Abstract
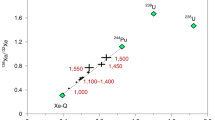
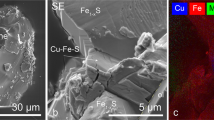
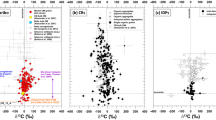
SMALL crystals of silicon carbide, probably of interstellar origin, have previously been isolated from primitive meteorites by dissolution of the host meteorite with acid1–8. Here we report the first in situ observations of isotopically anomalous SiC9,10. The grains were found by X-ray mapping of polished sections of two chondritic (group CM) meteorites, Cold Bokkeveld and Murchison. Ion microprobe measurements showed 13C enrichments, δ13C, from 199 to 2,800‰, proving that the grains are indigenous. Calculations of the condensation of grains in circumstellar envelopes of different compositions and C/O ratios have suggested that other phases, such as metal carbides, nitrides and sulphides, could form in association with SiC11,12. Etching methods may have destroyed any such phases, had they existed in association with SiC, but our direct detection reveals SiC grains only as isolated matrix particles. This rules out also the possibility that SiC grains were brought into the Solar System as inclusions in larger grains, which protected them from destruction in the solar nebula. Several of the SiC grains we have found are cracked, suggesting that the etching treatment may result in size distributions biased towards smaller grains.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernatowicz, T. et al. Nature 330, 728–730 (1987).
Zinner, E., Tang, M. & Anders, E. Nature 330, 730–732 (1987).
Tang, M. & Anders, E. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 52, 1235–1244 (1988).
Tang, M., Anders, E., Hoppe, P. & Zinner, E. Nature 339, 351–354 (1989).
Zinner, E., Tang, M. & Anders, E. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 53, 3273–3290 (1989).
Alexander, C. M. O'D. et al. Meteoritics 24, 247 (1989).
Alexander, C. M. O'D., Arden, J. W., Pier, J., Walker, R. M. & Pillinger, C. T. Proc. lunar planet. Sci. Conf. 21, 9–10 (1990).
Alexander, C. M. O'D., Prombo, C., Walker, R. M., Zinner, E. & Arden, J. W. Meteoritics (in the press).
Alexander, C. M. O'D., Swan, P. D. & Walker, R. M. Proc. lunar planet. Sci. Conf. 21, 11–12 (1990).
Alexander, C. M. O'D., Swan, P. & Walker, R. M. Geol. Soc. Aust. Abstr. 27, 2 (1990).
Lattimer, J. M., Schramm, D. N. & Grossman, L. Astrophys. J. 219, 230–249 (1978).
Lattimer, J. M. & Grossman, L. in Moon & Planets 19, 169–184 (1978).
Swan, P. S., Walker, R. M. & Yuan, J. Proc. lunar planet. Sci. Conf. 20, 1093–1094 (1989).
McKeegan, K. D., Walker, R. M. & Zinner, E. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 49, 1971–1987 (1985).
Bunch, T. E., & Chang, S. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 44, 1543–1577 (1980).
Barber, D. J. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 45, 945–970 (1981).
Stone, J., Hutcheon, I. D., Epstein, S. & Wasserburg, G. J. Proc. lunar planet. Sci. Conf. 21, 1212–1213 (1990).
Amari, S., Anders, E., Virag, A. & Zinner, E. Nature 345, 238–240 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexander, C., Swan, P. & Walker, R. In situ measurement of interstellar silicon carbide in two CM chondrite meteorites. Nature 348, 715–717 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/348715a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/348715a0
This article is cited by
-
On laboratory studies of grains from outside the solar system
Journal of Earth System Science (1998)
-
Interstellar grains in meteorites
Nature (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.