Summary
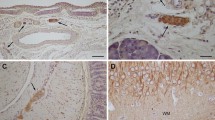
Taxol, an agent known to stabilize and increase the assembly of microtubules, causes long-lasting nerve damage when injected into peripheral nerve. In the present study, the cellular response to taxol in rat sciatic nerve was studied for up to 6 months after a single injection. The initial response of Schwann cells to taxol at the lesion site involved the accumulation of cytoplasmic microtubules which persisted up to 4 months after injection. Some novel microtubule-related cytoplasmic structures were also noted; these included microtubule-lined cytoplasmic crypts and channels. Despite these structural abnormalities, Schwann cells were able to produce myelin sheaths around taxol-induced axonal bulbs. This myelination showed some anomalies up to 4 months consisting of the widening of myelin lamellae, variability in sheath thickness, paranodal myelin infoldings and myelin protrusions. With time the diameter of the axonal bulbs decreased and, concomitant with this, more normal-appearing remyelination occurred. By 5 months, the previously noted myelin abnormalities were rare. By 6 months only a few naked axonal segments occurred at the lesion site. In endoneurial fibroblasts and macrophages cytoplasmic lamellar microtubule formations were frequent at 10 weeks. Needle-like cytoplasmic structures appeared within endoneurial cells at the site of the lesion after 10 weeks. By 3 months these inclusions were numerous and were often surrounded by extended cytoplasmic processes. The needles were up to 50 μm long and 3 μm wide and probably represented cholesterol. By 4 months the number of cytoplasmic needles decreased and at 5 months onwards none was observed. The present findings confirm and extend previous findings that taxol has a long-lasting effect upon both Schwann cells and endoneurial cells and that this is related to abnormal tubulin synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R. J. &Bray, D. (1983) Rapid transport of foreign particles microinjected into crab axons.Nature 303, 718–20.
Aguayo, A. J. &Bray, G. M. (1984) Cell interactions studied in the peripheral nerves of experimental animals. InPeripheral Neuropathy (edited byDyck, P. J., Thomas, P. K., Lambert, E. H. &Bunge, R. P.), Vol. 1, pp. 360–77. Philadelphia: WB Saunders.
Bonn'aud-Toulze, E. N. &Raine, C. S. (1980) Remodelling during remyelination in the peripheral nervous system.Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 6, 279–90.
Bornstein, M. B. &Raine, C. S. (1976) The initial structural lesions in serum-induced demyelinationin vitro.Laboratory Investigation 35, 391–401.
Bridgman, P. (1987) Structure of cytoplasm as revealed by modern electron microscopy techniques.Trends in Neurosciences 10, 321–5.
Crang, A. J. &Blakemore, W. F. (1986) Observations on Wallerian degeneration in expiant cultures of cat sciatic nerve.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 471–82.
Dubas, F., Pouplard-Barthelaix, A., Delestre, F. &Emilie, J. (1987) Polyneuropathies avec gammopathie monoclonale IgM.Revues Neurologique (Paris) 143, 670–83.
Dustin, P. (1984)Microtubules, 2nd edn, p. 308. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Gibbons, I. R. (1987) New jobs for dynein ATPases.Nature 330, 600.
Griffin, J. W., Drucker, N., Gold, B. G., Rosenfeld, J., Benzaquem, M., Charnas, L. R., Fahnestock, K. E. &Stocks, E. A. (1987) Schwann cell proliferation and migration during paranodal demyelination.Journal of Neuroscience 7, 682–99.
Hall, S. M. &Williams, P. L. (1970) Studies on the ‘indsures’ of Schmidt and Lanterman,Journal of Cell Science 6, 767–91.
Hoffstein, S. T. (1981) The role of microtubules and microfilaments in lysosomal enzyme release from poly-morphonuclear leukocytes.Methods in Cellular Biology 23, 259–82.
Hughes, R. A. C., Atkinson, P. H., Cray, I. A. &Taylor, W. A. (1987) Major histocompatibility antigens and lymphocyte subsets during experimental allergic neuritis in the Lewis rat.Journal of Neurology 234, 390–5.
Jessen, K. R., Mirsky, R. &Morgan, L. (1987) Myelinated, but not unmyelinated, axons reversibly down-regulate N-CAM in Schwann cells,Journal of Neurocytology 16, 681–8.
Johannessen, J. V. (1976) InElectron Microscopy in Human Medicine (edited byJohannessen, J. V.), Vol. 2, pp. 175. London: McGraw-Hill International Book Company.
Kalderon, N. (1984) Schwann cell proliferation and localized proteolysis: expression of plasminogen-activator activity predominates in the proliferating cell populations.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 81, 7216–20.
Keteibant-Blasse, P. &Neve, P. (1976) New ultrastructural features on the cream hamster thyroid with special reference on the second kind of follicle.Cell and Tissue Research 166, 49–63.
Lubinska, L. (1961) Sedentary and migratory states of Schwann cells.Experimental Cell Research 8, 74–90.
Malawista, S. E. (1971) Vinblastine: colchicine-like effects on human blood leukocytes during phagocytosis.Blood 37, 519–29.
Masurovsky, E., Peterson, E., Crain, S. &Horwitz, S. (1981) Morphologic alterations in satellite and Schwann cells after exposure of fetal mouse dorsal root ganglia — spinal cord cultures to taxol.International Research Communications Service;Medical Sciences 9, 968–9.
Olsson, T., Holmdahl, R., Klareskog, L., Forsum, U. &Kristennson, K. (1984) Dynamics in la-expressing cells and T-lyphocytes of different subsets during experimental allergic neuritis in Lewis rats,Journal of the Neurological Sciences 66, 141–9.
Paschal, B. M. &Vallee, B. (1987) Retrograde transport by the microtubule-associated protein, MAP 1C.Nature 330, 181–3.
Powell, H. C., Rodriguez, M. &Hughes, R. A. C. (1984) Microangiopathy of vasa nervorum in dysglobulinemic neuropathy.Annals of Neurology 15, 386–94.
Propp, R. P., Means, E., Deibel, R., Sherer, G. &Barron, K. (1975) Waldenström's macrogammaglobulinemia and neuropathy. Deposition of M-component on myelin sheaths.Neurology 25, 980–8.
Raine, C. S. &Bornstein, M. B. (1979) Experimental allergic neuritis: ultrastructure of serum-induced myelin aberrations in peripheral nervous system cultures.Laboratory Investigation 40, 423–32.
Raine, C. S., Röyttä, M. &Dolich, M. (1987) Microtubule-mitochondrial associations in regenerating axons after taxol intoxication.Journal of Neurocytology 16, 461–8.
Rebhun, L. I. (1972) Polarized intracellular particle transport: saltatory movements and cytoplasmic streaming.International Review of Cytology 32, 93–139.
Röyttä, M., Horwitz, S. B. &Raine, C. S. (1984) Taxol-induced neuropathy: short-term effects of local injection.Journal of Neurocytology 13, 685–701.
Röyttä, M., Lyman, W. D., Roth, G. A., Bornstein, M. B. &Raine, C. S. (1985) Preliminary analysis of cell and serum-induced demyelinationin vitro using a syngeneic system.Acta Neurologica Scandinavian 71, 226–36.
Röyttä, M. &Raine, C. S. (1985) Taxol-induced neuropathy: further ultrastructural studies of nerve fibre changesin situ, Journal of Neurocytology 14, 157–75.
Röyttä, M. &Raine, C. S. (1986) Taxol-induced neuropathy: chronic effects of local injection.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 483–96.
Röyttä, M. &Salonen, V. (1988) Long-term endoneurial changes after nerve transection.Acta Neuropathologica (Berlin) 76, 35–45.
Röyttä, M., Salonen, V. &Peltonen, J. (1987) Reversible endoneurial changes after nerve injury.Acta Neuropathologica (Berlin) 73, 323–9.
Sa1da, K., Saida, T., Kayama, H. &Nishitani, H. (1984) Rapid alterations of the axon membrane in antibody-mediated demyelination.Annals of Neurology 15, 581–9.
Salzer, J. L. &Bunge, R. P. (1980) Studies of Schwann cell proliferation. I. Analysis in tissue culture of proliferation during development. Wallerian degeneration and direct injury,Journal of Cell Biology 84, 739–52.
Salzer, J. L., Bunge, R. P. &Glaser, L. (1980) Studies of Schwann cell proliferation III. Evidence for the surface localization of the neurite mitogen.Journal of Cell Biology 84, 767–78.
Schröder, J. M. (1970) Zur pathogenese der isoniazid-neuropathie.Acta Neuropathologica (Berlin) 16, 301–23.
Shiraishi, S., Le Quesne, P., Gajree, T. &Cavanagh, J. B. (1985) Morphometric effects of vincristine on nerve regeneration in the rat.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 71, 165–81.
Sobue, G., Kreider, B., Asbury, A. K. &Pleasure, D. (1983) Specific and potent mitogenic effect of axolemmal fraction on Schwann cells from rat sciatic nerves in serum-containing and defined media.Brain Research 280, 263–75.
Spencer, P. S. &Thomas, P. K. (1974) Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process II. The sequestration and removal by Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes of organelles from normal and diseased axons.Journal of Neurocytology 3, 763–83.
Vale, R. D., Schnapp, B. J., Mitchison, T., Steuer, E., Reese, T. S. &Sheetz, M. P. (1985) Different axoplasmic proteins generate movement in opposite directions along microtubulesin vitro.Cell 43, 623–32.
Vuorinen, V., Röyttä, M. &Raine, C. S. (1988a) The acute response of Schwann cells to taxol after nerve crush.Acta Neuropathologica (Berlin) 76, 17–25.
Vuorinen, V., Röyttä, M. &Raine, C. S. (1988b) The acute effects of taxol upon regenerating axons after nerve crush.Acta Neuropathologica (Berlin) 76, 26–34.
Vuorinen, V., Röyttä, M. &Raine, C. S. (1989) The long-term effects of a single injection of taxol upon peripheral nerve axons.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 775–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuorinen, V., Röyttä, M. & Raine, C.S. The long-term cellular response to taxol in peripheral nerve: Schwann cell and endoneurial cell changes. J Neurocytol 18, 785–794 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01187231
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01187231