Abstract
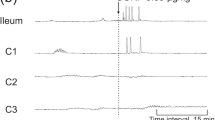
Coherin, a substance isolated from the bovine posterior pituitary gland exists as a complex which is dissociated to yield at least two distinct enteroactive polypeptides, coherin A and B, and a third having little or no activity, coherin C. The effects of intravenous injection of nondissociated coherin (coherin G-25), coherin A, coherin B, vasopressin, and normal saline solution on the BER of the ileal Biebl loop in fasting dogs were investigated. The BER patterns in preinjection and postinjection periods were compared for each substance. The effects on the BER of each substance were compared with that of saline. Monopolar recordings were made from six electrodes 5 mm apart inserted into the ileal musculature of the Biebl loops. Coherin A significantly altered the electroenterograms in two ways. It increased phase locking in the ileal BER of the fasting dog and increased the amount of caudad BER propagation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodman I, Hiatt RB: Coherin, a new peptide of the bovine neurohypophysis with activity on gastrointestinal activity. Science 178:419–421, Oct. 27, 1972.
Hiatt RB, Goodman I, Overweg NIA: Intestinal motility I. Control mechanisms in the basic electrical rhythm of the canine small intestine. J Surg Res 11:454–463, 1971
Hiatt RB, Goodman I, Overweg NIA: Intestinal motility II. Electro-motor correlations in the canine small intestine. J Surg Res 11:464–470, 1971
Christensen J, Weisbrodt NW, Hansen RL: Electrical slow wave of the proximal colon of the cat in diarrhea. Gastroenterology 62:1167–1173, 1972
Sarna SK, Daniel EE, Kingma YJ: Simulation of slow wave electrical activity of small intestine. Am J Physiol 221:166–175, 1971
Code CF, Szurszewski JH, Kelly KA, Smith IB: Concept of control of gastrointestinal motility. Handbook of Physiology, Sec. 6, Vol. 5, Washington, D.C., American Physiological Society, 1968, pp 2885–2892
Diamant NE and Bortoff A: Nature of the intestinal slow wave frequency gradient. Am J Physiol 216:301–307, 1969
Diamant NE and Bortoff A: Effects of transection on the intestinal slow wave frequency gradient. Am J Physiol 216:734–743, 1969
Daniel EE, Carlow DR, Wachter BT, Sutherland WH and Bogoch A: Electrical activity of the small intestine. Gastroenterology 37:268–281, 1959
Wood JD: Neurophysiology of Auerbach's plexus and control of intestinal motility. Physiol Rev 55:307–324, 1975
Tomita T: Electrical properties of mammalian smooth muscle. In: Smooth Muscle, edited by E. Bulbring, A. F. Brading, A. W. Jones, and T. Tomita. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkins, 1970, pp 197–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiatt, R.B., Goodman, I., Sandler, B. et al. The effect of coherin on the basic electrical rhythm of the dog ileumin vivo . Digest Dis Sci 22, 108–112 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01072951
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01072951