Abstract
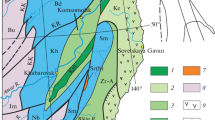
The Bodie mining district in Mono County, California, is zoned with a core polymetallic-quartz vein system and silver- and gold-bearing quartz-adularia veins north and south of the core. The veins formed as a result of repeated normal faulting during doming shortly after extrusion of felsic flows and tuffs, and the magmatic-hydrothermal event seems to span at least 2 Ma.
Epithermal mineralization accompanied repeated movement of the normal faults, resulting in vein development in the planes of the faults. The veins occur in a very large area of argillic alteration. Individual mineralized structures commonly formed new fracture planes during separate fault movements, with resulting broad zones of veinlets growing in the walls of the major vein-faults. The veinlet swarms have been found to constitute a target estimated at 75,000,000 tons, averaging 0.037 ounce gold per ton. The target is amenable to bulkmining exploitation.
The epithermal mineralogy is simple, with electrum being the most important precious metal mineral. The host veins are typical low-sulfide banded epithermal quartz and adularia structures that filled voids created by the faulting. Historical data show that beneficiation of the simple vein mineralogy is very efficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchanan, L.J., 1981, Precious-metal deposits associated with volcanic environments in the Southwest,in Dickinson, W.R., and Payne, W.D., eds., Relations of tectonics to ore deposits in the Southern Cordillera: Arizona Geological Society Digest, v. 14, p. 237–262.
Chesterman, C.W., 1968, Volcanic geology of the Bodie Hills, Mono County, CA,in Coast, R.R., Hay, R.L., and Anderson, C.A., eds., Studies in volcanology, a memoir in honor of Howell Williams: Geological Society of America Memoir 116, p. 45–68.
Chesterman, C.W. Chapman, R.H., and Gray, C.H., Jr., 1986, Geology and ore deposits of the Bodie mining district, Mono County, California: California Division of Mines and Geology, Bulletin 206, 36 p.
Gumble, G.E., Warren, M.L., Whitehead, M.L., and Enders, M.S., 1991, Summary of the geology of the northern part of the Bodie mining district, Mono County, California,in Buffa, R.H., and Coyner, A.R., eds., Geology and ore deposits of the Great Basin, Field Trip Guidebook Compendium: Geological Society of Nevada, v. 2, p. 619–623.
Herrera, P.A., 1988, Geology, alteration, and trace element distribution in the northern portion of the Bodie mining district, Mono County, California: Golden, Colorado, Colorado School of Mines, M.S. thesis, 272 p.
Hollister, V.F., and Silberman, M.L., in press, Silver-gold and polymetallic quartz veins in the Bodie mining district, California —Are they related to a porphyry Cu−Mo system at depth?: Arizona Geological Society.
Kleinhampl, F.J., Davis, W.E., Silberman, M.L., Chesterman, C.W., and Gray, C.H., Jr., 1975, Aeromagnetic and limited gravity studies and generalized geology of the Bodie Hills: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1384, 38 p.
O'Neil, J.R., Silberman, M.L., Fabbi, B.P., and Chesterman, C.W., 1973. Stable isotope and chemical relations during mineralization in Bodie: Economic Geology, v. 68, p. 765–784.
Silberman, M.L., Chesterman, C.W., Kleinhampl, F.J., and Gray, C.H., Jr., 1972, K-Ar ages of volcanic rocks and gold-bearing quartz-adularia veins in the Bodie mining district, Mono County, California: Economic Geology, v. 67, p. 597–604.
Wisser, E.H., 1960. Relation of ore deposition to doming in the American Cordillera: Geological Society of America Memoir 77, p. 70–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On the cover: Southeast view of Bodie mining district in Mono County, California, one of the more famous pioneer epithermal gold producers in the western U.S. Recent exploration drilling suggests an additional resource of 2 million ounces of gold. The townsite is at the intersection of roads near the center of the photo. The foreground is mainly tuff breccia of the Bodie Hills volcanic field. Arcuate lines in the valley beyond the hills are old Mono Lake shorelines. The White Mountains form the ridge on the skyline. Photo by Frank Kleinhampl, about 1970.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollister, V.F., Silberman, M.L. Geology of epithermal silver-gold bulk-mining targets, bodie district, Mono County, California. Nat Resour Res 4, 129–137 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02259036
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02259036