Abstract
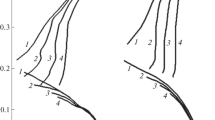
The analytical and potentiometric study (using an Ag/Ag+ reference electrode) of the behaviour of pure iron in molten sodium metaphosphate at 750°C shows that a non-polarized electrode corrodes: iron is oxidized to soluble Fe2+ ions and, simultaneously, an Fe2P and FeP2 deposit resulting from phosphate anion reduction is formed on the electrode surface.
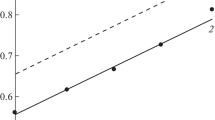
The variations of the mixed potential and of the total mass of oxidized iron show that the corrosion rate decreases as the immersion time increases. Such an inhibition comes from the gradual coating of the electrode surface with the iron phosphides: the corrosion rate is controlled by the iron diffusion through the deposit, the thickness of which increases with time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. J. Pryor and M. Cohen,J. Electrochem. Soc.,98 (1951) 263.
E. J. Casey and A. R. Dubois,Can. J. Chem.,49 (1971) 2733.
R. D. Caton and C. R. Wolfe,Anal. Chem.,43 (1971) 660.
I. Wynn Jones and L. J. Miles,Proc. Brit. Ceram. Soc.,19 (1971) 179.
R. D. Caton and H. Freund,Anal. Chem.,35 (1963) 2103.
A. Simon and E. Steger,Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.,277 (1954) 209.
W. Bues and H. W. Gehrke,Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.,288 (1956) 291.
D. J. Williams, B. T. Braddury and W. R. Maddocks,J. Soc. Glass. Technol.,43 (1959) 337.
A Winkler and E. Thilo,Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.,298 (1959) 302.
J. R. Van Waser,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,72 (1950) 639.
A. E. R. Westman and J. Growther,Can. J. Chem.,32 (1954) 42.
A. E. R. Westman and J. Growther,J. Am. Ceram. Soc.,37 (1954) 420.
A. E. R. Westman and P. A. Cartagenis,J. Am. Ceram. Soc.,40 (1957) 293.
T. R. Meadowcroft and F. D. Richardson,Trans. Faraday Soc.,59 (1963) 1564.
J. R. Van Waser, ‘Phosphorus and its Compounds’, Vol. 1, p. 779, Interscience, New York (1958).
N. K. Voskresenskaya and P. D. Sokolova,Russ. Chem. Renews,38 (1969) 862.
P. N. Yocom, Ph. D. Thesis, University of Illinois (1958).
E. Franks and D. Inman,J. Electroanal. Chem.,26 (1970) 13.
H. A. Laitinen and K. R. Lucas,J. Electroanal. Chem.,12 (1966) 553.
M. Chene, Thesis, Grenoble (1940).
K. J. Vetter, ‘Electrochemical Kinetics,’ pp. 433–5, Academic Press, New York (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belcadi, S., Rameau, J.J. & Barbier, M.J. Corrosion of pure iron in fused sodium methaphosphate. J Appl Electrochem 3, 185–191 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619160
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619160