Abstract
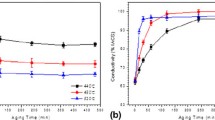
The microstructural and mechanical stability of Cu-6 wt. % Ag alloy obtained by cold rolling combined with intermediate heat treatments have been investigated. The stress-strain responses and fracture behavior of Cu-6 wt. % Ag alloy were examined and correlated with the microstructural change caused by thermo-mechanical treatments. The deformation bands stabilized by silver precipitates were observed in heavily rolled Cu-6 wt. % Ag alloy. The highly deformed microstructure stabilized by silver filament was observed to be unstable at temperatures above 200 °C. The strength of Cu-6wt.%Ag alloys were found to decrease remarkably if they were heat-treated above 300°C. The fracture surfaces of Cu-Ag two phase alloys showed typical ductile type fracture. The electrical conductivity did not change appreciably up to the aging temperature of 200°C and increased rapidly at temperatures above 300°C. The increase of the conductivity and the decrease of the strength can be associated with the microstructural coarsening of heavily deformed linear band structure. The difference of the UTS and the conductivity between the rolling direction and the direction perpendicular to the rolling direction (on the rolling plane) were found to be relatively small.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Benghalem and D. G. Morris, Acta Mater. 45 (1997) 397.
S. I. Hong and M. A. Hill, ibid. 46 (1998) 4111.
S. I. Hong, M. A. Hill, Y. Sakai, J. T. Wood and J. D. Embury, Acta Metall. Mater. 43 (1995) 3313.
S. I. Hong and M. A. Hill, Mater. Sci. Eng. A264 (1999) 151.
S. I. Hong, Scripta Mater. 39 (1998) 1685.
J. D. Verhoeven, L. S. Chumbley, F. C. Laabs and W. A. Spitizig, Acta Metall. Mater. 39 (1991) 2825.
U. Hangen and D. Raabe, ibid. 43 (1995) 4075.
P. D. Funkenbusch and T. H. Courtney, Metall. Trans. 18 (1987) 1249.
Y. Sakai and H. J. Schneider-muntau, Acta Mater. 45 (1997) 1017.
Y. Sakai, K. Inoue and Maeda, Acta Metall. Mater. 43 (1995) 1517.
Y. Sakai, K. Inoue, T. Asano, H. Wada and H. Maeda, Appl. Phys. Lett. 59 (1991) 2965.
D. Kuhlmann-wilsdorf, Acta Mater. 47 (1999) 1697.
S. S. Kulkarni, E. A. Starke JR. and D. Kuhlmann-wilsdorf, ibid. 46 (1998) 5283.
M. Hatherly and A. S. Malin, Metal Technol. 7 (1979) 308.
A. Korbel, J. D. Embury, M. Hatherly, P. L. Martin and H. W. Erbsloh, Acta Metall. 34 (1986) 1999.
R. P. Singh, A. Lawley, S. Friedman and Y. V. Murty, Mater. Sci. Eng. A145 (1991) 243.
C. S. Lee and B. J. Duggan, Acta Metall. Mater. 41 (1993 2691.
C. S. Lee, B. J. Duggan and R. E. Smallman, ibid. 41 (1993) 2265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, M.S., Song, J.S. & Hong, S.I. Microstructural and mechanical stability of Cu-6 wt. % Ag alloy. Journal of Materials Science 35, 4557–4561 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004876806313
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004876806313