Conclusion
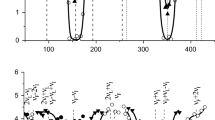
As is demonstrated in the present work, the zero-field technique is a powerful method in studying diffusion/trapping of the μ+, especially for the case of slow hopping. In the case of MnSi, the hopping time τc has been determined to be longer than 20 μsec, with the width of the nuclear random fields Δ/γμ = 3.80 ± 0.4 Oe. The role of the μ+ in low-field relaxation studies is unique, since it provides information inaccessible to NMR techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Hartmann, Phys. Rev. Lett. 39, 832 (1977)
R. S. Hayano, Y. J. Uemura, J. Imazato, N. Nishida, K.Nagamine, T. Yamazaki, H. Yasuoka and Y. Ishikawa, contribution to this conference.
R. Kubo and T. Toyabe, in Magnetic Resonance and Relaxation (ed. R. Blinc, North-Holland Pub. Co., Amsterdam) p. 810.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Toray Science Foundation, the Grant-in-Aid of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture and Science, and the Atomic Energy Control Board and National Research Council of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayano, R.S., Uemura, Y.J., Imazato, J. et al. Zero- and low-field μ+ spin relaxation behavior in MnSi. Hyperfine Interact 6, 133–136 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01028781
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01028781