Conclusions
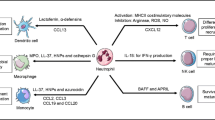
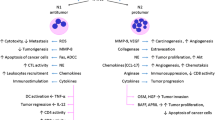
Our studies show that stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes produce a neutrophil-activating factor (NAF). Lymphocytes do not appear to produce NAF or to influence its production. The results indicate that NAF is selective for neutrophils and induces activation via its own surface receptor through a signal transduction process to that initiated by fMLP and C5a. In functional terms, NAF may be regarded as homologous to fMLP and C5a. NAF differs, however, in several important aspects from either chemotactic peptide. It is of host origin, like C5a, but is generated by inflammatory cells (the mononuclear phagocytes) rather than by the activation of a humoral cascade. Most importantly, unlike C5a, NAF is not inactivated by peptidases in plasma or exudate and could therefore accumulate in inflamed tissues. While C5a and N-formyl-methionyl peptides are early mediators of neutrophil activation upon infection, NAF is likely to act as a second-wave mediator, generated at later stages, when a lesion is populated by mononuclear phagocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Peveri, A. Walz, B. Dewald and M. Baggiolini,A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J. Exp. Med.167, 1547–1559 (1988).
A. Walz, P. Peveri, H. Aschauer and M. Baggiolini,Purification and amino acid sequencing of NAF, a novel neutrophilactivating factor produced by monocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.149, 755–761 (1987).
T. Yoshimura, K. Matsushima, S. Tanaka, E. A. Robinson, E. Appella, J. J. Oppenheim and E. J. Leonard,Purification of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor that shares sequence homology with other host defense cytokines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA84, 9233–9237 (1987).
J. Schmid and C. Weissmann,Induction of mRNA for a serine protease and a β-thromboglobulin-like protein in mitogenstimulated human leukocytes. J. Immunol.139, 250–256 (1987).
J.-M. Schroeder, U. Mrowietz, E. Morita and E. Christophers,Purification and partial biochemical characterization of a human monocyte-derived, neutrophil-activating peptide that lacks interleukin 1 activity. J. Immunol.139, 3474–3483 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walz, A., Peveri, P., Aschauer, H. et al. Structure and properties of a novel neutrophil-activating factor (NAF) produced by human monocytes. Agents and Actions 26, 148–150 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02126588
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02126588