Abstract
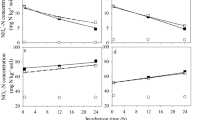
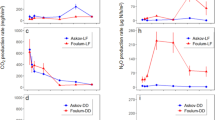
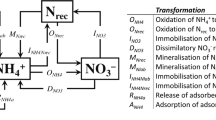
The biodegradation of hexadecane (C as hexadecane-C) was assessed under 34 different external nitrogen (N supplied as NO3-N) and phosphorus (P supplied as PO4-3-P) supply conditions in order to determine how different nutrient formulations affected nutrient limitation conditions during degradation. CO2 production yields indicated that shifts in N and P supply levels resulted in variable biodegradation responses due to shifts in the limiting-nutrient (e.g., from N to P). For example, the estimated maximum fractional CO2 yield ratio was 0.24 (mg CO2-C produced mg-1 hexadecane-C) for P-limited nutrient formulations (P:hexadecane-C<0.01), whereas the yield ratio was more than two times greater when the system was not P- limited. Similar effects were observed for N-limited (N:hexadecane- C<0.15) versus non-N-limited formulations. The relative bioavailability of natural soil-N and soil-P also was examined. In the soil studied, background soil-N was 96.3% organic-N and was found to be largely nonbioavailable. In contrast, high CO2 yields were observed even when no external P was supplied. An iterative mathematical procedure indicated that the Olsen soil-P subfraction (inorganic soil-P plus soluble organic soil- P) best approximated bioavailable soil-P for this soil. Our results indicate that both N and P additions affect biodegradation yields, but that stoichiometrically inappropriate nutrient mixes produce suboptimal CO2 yields. We also found that the bioavailable fractions of soil-N and soil-P should be incorporated into estimating the most suitable nutrient formulations for a given contamination scenario.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation; 1992, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater-18th Edition., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Atlas, R. M.: 1981, Microbiol. Rev. 45, 180.
Atlas, R. M. and Bartha, R.: 1972, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 14, 196.
Barth, E. F.: 1979, Biodegradation and Treatability of Specific Pollutants, EPA-600/9-79-034., U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C.
Bossert, I. and Bartha, R.: 1984, in R. M. Atlas <nt>(ed.)</nt>, Petroleum Microbiology, Macmillan Publishing Company, New York, NY, pp. 434–474.
Braddock, J. F., Ruth, M. L., Catterall, P. H., Walworth, J. L. and McCarthy, K. A.: 1997, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2078.
Bragg, J. R., Prince, R. C., Harner, E. J. and Atlas, R. M.: 1994, Nature 368, 413.
Cosgrove, D. J.: 1977, Adv. Microb. Ecol. 1, 95.
Ehrlich, H. L.: 1990, Geomicrobiology 2nd Edition, Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York, NY.
Enriquez, S., Duarte, C. M. and Sand-Jensen, K.: 1993, Oecologia 94, 457.
Fenchel, T. and Blackburn, T. H.: 1979, Bacteria and Mineral Cycling, Academic Press, London.
Foght, J. M., Fedorak, P. M. and Westlake, D. W. S.: 1990, Can. J. Microbiol. 36, 169.
Fox, T. R. and Comerford, N. B.: 1992, Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 579.
Glaser, B.: personal communication.
Graham, D. W., Chaudhary, J. A., Hansen, R. S. and Arnold, R. G.: 1993, Microbial Ecology 25, 1.
Graham, D. W., Smith, V. H. and Law, K. P.: 1995, in Hinchee, R. E., Hoeppel, R. E. and Anderson, D. B. (eds.), Bioremediation of Recalcitrant Organics, Batelle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 331–340.
Goldman, J. C., Caron, D. A. and Dennett, M. R.: 1987, Limnol. Oceanogr. 32, 1239.
Harder, H., Kurzel-Seidal, B. and Hopner, T.: 1991, Erdoel Kohle-Erdgas 44, 59.
Harder, W. and Dujkhuisen, L.: 1982, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. B.,297, 459.
He, Z. L., Wilson, M. J., Campbell, C. O., Edwards, A. C. and Chapman, S. J.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 83, 69.
Ishihari, M., Sugiura, K., Asaumi, M., Goto, M., Sasaki, E. and Harayama, S.: 1995, in Hinchee, R. E., Vogel, C. M. and Brockman, F. J. (eds.), Microbial Processes for Bioremediation, Batelle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 101–116.
Larsen, R. J. and Marx, M. L.: 1981, An Introduction to Mathematical Statistics and Its Applications, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Leahy, J. G. and Colwell, R. R.: 1990, Microbiol. Rev. 54, 305.
Liebig, J.: 1840, Chemistry in Its Application to Agriculture and Physiology, Taylor and Walton, London.
Lindstrom, J. E., Prince, R. C, Clark, J.C., Grossman, M. J., Yeager, T. R., Braddock, J. F. and Brown, E. J.: 1991, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 2514.
Manilal, V. B. and Alexander, M.: 1991, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35, 401.
Morgan, P. and Watkinson, R. J.: 1989, Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 8, 305.
Morgan, P. and Watkinson, R. J: 1992, Wat. Res. 26, 73.
Nordgren, A.: 1991, Biol. Fertil. Soils 13, 195.
Olsen S. R., Cole, C. V., Watanabe, F. S. and Dean, L. A.: 1954, Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction With Sodium Bicarbonate, USDA Circ. 939.
Pankow, J. F.: 1991, Aquatic Chemistry Concepts, Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, MI.
Parsons, T. R., Takahashi, M. and Hargrove, B.: 1972, Biological Oceanographic Processes, 1972.
Prince, R. C.: 1995, in Hinchee, R. E., Kittel, J. A. and Reisinger, H. J. (eds.), Applied Bioremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons, Batelle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 101–106.
Prince, R. C., Clark, J. R., Lindstrom, J. E., Butler, E. L., Brown, E. J., Winter, G., Grossman, M. J., Parrish, P. R., Bare, R. E., Braddock, J. F., Steinhauer, W. G., Douglas, G. S., Kennedy, J. M., Barter, P. J., Bragg, J. R., Harner, E. J. and Atlas, R. M.: 1994, in Hinchee, R. E., Alleman, B. C., Hoeppel, R. E. and Miller, R. M. (eds.), Hydrocarbon Bioremediation, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 107–124.
Rasiah, V., Voroney, R. P. and Kachanoski, R. G.: 1992, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 65, 143.
Raymond, R. L., Hudson, J. O. and Jamison, V. W.: 1976, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31, 522.
Recous, S., Mary, B. and Faurie, G.: 1990, Soil. Biol. Biochem. 7, 913.
Rigler, F.: 1966, Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 16, 465.
Riser-Roberts, E.: 1992, Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Sites, C. K. Smoley, Boca Raton, FL.
Robertson, B. K. and Alexander, M.: 1992, Appl. Environ, Microbiol. 58, 38.
Schoenau, J. J. and Huang, W. Z.: 1991, Commun. In Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 22, 465.
Sharabi, N. E.-D. and Bartha, R.: 1993, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 1201.
Simkins, S. and Alexander, M.: 1984, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47, 1299.
Sposito, G.: 1989, The Chemistry of Soils, Oxford University Press, New York, NY.
Stotzky, G. and Norman, A. G.: 1961, Archiv. Mikrobiol. 40, 341.
Strong-Gunderson, J. M. and Palumbo, A. V.: 1995, in Hinchee, R. E., Vogel, C. M. and Brockman, F. J. (eds.), Microbial Processes for Bioremediation, Batelle Press, Columbus, OH, pp. 33–40.
Swift, M. J., Heal, O. W. and Anderson, J. M.: 1979, Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Studies in Ecology, Volume 5, University of California Press, Berkeley, CA.
Tiessen, H., Stewart, W. B. and Cole, C. V.: 1984, Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 48, 853.
Venosa, A. D., Suidan, M. T., Wrenn, K. L., Strohmeier, J. R., Haines, B. L., Eberhart, D., King, B. and Holder, E.: 1996, Env. Sci. Tech. 30, 1764.
Walworth, J. L., Woolard, C. R., Braddock, J. F. and Reynolds, C. M.: 1997, J. Soil. Cont.(in press).
Wilkinson. L.: 1988, SYSTAT: The System for Statistics, SYSTAT Inc., Evanston, IL.
Wrenn, B. A., Haines, J. R., Venosa, A. D., Kadkhodayan, M. and Suidan, M. T.: 1994, J. Ind. Microbiol. 13, 279.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graham, D.W., Smith, V.H., Cleland, D.L. et al. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Supply on Hexadecane Biodegradation in Soil Systems. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 111, 1–18 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005091427942
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005091427942