Abstract
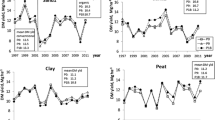
The effects of Na fertiliser (supplied as an NPK-Na compound) on herbage yield and composition were examined at two different sites to see if pasture responses to Na were affected by differences in K and moisture availability. At one site, pasture was grown under conditions of moisture stress and limited K availability, whereas at the other site the pasture was grown under comparatively non-stress conditions.
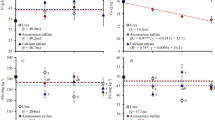
The results were interesting in that Na fertilisation appeared to be detrimental to pasture yield and quality under conditions of moisture stress and suboptimal K supply, whereas under the non-stress conditions it actually increased herbage N offtake, marginally improved the nutritional quality of the pasture and produced appreciable (albeit non-significant) increases in DM yield. It was suggested that an important effect of Na on grass production may have been its ability to enhance the rate of NO3 − uptake by plants, thereby minimising NO3 −-N losses from the soil-plant system by denitrification. However, because the amount of N fertiliser used in the experiments (i.e. 390 kg N ha−1 yr−1) was close to that normally required for maximum yield production (N max) under Northern Ireland conditions, the scope for yield increases in response to Na-elicited improvements in N offtake were thought to have been very limited at both experimental sites.
On the basis of results from both the present study and previous field trials, a unifying theory is presented to explain the differential effects of Na on NO3 − uptake and herbage growth under different sets of circumstances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams S N 1973 The response of pastures in Northern Ireland to N, P and K fertilisers and to animal slurries: II. Effects on dry-matter yield. J. Agric. Sci., Camb. 81, 411–417.
Bailey J S 1989 Potassium-sparing effect of calcium in perennial ryegrass. J. Plant Nutr. 12, 1019–1027.
Bailey J S 1993 Sustainable fertiliser use. Proc. Fert. Soc. No. 343.
Blevins D G, Barnett N M and Frost W B 1978 Role of potassium and malate in nitrate uptake and translocation by wheat seedlings. Plant Physiol. 62, 784–788.
Butler E J 1963 The mineral element content of spring pasture in relation to the occurrence of grass tetany and hypomagnesaemia in dairy cows. J. Agric. Sci., Camb. 60, 329–340.
Chiy P C and Phillips C J C 1991 The effect of sodium application to dairy cow pastures on pasture and cow production and grazing preference. Grass For. Sci. 46, 325–331.
Chiy P C and Phillips C J C 1993a Sodium fertiliser application to pasture. 1. Direct and residual effects on pasture production and composition. Grass For. Sci. 48, 189–202.
Chiy P C, Phillips C J C and Bello M R 1993 Sodium fertiliser application to pasture. 2. Effects on dairy cow production and behaviour. Grass For. Sci. 48, 203–212.
Chiy P C and Phillips C J C 1993b Sodium fertiliser application to pasture. 4. Effects on mineral uptake and the sodium and potassium status of steers. Grass For. Sci. 48, 260–270.
Chiy P C, Phillips C J C and Ajele C L 1994 Sodium fertiliser application to pasture. 5. Effects on herbage digestibility and mineral availability to sheep. Grass For. Sci. 49, 25–33.
Cram W J 1974 Effects of Cl− on HCO3 − and malate fluxes and CO2 fixation in carrot and barley root cells. J. Exp. Bot. 25, 253–268.
Cushnahan A and Bailey J S 1994 Growth responses of perennial ryegrass (Cv. Talbot) to sodium with varying levels of potassium and nitrogen application. In Sodium in Agriculture. Eds. C J Phillips and P Chiy. pp 208–209. Chalcombe Publications, Canterbury, Kent, UK.
Dampney P M R 1992 The effect of timing and rate of potash application on the yield and herbage composition of grass grown for silage. Grass For. Sci. 47, 280–289.
Frost W B, Blevins D G and Barnett N M 1978 Cation pretreatment effects on nitrate uptake, xylem exudate and malate levels in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiol. 61, 323–326.
Garrett M K, Watson C J, Jordan C, Steen R W J and Smith R V 1992 The nitrogen economy of grazed grassland. Proc. Fert. Soc. No. 326.
Hampe T and Marschner H 1982 Effect of sodium on morphology, water relations and net photosynthesis in sugar beet leaves. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 108, 151–162.
Haynes R J and Sherlock R R 1986 Gaseous losses of nitrogen. In Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-Soil System. Ed. R J Haynes. pp 242–285. Academic Press Inc., London, UK.
Jackson W A, Kwik K D, Volk R J and Butz R G 1976 Nitrate influx and efflux by intact wheat seedlings: Effects of prior nitrate nutrition. Planta 132, 149–156.
Jarvis S C 1982 Sodium absorption and distribution in forage grasses at different potassium status. Ann. Bot. 49, 199–206.
Jordan C 1989 The effect of fertiliser type and application rate on denitrification losses from cut grassland in Northern Ireland. Fert. Res. 19, 45–55.
Kemp A and T'Hart M L 1957 Grass tetany in grazing milking cows. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 5, 4–17.
Leigh R A and Wyn Jones R G 1984 A hypothesis relating critical potassium concentrations for growth to the distribution and function of this ion in the plant cell. New Phytol. 97, 1–13.
Linehan P A and Lowe J 1960 Grassland output and vegetational changes on a heavy County Fermanagh soil, as influenced by type of seeds sown and by rate of nitrogenous manuring. Res. Exp. Rec. Min. Agric. NI 10, 55–84.
Marschner H 1986 Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press Inc., London, UK.
Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food 1986 The Analysis of Agricultural Materials, Third Edition, Reference Book 427. HMSO, London, UK.
Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food 1988 Fertiliser Recommendations, Fifth Edition, Reference Book 209. HMSO, London, UK.
Minotti P L, Craig Williams D and Jackson W A 1968 Nitrate uptake and reduction as affected by calcium and potassium. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 32, 692–698.
Minotti P L, Craig Williams D and Jackson W A 1969 Nitrate uptake by wheat as influenced by ammonium and other cations. Crop Sci. 9, 9–14.
Morrison J, Jackson M V and Sparrow P F 1980 The response of perennial ryegrass to fertiliser nitrogen in relation to climate and soil. Grassl. Res. Inst. Tech. Rep. No. 27.
Raven J A 1985 Tansley Review No 2. Regulation of pH and generation of osmolarity in vascular plants: a cost-benefit analysis in relation to efficiency of use of energy, nitrogen and water. New Phytol. 101, 25–77.
Rufty T WJr., Jackson W A and Raper C DJr. 1981 Nitrate reduction in roots as affected by the presence of potassium and by flux of nitrate through the roots. Plant Physiol. 68, 605–609.
Smith F A 1973 The internal control of nitrate uptake into excised barley roots with differing salt contents. New Phytol. 72, 769–782.
Smith G S, Middleton K R and Edmonds A S 1978 A classification of pasture and fodder according to their ability to translocate sodium from their roots into the aerial parts. NZ. J. Exp. Agric. 6, 183–188.
Watson C J, Jordan C, Taggart P J, Laidlaw A S, Garrett M K and Steen R W J 1992 The Leaky N-cycle. Aspects Appl. Biol. 30, 215–222.
Wilkinson S R, Stuedemann J A, Grunes D L and Devine O J 1987 Relation of soil and plant magnesium to nutrition of animal and man. Magnesium 6, 74–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cushnahan, A., Bailey, J.S. & Gordon, F.J. Some effect of sodium application on the yield and chemical composition of pasture grown under differing conditions of potassium and moisture supply. Plant Soil 176, 117–127 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017682
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017682