Abstract
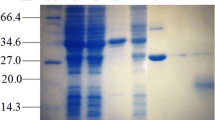
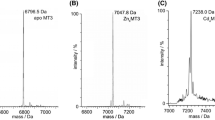
The sequence of six amino acid residues -Ser-Cys-Cys-Ser-Cys-Cys- is present in all mammalian metallothionein sequences and has been highly conserved during evolution, although the metallothioneins have divergent primary sequences. To determine whether two serines in the sequence play a crucial role in metalbinding of metallothioneins, a mutant metallothionein with these two serines replaced by leucines was obtained using anEscherichia coli expression system. The expressed protein was analyzed for its chemical and spectroscopic properties. It was confirmed that the mutant metallothionein (MT) bound cadmium through a metal-thiolate complex and that there was no strong difference between the mutant and the wild-type MTs in retaining the metal-binding cluster. However, the metal-binding cluster of the mutant metallothionein was more unstable than that of the wild-type metallothionein. The two conservative serines could play a role in the stability of metal-binding ligands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berka, T., Shatzman, A., Zimmerman, J., Strickler, J., and Rosenberg, M. (1988). Efficient expression of yeast metallothionein gene inEscherichia coli.J. Bacteriol. 17021.
Bremner, I. (1987). Nutritional and physiological significance of metallothionein.Experientia Suppl. 5281.
Chernaik, M. L., and Huang, P. C. (1991). Differential effect of cysteine-to-serine substitutions in metallothionein on cadmium resistance.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 883024.
Cismowski, M. J., and Huang, P. C. (1991). Effect of cysteine replacements at positions 13 and 50 in metallothionein structure.Biochemistry 306626.
Cismowski, M. J., Narula, S. S., Armitage, I. M., Chernaik, M. L., and Huang, P. C. (1991). Mutation of invariant cysteines of mammalian metallothionein alters metal binding capacity, cadmium resistance, and113Cd NMR spectrum.J. Biol. Chem. 26624390.
Cody, C. W., and Huang, P. C. (1993). Metallothionein detoxification function is impaired by replacement of both conserved lysines with glutamines in the hinge between the two domains.Biochemistry 325127.
Cody, C. W., and Huang, P. C. (1994). Replacement of all α-domain lysines with glutamate reduces metallothionein detoxification function.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 202954.
Ecker, D. J., Butt, T. R., Sternberg, E. J., Neeper, M. P., Debouck, C., Gorman, J. A., and Crooke, S. T. (1986). Yeast metallothionein function in metal ion detoxification.J. Biol. Chem. 26116895.
Hamer, D. H. (1986). Metallothionein.Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55913.
Kägi, J. H. R. (1993). Evolution, structure and chemical activity of class I metallothioneins: An overview. In Suzuki, K. T., Imura, N., and Kimura, M. (eds.),Metallothionein III Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp. 29–55.
Kägi, J. H. R., and Kojima, Y. (1987). Chemistry and biochemistry of metallothionein.Experientia Suppl. 5225.
Kägi, J. H. R., and Vallee, B. L. (1960). Metallothionein: A cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex.J. Biol. Chem. 2353460.
Kägi, J. H. R., and Vallee, B. L. (1961). Metallothionein: A cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex II.J. Biol. Chem. 2362435.
Kägi, J. H. R., Vasak, M., Lerch, K., Gilg, D. E. O., Hunziker, P., Bernhard, W. R., and Good, M. (1984). Structure of mammalian metallothionein.Environ. Health Perspect. 5493.
Karin, M., and Richards, R. I. (1982). Human metallothionein genes: Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 103165.
Kille, P., Lees, W. E., Darke, B. M., Winge, D. R., Dameron, C. T., Stephens, P. E., and Kay, J. (1992). Sequestration of cadmium and copper by recombinant rainbow trout and human metallothioneins and by chimeric (mermaid and fishman) proteins with interchanged domains.J. Biol. Chem. 2678042.
Kille, P., Stephens, P., Cryer, A., and Kay, J. (1990). The expression of a synthetic rainbow trout metallothionein gene inE. coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1048178.
Kojima, Y., and Kägi, J. H. R. (1978). Metallothionein.TIBS 390.
Kojima, Y., Berger, C., Vallee, B. L., and Kägi, J. H. R. (1976). Amino-acid sequence of equine renal metallothionein-1B.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 733413.
Murooka, Y., and Nagaoka, T. (1987). Expression of cloned monkey metallothionein inEscherichia coli.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53204.
Nordberg, M., and Kojima, Y. (1979). Metallothionein and other low molecular weight metal-binding proteins.Experientia Suppl. 3441.
Odawara, F., Kurasaki, M., Suzuki-Kurasaki, M., Oikawa, S., Emoto, T., Yamasaki, F., Linde Arias, A. R., and Kojima, Y. (1995). Expression of human metallothionein-2 inEscherichia coli: Cadmium tolerance of transformed cells.J. Biochem. 1181131.
Pan, P. K., Hou, F. Y., Cody, C. W., and Huang, P. C. (1994). Substitution of glutamic acids for the conserved lysines in the α domain affects metal binding in both α and β domains of mammalian metallothionein.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 202621.
Sayers, Z., Brouillon, P., Vorgias, C. E., Nolting, H. F., Hermes, C., and Koch, M. H. J. (1993). Cloning and expression ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae copper-metallothionein gene inEscherichia coli and characterization of the recombinant protein.Eur. J. Biochem. 212521.
Schram, E., Moore, S., and Bigwood, E. J. (1954). Chromatographic determination of cysteine as cysteic acid.Biochem. J. 5733.
Thrower, A. R., Byrd, J., Tarbet, E. B., Mehra, R. K., Hamer, D. H., and Winge, D. R. (1988). Effect of mutation of cysteinyl residues in yeast Cu-metallothionein.J. Biol. Chem. 2637037.
Vasak, M., and Kägi, J. H. R. (1987). In Sigel, H. (ed.),Metal Ions in Biological Systems Marcel Dekker, New York, Vol. 15, pp. 213–273.
Wang, Y., Mackay, E. A., Kurasaki, M., and Kägi, J. H. R. (1994). Purification and characterization of recombinant sea urchin metallothionein expressed inEscherichia coli.Eur. J. Biochem. 225449.
Willner, H., Vasak, M., and Kägi, J. H. R. (1987). Cadmium-thiolate clusters in metallothionein: spectrophotometric and spectropolarimetric features.Biochemistry 266287.
Winge, D. R., and Miklossy, K.-A. (1982). Domain nature of metallothionein.J. Biol. Chem. 2573471.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emoto, T., Kurasaki, M., Oikawa, S. et al. Roles of the conserved serines of metallothionein in cadmium binding. Biochem Genet 34, 239–251 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407022
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407022