Abstract
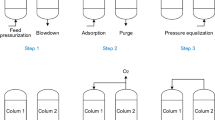
A novel rapid pressure swing adsorption (RPSA) process is described for production of 25–50% oxygen enriched air. The embodiment consists of one or more pairs of adsorbent layers contained in a single adsorption vessel. The layers undergo simultaneous pressurization-adsorption and simultaneous depressurization-purge steps. A total cycle time of 6–20 seconds is used. The process yields a very large specific oxygen production rate and a reasonable oxygen recovery for production of 20–50 mole% oxygen enriched gas.
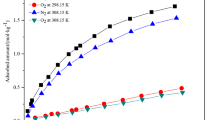
It is demonstrated by a simple mathematical model of isothermal single adsorbate pressure swing ad(de)sorption concept on a single adsorbent particle that the specific production rate of a PSA process cannot be indefinitely increased by reducing the cycle time of operation when adsorbate mass transfer resistances are finite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chou, C. and H.C. Wu,Zeolites and Related Microporous Materials: State of the Art, J. Weitkamp et al. (Eds.),84, p. 1255 (1994).
Dangieri, T.J. and R.T. Cassidy, “RPSA Processes,” U.S. Patent 4,406,675 (1983).
Earls, D.E. and G.N. Long, “Multiple Bed Rapid Pressure Swing Adsorption for Oxygen,” U.S. Patent 4,194,891 (1980).
Jones, R.L., G.E. Keller, and R.C. Wells, “Rapid Pressure Swing Adsorption with High Enrichment Factor,” U.S. Patent 4,194,892 (1980).
Keller, G.E., R.A. Anderson, and C.M. Yon, “Adsorption” inHandbook of Separation Technology, R.W. Rousseau (Ed.) John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987.
Pritchard, C.L. and G.K. Simpson,Chem. Eng. Res. Dev.,64, p. 467 (1986).
Ruthven, D.M., S. Farouq, and K.S. Knabel,Pressure Swing Adsorption, VCH Publishers, New York, 1994.
Sakoda, A. and M. Suzuki, “Performance and Potential of Piston-Driven Rapid Pressure Swing Adsorption,” paper presented at annual AlChE meeting (Extended Abstract 10d), Miami Beach, Florida (1992).
Sircar, S. “Pressure Swing Adsorption Technology,’ inAdsorption: Science and Technology (NATO ASI Series E), A.I. Rodrigues et al. (Eds.), Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, 1989.
Sircar, S. “Gas Separation by Rapid Pressure Swing Adsorption,” U.S. Patent 5,071,449 (1991).
Skarstrom, C.W., “Heatless Fractionation of Gases Over Solid Adsorbents,’ inRecent Developments in Separation Science, N.N. Li (Ed.), CRC Press, Cleveland, 1972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sircar, S., Hanley, B.F. Production of oxygen enriched air by rapid pressure swing adsorption. Adsorption 1, 313–320 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707354
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707354