Abstract
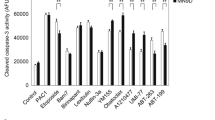
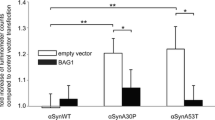
It is currently believed that excessive oxidant stress induced by metabolism of dopamine (DA), plays a major role in the pathogenesis of the selective nigrostriatal neuronal loss in Parkinson's disease. We recently showed that the neurotransmitter DA, in physiological concentrations, is capable of initiating apoptosis in cultured, post-mitotic sympathetic neurons. Bcl-2 is a proto-oncogene that blocks apoptosis. We now report that Bcl-2 is a powerful inhibitor of DA toxicity in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. We induced stable expression of Bcl-2 in PC-12 cells by transfection with recombinant pCMV5 expression vector, containing mouse bcl-2 (coding-sequence) cDNA. Cells expressing Bcl-2 manifested marked resistance to otherwise lethal (300 uM) in vitroconcentrations of DA. This protective effect was reflected in the trypan-blue test of cell survival, 3 H-thymidine incorporation and inhibition of the characteristic apoptotic morphologic alterations in scanning electron microscopic studies. Bcl-2 and associated control systems of apoptosis may have an important physiological role in restraining the apop-tosis-triggering potential of DA in nigrostriatal neurons. This novel field of research may yield insights into the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and lead to development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olanow CW. A radical hypothesis for neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci 1993; 16: 439–444.
Ziv I, Melamed E, Nardi N, Luria D, Achiron A, Offen D, Barzilai A. Dopamine induces apoptosis-like cell death in cultured sympathetic neurons — A possible novel pathogenetic mechanism in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 1994; 170: 136–140.
Mochizuki H, Goto K, Mori H, Mizuno Y. Histochemical detection of apoptosis in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci 1996; 137: 120–123.
Moldeus P, Nordenskjold M, Bolcsfoldi G, Aiche A, Haglund U, Lambert B. Genetic toxicity of dopamine. Mut Res 1983; 124: 9–23.
Reed JC. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 1–6.
Garcia I, Martinou I, Tsushimoto Y, Martinou JC. Prevention of programmed cell death of sympathetic neurons by the bcl-2 proto-oncogene. Science 1992; 258: 302–304.
Hockenberry DM, Zutter M, Hickey W. Bcl-2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 6961–6965.
Andersson S, Davis DN, Bahlback H. Cloning, structure and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome p-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 8222–8229.
Wiggler MS, Siverstein LS, Lee A. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine-kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell 1977; 11: 223–227.
Michel PP, Hefti F. Toxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine and dopamine for dopaminergic neurons in culture. J Neurosci Res 1990; 26: 428–435.
Mah SP, Zhong LT, Liu Y. The protooncogene bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis in PC-12 cells. J Neurochem 1993; 60: 1183–1186.
Vindelov LL, Christensen IJ, Nissen NI. A detergent-trypsin method for the preparation of nuclei for flow cytometric DNA analysis. Cytometry 1983; 5: 323–327.
Nicoletti I, Migliorato G, Pagliacci MC, Grimnani F, Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium-iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 1991; 139: 271–279.
Kane DJ, Sarafian TA and Anton R. Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death: decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science 1993; 262: 1274–1276.
Barinaga M. Cell suicide: by ICE, not fire. Science 1994; 263: 754–756.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziv, I., Offen, D., Haviv, R. et al. The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 inhibits cellular toxicity of dopamine: possible implications for Parkinson's Disease. Apoptosis 2, 149–155 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026408313758
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026408313758