Conclusions
-
1.
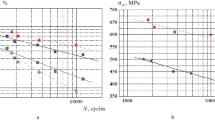
We determined the frequency dependence of the endurance limits of pearlitic steel 1Kh2M and austenitic steel Khl8N9 in tests at room and elevated temperatures within the frequency range 3–10,000 Hz: there is a slight change in the endurance limits within 3–500 Hz and a marked increase (∼40%) with an increase in loading frequency to 10 kHz.
-
2.
The temperature dependences of the endurance of steels 1Kh2M (within the range 20–470 °C) and Kh18N9 (within 20–600 °C) at loading frequencies of 3–10,000 Hz are similar at different frequencies. The frequency dependence of the endurance limits of the steels becomes weaker within the 3–500 Hz range as temperature is increased.
-
3.
In tests in a water spray, the frequency dependence of the endurance of the investigated steels is determined by time-dependent corrosion processes. Representation of the function σa-f on a limited time base showed that loading frequency has only a slight effect on the endurance of these steels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
S. V. Serensen, V. P. Kogaev, and R. M. Shneiderovich, Load-Carrying Capacity and the Strength Design of Machine Parts [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1975).
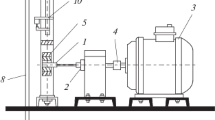
M. É. Garf, I. I. Ishchenko, É. Ya. Filatov et al., Unit MIR-ST for High-Temperature Tests of Specimens for Fatigue in Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Cyclic Axial Loading and Programmed Cyclic Loading (Information Letter No. 9, Institute of Mechanics of the Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR), Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1975).
G. G. Pisarenko and P. F. Kul'bashnyi, “Use of an electrodynamic vibrating stand for fatigue tests in symmetrical tension-compression,” Probl. Prochn., No. 8, 105–108 (1972).
S. V. Serensen, M. É. Garf, and V. A. Kuz'menko, Dynamics of Machines for Fatigue Tests [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1967).
V. A. Kuz'menko, I. A. Troyan, and Ya. I. Tsimbalistyi, “Unit for investigating endurance and vibrating creep under high-frequency loading,” Probl. Prochn., No. 11, 114–118 (1973).
A. I. Afonin, “Unit for fatigue tests in symmetrical cycles of tension-compression with a frequency of 10 kHz under conditions of heating,” Probl. Prochn., No. 1, 101–104 (1971).
I. A. Troyan and Ya. I. Tsimbalistyi, “Calculation of stresses in an asymmetrically vibrating specimen,” Probl. Prochn., No. 1, 95–97 (1973).
V. D. Bol'shakov, Theory of Observation Errors with Bases in Probability Theory [in Russian], Nedra, Moscow (1965).
M. É. Garf, I. I. Ishchenko, É. Ya. Filatov et al., “Unit for high-temperature tests of specimens for fatigue in axial loading,” Prikl. Mekh.,10, No. 5, 94–100 (1974).
E. G. Buglov, I. I. Ishchenko, P. I. Adamenko, V. P. Golub, and B. N. Sinaiskii, “System for stabilizing modes of loading in fatigue tests,” Zavod. Lab.,42, No. 3, 1136–1138 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Problemy Prochnosti, No. 4, pp. 35–40, April, 1980.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuz'menko, V.A., Ishchenko, I.I., Troyan, I.A. et al. Effect of loading frequency, temperature, and cycle asymmetry on the endurance of heat-resistant steels 1Kh2m and Kh18N9. Part 1. Strength Mater 12, 439–444 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00769398
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00769398