injectables: a MS/GC survey and a headspace/GC purity test. Chromatographia 28, 545–550 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02260674
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02260674