Abstract
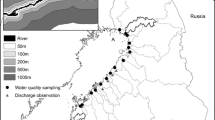
Concern about nitrogen loads in marine environments has drawn attention to the existence and possible causes of long-term trends in nitrogen transport in rivers. The present study was based on data from the Swedish environmental monitoring programme for surface water quality; the continuity of these data is internationally unique. A recently developed semiparametric method was employed to study the development of relationships between runoff and river transport of nitrogen since 1971; the observed relationships were then used to produce time series of flow-normalised transports for 66 sites in 39 river basins. Subsequent statistical analyses of flow-normalised data revealed only few significant downward trends (p ≤0.05) during the time period 1971–1994, and the most pronounced of these downward trends were caused by reduced point emissions of nitrogen. The number of significant upward trends was substantially larger (15 for total-N and 18 for NO3-N). Closer examination of obtained results revealed the following: (i) the most pronounced upward trends were present downstream of lakes, and (ii) observed increases in nitrogen transport coincided in time and space with reduced point emissions of phosphorus or organic matter. This indicated that changes in the retention of nitrogen in lakes were responsible for the upward nitrogen trends. The hypothesis that nitrogen saturation of forest soils has caused a general increase in the riverine export of nitrogen from forested catchments in Sweden was not confirmed. Neither did the results indicate that improved agricultural practices have reduced the export of nitrogen from agricultural catchments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber, J.-D., Nadelhoffer, K.-J., Steudler, P. and Melillo, J.-M.: 1989, ‘Nitrogen saturation in Northern forest ecossytem. Excess nitrogen from fossil fuel combustion may stress the biosphere’, Bioscience 39, 378–386.
Admiraal, W. and van der Vlugt, J.-C.: 1988, ‘High rates of denitrification storage reservoir fed with water of the River Rhine’, Archiv für Hydrobiologia 113, 593–605.
Ahl, T.: 1990, ‘Eutrofiering av Västerhavet – mekanismer, orsaker och åtgärder. Näringsbelastning på Västerhavet – källfördelning’, Kungliga Skogs-och Lantbruksakademiens Tidskrift 129, 135–143 (in Swedish).
Areskoug, H.: 1993, ‘Nedfall av kväve och fosfor till Sverige, Östersjön och Västerhavet’, Report No. 4148, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Solna, Sweden (in Swedish).
Bergström, S.: 1993, ‘Sveriges hydrologi – grundläggande hydrologiska förhållanden’, SMHI Report, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, Norrköping, Sweden (in Swedish).
Behrendt, H.: 1988, ‘Changes in nonpoint nutrient loadings into European freshwaters: trends and consequences since 1950 and not-impossible changes until 2080’, Report No. WP-88-026, IIASA, Laxenburg, Austria.
Behrendt, H.: 1993, ‘Separation of point and diffuse loads of pollutants using monitoring data of rivers’, Water Science and Technology 28, 165–175.
Behrendt, H.: 1996, ‘Inventories of point and diffuse sources and estimated nutrient loads – a comparison for different river basins in Central Europe’, Water Science and Technology 33, 175–181.
Billen, G., de Becker, E., Lancelot, C., Sevais, P., Somville, M. and Stainier, E.: 1992, ‘Études des processus de transfert, d'immobilisation et de transformation d'azote dans son acheminement depuis les sols agricoles jusqu'a la mer’, Rapp. Eur. Econ. Commun., Paris contract No. ENV-522-B (RS).
Brandt, M.: 1990, ‘Modelling nitrogen transport from a basin with mixed land use – example from the lake Ringsjön area, Sweden’, Vannet i Norden 3, 39–57.
Dijk, G.-M. van, Stålnacke, P., Grimvall, A., Tonderski, A., Sundblad, K. and Schäfer, A.: 1996, ‘Long-term trends in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in the Lower River Rhine’, Archiv für Hydrobiologia 113, 99–109.
Dillon, P.-J. and Kirchner, W.-B.: 1975, ‘The effects of geology and land use on the export of phosphorus from watersheds’, Water Research 9, 135–148.
Dillon, P.-J. and Molot, L.-A.: 1990, ‘The role of ammonium and nitrate retention in the acidification of lakes and forested catchments’, Biogeochemistry 11, 23–43.
Dillon, P.-J., Molot, L.-A. and Scheider, W.-A.: 1991, ‘Phosphorus and nitrogen export from forested stream catchments in Central Ontario’, Journal of Environmental Quality 20, 857–864.
Elser, J.-J., Marzolf, E.-R. and Goldman, C.-R.: 1990, ‘Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation of phytoplankton growth in the freshwaters of North America: A review and critique of experimental enrichments’, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 47, 1468–1477.
Engle, R.-F., Grangler, C.-W.-J., Rice, J.-A. and Weiss, A.: 1986, ‘Semiparametric estimates of the relation between weather and electricity sales’, Journal of American Statistical Association 81, 310–320.
Fleischer, S. and Stibe, L.: 1989, ‘Agriculture kills marine fishs in the 1980's. Who is responsible for fish kills in the year 2000?’, Ambio 18, 347–350.
Gahnström, G., Blomqvist, P. and Fleischer, S.: 1993, ‘Are key nitrogen fluxes changed in the acidified aquatic ecosystem’, Ambio 22, 318–324.
Granat, L.: 1991, ‘Luft-och nederbördskemiska stationsnätet inom PMK. Rapport från verksamheten 1990’, Report No. 3942, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Solna, Sweden (in Swedish).
Green, P.J. and Silverman, B.W.: 1994, Nonparametric Regression and Generalized Linear Models – A Roughness Penalty Approach, Chapman and Hall, London.
Grimvall, A.: 1996, ‘Uncertainty of Estimates of Riverine Loads of Pollutants’, in Riverine Input to Coastal Areas – Notes from a Workshop on Methodology, Nordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen, Denmark, TemaNord 1996: 529, 71–81.
Grimvall, A. and Stålnacke, P.: 1996, ‘Statistical methods for source apportionment of riverine loads of pollutants’, Environmetrics 7, 201–213.
Grimvall, A., Stålnacke, P., Sundblad, K., Niemirycz, E., Pitkänen, H. and Bruhn, A.: 1991, ‘Trend Analysis of Nutrient Concentrations in Baltic Sea Rivers’, In: J. Fenger et al. (eds.), Environment, Energy and Natural Resource Management in the Baltic Region – 3rd International Conference on System AnalysisNordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen, Denmark, May 7–10, 1991, Nord1991: 48, 333–344.
Grimvall, A., Stålnacke, P. and Tonderski, A.: 1997, ‘Timescales of nutrient losses from land to sea – a European perspective’, Ecological Engineering(submitted).
Grip, H. and Rodhe, A.: 1988, ‘Vattnets väg från regn till bäck’, Hallgren and Fallgren Studieförlag AB, Uppsala, Sweden (in Swedish).
Gundersen, P.: 1995, ‘Nitrogen deposition and leaching in European forests – preliminary results from a data compilation’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 1179–1184.
Hill, A.-R.: 1978, ‘Factors affecting the export of nitrate-nitrogen from drainage basins in Southern Ontario’, Water Research 12, 1045–1057.
Hirsch, R.-M. and Slack, J.-R.: 1984, ‘A nonparametric trend test for seasonal data with serial dependence’, Water Resources Research 20, 727–732.
Jansson, M., Persson, G. and Broberg, O.: 1986, ‘Phosphorus in acidified lakes: the example of lake Gårdsjön, Sweden’, Hydrobiologia 139, 81–96.
Johnson, D.-W.: 1992, ‘Nitrogen retention in forest soils’, Journal of Environmental Quality 21, 1–12.
Johnsson, H. and Hoffmann, M.: 1998, ‘Nitrogen leaching from agricultural land in Sweden – standard rates and gross loads in 1985 and 1994’, Ambio(in press).
Jönsson, E.: 1966, ‘The determination of Kjeldahl nitrogen in natural water’, Vattenhygien 22, 10–14.
Kendall, M.-G.: 1975, ‘Rank correlation methods’, 4th edition, Charles Griffin, London.
Kirchner, W.-B.: 1975, ‘An examination of the relationships between drainage basin morphology and the export of phosphorus’, Limnology and Oceanography 20, 267–270.
Kronvang, B. and Bruhn, A.: 1996, ‘Choice of sampling strategy and estimation method for calculating nitrogen and phosphorus transport in small lowland streams’, Hydrological Processes 10, 1483–1501.
Lepistö, A., Andersson, L., Arheimer, B. and Sundblad, K.: 1995, ‘Influence of catchment characteristics, forestry activities and deposition on nitrogen export from small forested catchments’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 84, 81–102.
Lepistö, A., Sundblad, K., Stålnacke, P. and Andersson, L.: 1991, ‘Nitrogen Loading from Forested Catchments in Finland and Sweden – Trend Analysis of Concentration Data’, in J. Fenger et al. (eds.), Environment, Energy and Natural Resource Management in the Baltic Region – 3rd International Conference on System AnalysisNordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen, Denmark, May 7–10, 1991, Nord1991: 48, 273–284.
Löfgren, S.: 1991, ‘Naturliga och antropogena källors betydelse för de ökande halterna av kväve och organiskt material i Västerdalälven och Klarälven, 1965–1989’, Report No. 3902, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Uppsala, Sweden, (in Swedish).
Löfgren, S. and Olsson, H.: 1990, ‘Nitrogen and phosphorus entering water courses in inland Sweden’, Report No. 3692, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Uppsala, Sweden, (in Swedish with summary in English).
McLeod, A.-I., Hipel, K.-W. and Comancho, F.: 1983, ‘Trend assessment of water quality time series’, Water Resources Bullentin 19, 537–547.
Nordic Council of Ministers: 1992, ‘Critical loads for nitrogen’, Nord 1992:41, Nordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Persson, G., Olsson, H., Wiederholm, T. and Willén, E.: 1989, ‘Lake Vättern, Sweden: A 20-year perspective’, Ambio 18, 208–215.
SEPA: 1994, ‘Eutrophication of soil, freshwater and the sea’, Report No. 4244, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Solna, Sweden.
Schröder, H.: 1985, ‘Nitrogen losses from Danish agriculture – trends and consequences’, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 14, 279–289.
Silverman, B.-W.: 1985, ‘Some aspects of the spline smooothing approach to nonparametric regression curve fitting’, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B 47, 1–52.
SIS: 1991, ‘Determination of the sum of nitirite and nitrate nitrogen content of water’, SS 028133-2, Standardiseringskommisionen i Sverige, (in Swedish).
SMHI: 1994, ‘Vattenföring i Sverige. Del 1. Vattendragen till Bottenviken’, SMHI Hydrologi No. 40, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, Norrköping, Sweden, (in Swedish).
Spooner, J., Huffman, R.-L., Line, D.-E., Gale, J.-A., Arnold, J.-A., Wyatt, L., Osmond, D.-L. and Haseeb, S.-K.: 1992, ‘Nonpoint sources’, Water Environment Research 64, 503–514.
Stålnacke, P. and Grimvall, A.: 1997, ‘Semiparametric approaches to flow-normalisation and source apportionment of substance transport in rivers’, Environmetrics(in press).
Theil, H.: 1950, ‘A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis, 1, 2 and 3’, Ned. Akad. Wentsch Proc. 53, 386–392, 521–525, 1397–1412.
Tonderski, A., Grimvall, A., Dojlido, J. and van Dijk, G.: 1995, ‘Monitoring nutrient transport in large rivers’, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 34, 245–269.
Tsirkunov, V.-V., Nikanorov, A.-M., Laznik, M.-M. and Dongwei, Z.: 1992, ‘Analysis of long-term and seasonal river water quality changes in Latvia’, Water Research 26, 1203–1216.
Werner, W., Olfs, H.-W., Auerswald, K. and Isermann, K.: 1991, Stickstoff-und Phosphoreintrag in Oberflächengewässer über ‘diffuse Quellen’, in A. Hamm (ed.), Studie über Wirkungen and Qualitätsziele von Nährstoffen in FliessgewässernAcademia Verlag, Saunt Augustin, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stålnacke, P., Grimvall, A., Sundblad, K. et al. Trends in Nitrogen Transport in Swedish Rivers. Environ Monit Assess 59, 47–72 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006007711735
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006007711735