Abstract
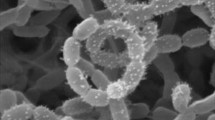
Two strains of an undescribed species of the genusKluyveromyces were recovered from the rhizosphere of spruce. A description of the new species,Kluyveromyces piceae, is given and its classification on basis of ascospore shape, substrate utilization, G + C-content, DNA-DNA-reassociation data and habitat specifity is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer R & Oberwinkler F (1988) Nuclear degeneration during ballistospore formation ofCronartium asclepiadeum (Uredinales). Botanica Acta 101: 272–282
Cryer DR, Eccleshall R, Marmur J (1975) Isolation of yeast DNA. In: Prescott DM (Ed) Methods of Cell Biology, Vol. XII (pp 39–44). Academic Press, New York, San Francisco, London
Johannsen E (1980) Hybridization studies within the genusKluyveromyces. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 46: 177–189
Kock JLF, Coetzee DJ & Pretorius GHJ (1988) The phylogenetic development of species representing the genusKluyveromyces. System. Appl. Microbiol. 10: 293–296
Kurtzman CP, Smiley JM, Johnson CJ, Wickerham LJ & Fuson GB (1980) Two closely related and heterothallic species,Pichia amylophila andPichia mississipiensis: Characterization by hybridization and deoxyribunucleic acid reassociation. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 30: 208–216
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF & Sambrook J (1982) Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Guide. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Martini A (1973) Ibridazioni DNA/DNA tra specie di lieviti del genereKluyveromyces Ann. Fac. Agrar. Univ. Studi Perugia 28: 157–171
Nakase T & Suzuki M (1985) Taxonomic studies onDebaryomyces hansenii (Zopf) Lodder et Kreger-van Rij and related species. I. Chemotaxonomic investigations. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 31: 49–69
Owen RJ, Hill LR & Lapage SP (1969) Determination of DNA base compositions from melting profiles in dilute buffers. Biopolymers 7: 503–516
Poncet S (1973) Taxonomie numérique du genreKluyveromyces. Mycopathol. Mycol. Appl. 51: 267–281
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol 17: 208–212
Seidler RJ & Mandel M (1971) Quantitative aspects of deoxyri-bonucleic acid renaturation: base composition, site of chromosome replication and polynucleotide homologies. J. Bacteriol. 106: 608–614
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26: 31–43
Walt JP van der (1970)Kluyveromyces van der Walt emend. van der Walt. In: Lodder J (Ed) The Yeasts, a Taxonomic Study, 2nd ed. (pp 316–378). North-Holland Publishing Company
Walt JPvan der & Johannsen E (1984)Kluyveromyces van der Walt emend. van der Walt. In: Kreger-van Rij NJW (Ed) The Yeasts, a Taxonomic Study, 3rd ed. (pp 224–251). Elsevier Science Publ., Amsterdam
Walt JPvan der & Yarrow D (1984) Methods for isolation, maintenance, classification and identification of yeasts. In: Kreger-van Rij NJW (Ed) The Yeasts, a Taxonomic Study, 3rd ed. Elsevier Science Publ. B.V., Amsterdam
Weber G (1990) Untersuchungen der Mikropilzflora im Wurzelbereich von Fichten verschiedener Schadstufen. PhD Thesis, Universität, Tübingen
Wickerham LJ & Burton KA (1954) A simple technique for obtaining mating types in heterothallic diploid yeasts, with special reference to their uses in the genusHansenula. J. Bacteriol. 67: 303–308
& Burton KA (1956a) Hybridization studies involvingSaccharomyces lactis 0 andZygasaccharomyces ashbyii. J. Bacteriol. 71: 290–295
& Burton KA (1956b) Hybridization studies involvingSaccharomyces fragilis 0 andZygosaccharomyces dobzhanskii. J. Bacteriol. 71: 296–302
Yamada Y & Kondô K (1971) Significance of coenzyme Q system in yeasts and yeast-like fungi (1). Proc. 1st Special Int. Symp. Yeasts. Smolonice (pp 363–373)
& Kondô K (1973) Coenzyme Q system in the classification of the yeast 0 generaRhodotorula andCryptococcus, and the yeast like generaSporobolomyces andRhodosporidium. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 19: 59–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, G., Spaaij, F. & van der Walt, J.P. Kluyveromyces piceae sp. nov., a new yeast species isolated from the rhizosphere ofPicea abies (L.) Karst. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 62, 239–244 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582585
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582585