Abstract
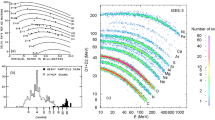
The relative abundances of low energy ions (0.6–2.0 MeV/n) in solar energetic particle (SEP) and corotating interaction region (CIR) events have been measured by the EPAC experiment aboard Ulysses since launch in October 1990 until the present time. We give an overview of the abundances of heavy ions (He, C, Ne, Fe) relative to oxygen during energetic particle events lasting longer than 5 days during the in- and out-of-ecliptic phase of the mission. While the period Oct. 1990 to Aug. 1992 was dominated by high solar activity the Ulysses out of ecliptic passage at solar latitudes up to 45° went parallel to the declining phase of solar activity. Thus a very clear structure of corotating interaction regions was observed. While the in-ecliptic composition is in general agreement with measurements made near the Earth, the development of the CIR-composition shows two phases: From Aug. 1992 to May 1993 the C/O-ratio is 0.55–0.70, afterwards it increases to 0.8–0.9. This increase is correlated to the disappearance of the current sheet at 30° solar latitude reported by Smithet al. (1993).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bame, S. J., et al.: 1993,Geophys. Res. Lett. 20 (21), pp. 2319–2326.
Gloeckler, G.: 1984,Adv. Space Res. 4 (2–3), pp. 127–137.
Gosling, J. T., et al.: 1993,Geophys. Res. Lett. 20(24), pp. 2789–2792.
Keppler, E., et al.: 1992,Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser. 92, pp. 317–331.
Keppler, E., et al.: 1994, this issue.
Krupp, N., et al.: 1992,Geophys. Res. Lett. 19(12), pp. 1255–1258.
Marsden, R. G. et al.: 1993,Adv. Space Res. 13(6), pp. 95–98.
Mason, G.M., et al.: 1994, ‘Heavy ion isotopic anomalies in3He-rich solar particle events’, subm. toAstrophys. J.
Maclennan C. G., et al.: 1993,Proc. 23rd ICRC, Calgary 3, pp. 330–333.
McDonald, F.B., et al.: 1994, ‘The effects of the intense solar activity of March/June 1991 observed in the outer heliosphere’, preprint.
Reames, D.V.: 1992,Proc. of the First SOHO. Workshop, ESA SP-348, pp. 315–323.
Reames D. V., et al.: 1994,Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 90, pp. 649–667.
Richardson, I. G. et al.: 1993,J. Geophys. Res. 98 (A1), pp. 13–32.
Reuss, M.K., et al.: 1994, this issue.
Roelof E. C., et al.: 1992,Geophys. Res. Lett. 19(12), pp. 1243–1246.
Smith, E. J. et al.: 1993,Geophys. Res. Lett. 20(21), pp. 2327–2330.
Whang, Y. C: 1991,Space Sci. Rev. 57, pp. 339–388.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fränz, M., Keppler, E., Krupp, N. et al. The elemental composition in energetic particle events at high heliospheric latitudes. Space Sci Rev 72, 339–342 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00768802
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00768802